SS7 for the
Common Man
Last modified: Sat, 01 Nov 2008 14:12:37 GMT
| Home |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
SDTI Technical Specification
Description: OpenSS7 Resources Library.
A PDF version of this document is available here.
Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI)
Signalling Data Terminal Interface
Preface
Security Warning
Permission to use, copy and distribute this documentation without modification, for any purpose and without fee or royalty is hereby granted, provided that both the above copyright notice and this permission notice appears in all copies and that the name of OpenSS7 Corporation not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to distribution of this documentation or its contents without specific, written prior permission. OpenSS7 Corporation makes no representation about the suitability of this documentation for any purpose. It is provided “as is” without express or implied warranty.
OpenSS7 Corporation disclaims all warranties with regard to this documentation including all implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, or title; that the contents of the document are suitable for any purpose, or that the implementation of such contents will not infringe on any third party patents, copyrights, trademarks or other rights. In no event shall OpenSS7 Corporation be liable for any direct, indirect, special or consequential damages or any damages whatsoever resulting from loss of use, data or profits, whether in an action of contract, negligence or other tortious action, arising out of or in connection with any use of this document or the performance or implementation of the contents thereof.
OpenSS7 Corporation is making this documentation available as a reference point for the industry. While OpenSS7 Corporation believes that these interfaces are well defined in this release of the document, minor changes may be made prior to products conforming to the interfaces being made available.
Abstract
This document is a Specification containing technical details concerning the implementation of the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) for OpenSS7. It contains recommendations on software architecture as well as platform and system applicability of the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI).
This document specifies a Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) Specification in support of the OpenSS7 Signalling Data Terminal (SDT) protocol stacks. It provides abstraction of the signalling data terminal interface to these components as well as providing a basis for signalling data terminal control for other data terminal control protocols.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to provide technical documentation of the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI). This document is intended to be included with the OpenSS7 STREAMS software package released by OpenSS7 Corporation. It is intended to assist software developers, maintainers and users of the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) with understanding the software architecture and technical interfaces that are made available in the software package.
Intent
It is the intent of this document that it act as the primary source of information concerning the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI). This document is intended to provide information for writers of OpenSS7 Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) applications as well as writers of OpenSS7 Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) Users.
Audience
The audience for this document is software developers, maintainers and users and integrators of the Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI). The target audience is developers and users of the OpenSS7 SS7 stack.
Disclaimer
Although the author has attempted to ensure that the information in this document is complete and correct, neither the Author nor OpenSS7 Corporation will take any responsibility in it.
Revision History
Take care that you are working with a current version of this documentation: you will not be notified of updates. To ensure that you are working with a current version, check the OpenSS7 Project website for a current version.
Only the texinfo or roff source is controlled. A printed (or postscript) version of this document is an UNCONTROLLED VERSION.
sdti.texi,v
Revision 0.9.2.9 2008-09-20 11:04:30 brian
- added package patchlevel
Revision 0.9.2.8 2008-08-03 06:03:32 brian
- protected agains texinfo commands in log entries
Revision 0.9.2.7 2008-08-03 05:05:16 brian
- conditional @syncodeindex frags out automake, fails distcheck
Revision 0.9.2.6 2008-07-11 09:36:12 brian
- updated documentation
Revision 0.9.2.5 2008-04-29 07:10:39 brian
- updating headers for release
Revision 0.9.2.4 2007/08/14 12:17:02 brian
- GPLv3 header updates
Revision 0.9.2.3 2007/07/14 01:33:50 brian
- make license explicit, add documentation
Revision 0.9.2.2 2007/07/09 09:12:59 brian
- working up SDTI specification
Revision 0.9.2.1 2007/07/04 08:24:57 brian
- added new files
1 Introduction
This document specifies a STREAMS-based kernel-level instantiation of the ITU-T Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) definition. The Signalling Data Terminal Interface (SDTI) enables the user of a a signalling data terminal service to access and use any of a variety of conforming signalling data terminal providers without specific knowledge of the provider's protocol. The service interface is designed to support any network signalling data terminal protocol and user signalling data terminal protocol. This interface only specifies access to signalling data terminal service providers, and does not address issues concerning signalling data terminal management, protocol performance, and performance analysis tools.
This specification assumes that the reader is familiar with ITU-T state machines and signalling data terminal interfaces (e.g. Q.703, Q.2210), and STREAMS.
1.1 Related Documentation
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.703 (White Book)
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.2210 (White Book)
- ANSI T1.111.3/2002
- System V Interface Definition, Issue 2 - Volume 3
1.1.1 Role
This document specifies an interface that supports the services provided by the Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) for ITU-T, ANSI and ETSI applications as described in ITU-T Recommendation Q.703, ITU-T Recommendation Q.2210, ANSI T1.111.3, ETSI ETS 300 008-1. These specifications are targeted for use by developers and testers of protocol modules that require signalling data terminal service.
1.2 Definitions, Acronyms, Abbreviations
- LM
- Local Management.
- LMS
- Local Management Service.
- LMS User
- A user of Local Management Services.
- LMS Provider
- A provider of Local Management Services.
- Originating SDT User
- A SDT-User that initiates a Signalling Data Terminal.
- Destination SDT User
- A SDT-User with whom an originating SDT user wishes to establish a Signalling Data Terminal.
- ISO
- International Organization for Standardization
- SDT User
- Kernel level protocol or user level application that is accessing the services
of the Signalling Data Terminal sub-layer.
- SDT Provider
- Signalling Data Terminal sub-layer entity/entities that provide/s the services of the
Signalling Data Terminal interface.
- SDTI
- Signalling Data Terminal Interface
- TIDU
- Signalling Data Terminal Interface Data Unit
- TSDU
- Signalling Data Terminal Service Data Unit
- OSI
- Open Systems Interconnection
- QOS
- Quality of Service
- STREAMS
- A communication services development facility first available with UNIX System V Release 3.
2 The Signalling Data Terminal Layer
The Signalling Data Terminal Layer provides the means to manage the association of SDT-Users into connections. It is responsible for the routing and management of data to and from signalling data terminal connections between SDT-user entities.
2.1 Model of the SDTI
The SDTI defines the services provided by the signalling data terminal layer to the signalling data terminal user at the boundary between the signalling data terminal provider and the signalling data terminal user entity. The interface consists of a set of primitives defined as STREAMS messages that provide access to the signalling data terminal layer services, and are transferred between the SDTS user entity and the SDTS provider. These primitives are of two types; ones that originate from the SDTS user, and other that originate from the SDTS provider. The primitives that originate from the SDTS user make requests to the SDTS provider, or respond to an indication of an event of the SDTS provider. The primitives that originate from the SDTS provider are either confirmations of a request or are indications to the CCS user that an event has occurred. Figure 1 shows the model of the SDTI.
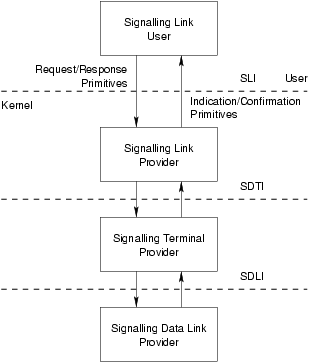
The SDTI allows the SDTS provider to be configured with any signalling data terminal layer user (such as a signalling link application) that also conforms to the SDTI. A signalling data terminal layer user can also be a user program that conforms to the SDTI and accesses the SDTS provider via putmsg(2s) and getmsg(2s) system calls. The typical configuration, however, is to place a signalling link module above the signalling data terminal layer.
2.2 SDTI Services
The features of the SDTI are defined in terms of the services provided by the SDTS provider, and the individual primitives that may flow between the SDTS user and the SDTS provider.
The SDTI Services are broken into two groups: local management services and protocol services. Local management services are responsible for the local management of streams, assignment of streams to physical points of attachment, enabling and disabling of streams, management of options associated with a stream, and general acknowledgement and event reporting for the stream. Protocol services consist of connecting a stream to a medium, exchanging data with the medium, and disconnecting the stream from the medium.
2.2.1 Local Management
Local management services are listed in Table 1.
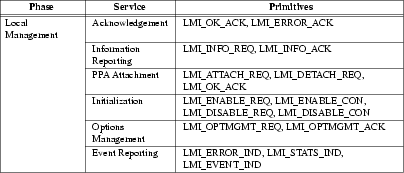
The local management services interface is described in Local Management Services, and the primitives are detailed in Local Management Service Primitives. The local management services interface is defined by the ss7/lmi.h header file (see LMI Header File Listing).
2.2.2 Protocol
Protocol services are listed in Table 2.
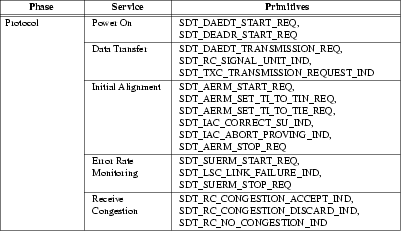
The protocol services interface is described in Protocol Services, and the primitives are detailed in Protocol Service Primitives. The protocol services interface is defined by the ss7/sdti.h header file (see SDTI Header File Listing).
2.3 Purpose of the SDTI
The SDTI is typically implemented as a device driver controlling a MPCC (Multi-Protocol Controller Chip) device that provides access to channels. The purpose behind exposing this low level interface is that almost all communications channel devices can be placed into a SS7 HDLC mode, where a data stream can be exchanged between the driver and the medium. The SDTI provides and inteface that, once implemented as a driver for a new device, can provide complete and verified SS7 signalling link capabilities by pushing generic SL (Signalling Link) modules over an open device stream.
This allows SL modules to be verified independently for correct operation and then simply used for all manner of new device drivers that can implement the SDTI interface.
3 SDTI Services Definition
3.1 Local Management Services
3.1.1 Acknowledgement Service
The acknowledgement service provides the LMS user with the ability to receive positive and negative acknowledgements regarding the successful or unsuccessful completion of services.
LMI_OK_ACK: TheLMI_OK_ACKmessage is used by the LMS provider to indicate successful receipt and completion of a service primitive request that requires positive acknowledgement.LMI_ERROR_ACK: TheLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage is used by the LMS provider to indicate successful receipt and failure to complete a service primitive request that requires negative acknowledgement.
A successful invocation of the acknowledgement service is illustrated in Figure 15.
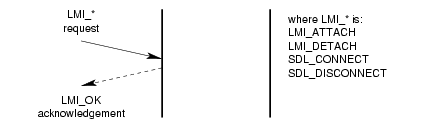
As illustrated in Figure 15, the
service primitives for which a positive acknowledgement may be returned are the
LMI_ATTACH_REQ and LMI_DETACH_REQ.
An unsuccessful invocation of the acknowledgement service is illustrated in Figure 16.
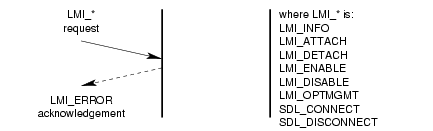
As illustrated in Figure 16, the service primitives for which a negative acknowledgement may be
returned are the LMI_INFO_REQ, LMI_ATTACH_REQ, LMI_DETACH_REQ,
LMI_ENABLE_REQ, LMI_DISABLE_REQ and LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ messages.
3.1.2 Information Reporting Service
The information reporting service provides the LMS user with the ability to elicit information from the LMS provider.
LMI_INFO_REQ: TheLMI_INFO_REQmessage is used by the LMS user to request information about the LMS provider.LMI_INFO_ACK: TheLMI_INFO_ACKmessage is issued by the LMS provider to provide requested information about the LMS provider.
A successful invocation of the information reporting service is illustrated in Figure 2.
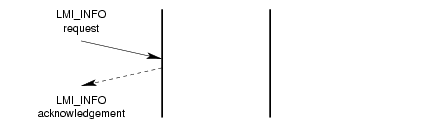
3.1.3 Physical Point of Attachment Service
The local management interface provides the LMS user with the ability to associate a stream to a physical point of appearance (PPA) or to disassociate a stream from a PPA. The local management interface provides for two styles of LMS provider:
Style 1 LMS Provider
A Style 1 LMS provider is a provider that associates a stream with a PPA at the time of the
first open(2) call for the device, and disassociates a stream from a PPA at the time of the
last close(2) call for the device.
Physical points of attachment (PPA) are assigned to major and minor device number combinations. When the major and minor device number combination is opened, the opened stream is automatically associated with the PPA for the major and minor device number combination. The last close of the device disassociates the PPA from the stream.
Freshly opened Style 1 LMS provider streams start life in the LMI_DISABLED state.
This approach is suitable for LMS providers implemented as real or pseudo-device drivers and is applicable when the number of minor devices is small and static.
Style 2 LMS Provider
A Style 2 LMS provider is a provider that associates a stream with a PPA at the time that the
LMS user issues the LMI_ATTACH_REQ message. Freshly opened streams are not associated with
any PPA. The Style 2 LMS provider stream is disassociated from a PPA when the stream is
closed or when the LMS user issues the LMI_DETACH_REQ message.
Freshly opened Style 2 LMS provider streams start life in the LMI_UNATTACHED state.
This approach is suitable for LMS providers implemented as clone real or pseudo-device drivers and is applicable when the number of minor devices is large or dynamic.
3.1.3.1 PPA Attachment Service
The PPA attachment service provides the LMS user with the ability to attach a Style 2 LMS provider stream to a physical point of appearance (PPA).
LMI_ATTACH_REQ: TheLMI_ATTACH_REQmessage is issued by the LMS user to request that a Style 2 LMS provider stream be attached to a specified physical point of appearance (PPA).LMI_OK_ACK: Upon successful receipt and processing of theLMI_ATTACH_REQmessage, the LMS provider acknowledges the success of the service completion with aLMI_OK_ACKmessage.LMI_ERROR_ACK: Upon successful receipt but failure to process theLMI_ATTACH_REQmessage, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure of the service completion with aLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage.
A successful invocation of the attachment service is illustrated in Figure 3.
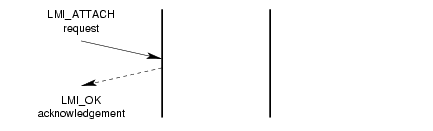
3.1.3.2 PPA Detachment Service
The PPA detachment service provides the LMS user with the ability to detach a Style 2 LMS provider stream from a physical point of attachment (PPA).
LMI_DETACH_REQ: TheLMI_DETACH_REQmessage is issued by the LMS user to request that a Style 2 LMS provider stream be detached from the attached physical point of appearance (PPA).LMI_OK_ACK: Upon successful receipt and processing of theLMI_DETACH_REQmessage, the LMS provider acknowledges the success of the service completion with aLMI_OK_ACKmessage.LMI_ERROR_ACK: Upon successful receipt but failure to process theLMI_DETACH_REQmessage, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure of the service completion with aLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage.
A successful invocation of the detachment service is illustrated in Figure 4.
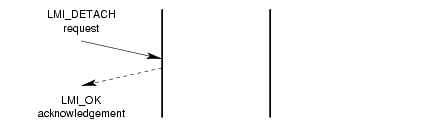
3.1.4 Initialization Service
The initialization service provides the LMS user with the abilty to enable and disable the stream for the associated PPA.
3.1.4.1 Interface Enable Service
The interface enable service provides the LMS user with the ability to enable an LMS provider stream that is associated with a PPA. Enabling the interface permits the LMS user to exchange protocol service interface messages with the LMS provider.
LMI_ENABLE_REQ: TheLMI_ENABLE_REQmessage is issued by the LMS user to request that the protocol service interface be enabled.LMI_ENABLE_CON: Upon successful enabling of the protocol service interface, the LMS provider acknowledges successful completion of the service by issuing aLMI_ENABLE_CONmessage to the LMS user.LMI_ERRORK_ACK: Upon unsuccessful enabling of the protocol service interface, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure to complete the service by issuing anLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage to the LMS user.
A successful invocation of the enable service is illustrated in Figure 5.
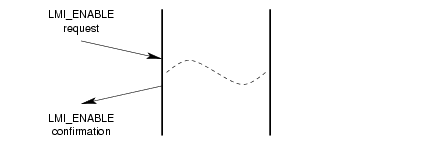
3.1.4.2 Interface Disable Service
The interface disable service provides the LMS user with the ability to disable an LMS provider stream that is associated with a PPA. Disabling the interface withdraws the LMS user's ability to exchange protocol service interface messages with the LMS provider.
LMI_DISABLE_REQ: TheLMI_DISABLE_REQmessage is issued by the LMS user to request that the protocol service interface be disabled.LMI_DISABLE_CON: Upon successful disabling of the protocol service interface, the LMS provider acknowledges successful completion of the service by issuing aLMI_DISABLE_CONmessage to the LMS user.LMI_ERRORK_ACK: Upon unsuccessful disabling of the protocol service interface, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure to complete the service by issuing anLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage to the LMS user.
A successful invocation of the disable service is illustrated in Figure 6.
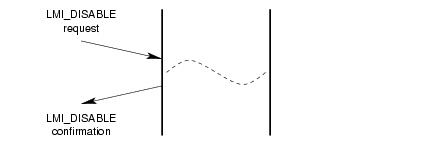
3.1.5 Options Management Service
The options management service provides the LMS user with the ability to control and affect various generic and provider-specific options associated with the LMS provider.
LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ: The LMS user issues aLMI_OPTMGMT_REQmessage when it wishes to interrogate or affect the setting of various generic or provider-specific options associated with the LMS provider for the stream upon which the message is issued.LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK: Upon successful receipt of theLMI_OPTMGMT_REQmessage, and successful options processing, the LMS provider acknowledges the successful completion of the service with anLMI_OPTMGMT_ACKmessage.LMI_ERROR_ACK: Upon successful receipt of theLMI_OPTMGMT_REQmessage, and unsuccessful options processing, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure to complete the service by issuing anLMI_ERROR_ACKmessage to the LMS user.
A successful invocation of the options management service is illustrated in Figure 7.
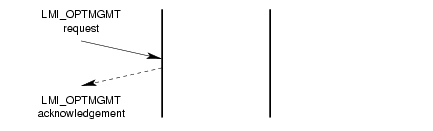
3.1.6 Error Reporting Service
The error reporting service provides the LMS provider with the ability to indicate asynchronous errors to the LMS user.
LMI_ERROR_IND: The LMS provider issues theLMI_ERROR_INDmessage to the LMS user when it needs to indicate an asynchronous error (such as the unusability of the communications medium).
A successful invocation of the error reporting service is illustrated in Figure 8.
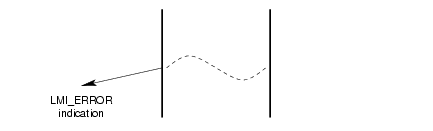
3.1.7 Statistics Reporting Service
LMI_STATS_IND:
A successful invocation of the statistics reporting service is illustrated in Figure 9.
3.1.8 Event Reporting Service
The event reporting service provides the LMS provider with the ability to indicate specific asynchronous management events to the LMS user.
LMI_EVENT_IND: The LMS provider issues theLMI_EVENT_INDmessage to the LMS user when it wishes to indicate an asynchronous (management) event to the LMS user.
A successful invocation of the event reporting service is illustrated in Figure 10.
3.2 Protocol Services
Protocol services are specific to the Signalling Data Terminal interface. These services consist of connection services that permit the transmit and receive directions to be connected to or disconnected from the medium, and data transfer services that permit the exchange of data between SDTS users.
The service primitives that implement the protocol services are described in detail in Protocol Service Primitives.
3.2.1 Power On Service
The power on service provides the SDTS user with the ability to power up the receive and trasmitters associated with the medium. Transmitters and receivers can be powered up independently. Data trasnfer cannot occur until the transmitters or receivers have been powered up.
SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that transmission of bits begin on the medium.SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that receiption of bits from the medium begin.
3.2.2 Data Transfer Service
The data transfer service provides the SDTS user with the ability to exchange signal units with the SDTS provider. Signal units may be sent to the SDTS provider for transmission and received signal units are delivered to the SDTS user by the SDTS provider. Timing queues can also be indicated by the SDTS provider.
SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request the transmission of a signal unit.SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when a signal unit has been received.SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when it is idle (that is, it is requesting transmission).
3.2.3 Initial Alignment Service
The initial alignment service provides for all of the mechanisms associated with the Alignment Error Rate Monitor (AERM). This includes the ability for the SDTS user to start and stop the AERM, set the proving period to either normal proving or emergency proving, to receive correct signal unit indications and indications of when the error rate exceeds the configured threshold.
SDT_AERM_START_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for alignment be started. This is normally performed when initial alignment begins on the signalling link.SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for alignment use the error threshold values for normal alignment.SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for alignment use the error threshold values for emergency alignment.SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when a signal unit has sucessfully been received during initial alignment.SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when the Alignment Error Rate Monitor (AERM) exceeds it threshold.SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for alignment be stopped. This is normally performed when initial alignement ends for the signalling link.
3.2.4 Error Rate Monitoring Service
The error rate monitoring service provides all of the mechanisms associated with the Signal Unit Error Rate Monitor (SUERM) or Errored Interval Monitor (EIM). This includes the ability for the SDTS user to start and stop the SUERM/EIM, and be notified when the error rate exceeds the configured threshold.
SDT_SUERM_START_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for normal operation be started. This is normally performed when intial alignment ends for the signalling link.SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when the Signal Unit Error Rate Monitor (SUERM) exceeds its threshold.SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ: This service primitive allows the SDTS user to request that the ERM for normal operation be stopped. This is normally performed when initial alignment begins for the signalling link.
3.2.5 Receive Congestion Service
The receive congestion service providers mechanisms to implement provider-specific receive congestion indications to the SDTS user.
SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when receive congestion has onset, but not to the point that it is dicarding signal units.SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when receive congestion has onset, and signal units are being dicarded.SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND: This service primitive allows the SDTS provider to indicate when receive congestion abates.
4 SDTI Primitives
4.1 Local Management Service Primitives
These service primitives implement the local management services (see Local Management Services).
4.1.1 Acknowledgement Service Primitives
These service primitives implement the acknowledgement service (see Acknowledgement Service).
4.1.1.1 LMI_OK_ACK
Description
This primitive is used to acknowledge receipt and successful service completion for primitives requiring acknowledgement that have no confirmation primitive.
Format
This primitive consists of one M_PCPROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_long lmi_correct_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_ok_ack_t;
Parameters
The service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_OK_ACK. lmi_correct_primitive- Indicates the service primitive that was received and serviced correctly. This field can be one of
the following values:
LMI_ATTACH_REQ- Attach request.
LMI_DETACH_REQ- Detach request.
lmi_state-
Indicates the current state of the LMS provider at the time that the primitive was issued.
This field can be one of the following values:
LMI_UNATTACHED- No PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ATTACH_REQ. LMI_UNUSABLE- Device cannot be used, STREAM in hung state.
LMI_DISABLED- PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ENABLE_REQ. LMI_ENABLED- Ready for use, awaiting primitive exchange.
State
This primitive is issued by the LMS provider in the LMI_ATTACH_PENDING or
LMI_DETACH_PENDING state.
New State
The new state is LMI_UNATTACHED or LMI_DISABLED, depending on thee primitive to
which the message is responding.
4.1.1.2 LMI_ERROR_ACK
Description
The error acknowledgement primitive is used to acknowledge receipt and unsuccessful service completion for primitives requiring acknowledgement.
Format
The error acknowledgement primitive consists of one M_PCPROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_errno;
lmi_ulong lmi_reason;
lmi_long lmi_error_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_error_ack_t;
Parameters
The error acknowledgement primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive-
Indicates the primitive type. Always
LMI_ERROR_ACK. lmi_errno-
Indicates the LM error number.
This field can have one of the following values:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
lmi_reason-
Indicates the reason for failure. This field is protocol-specific. When the
lmi_errnofield isLMI_SYSERR, thelmi_reasonfield is the UNIX error number as described inerrno(3). lmi_error_primitive-
Indicates the primitive that was in error.
This field can have one of the following values:
LMI_INFO_REQ- Information request.
LMI_ATTACH_REQ- Attach request.
LMI_DETACH_REQ- Detach request.
LMI_ENABLE_REQ- Enable request.
LMI_DISABLE_REQ- Disable request.
LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ- Options management request.
LMI_INFO_ACK- Information acknowledgement.
LMI_OK_ACK- Successful receipt acknowledgement.
LMI_ERROR_ACK- Error acknowledgement.
LMI_ENABLE_CON- Enable confirmation.
LMI_DISABLE_CON- Disable confirmation.
LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK- Options Management acknowledgement.
LMI_ERROR_IND- Error indication.
LMI_STATS_IND- Statistics indication.
LMI_EVENT_IND- Event indication.
lmi_state-
Indicates the state of the LMS provider at the time that the primitive was issued. This field can
have one of the following values:
LMI_UNATTACHED- No PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ATTACH_REQ. LMI_ATTACH_PENDING- Waiting for attach.
LMI_UNUSABLE- Device cannot be used, STREAM in hung state.
LMI_DISABLED- PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ENABLE_REQ. LMI_ENABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_ENABLE_CON. LMI_ENABLED- Ready for use, awaiting primitive exchange.
LMI_DISABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_DISABLE_CON. LMI_DETACH_PENDING- Waiting for detach.
State
This primitive can be issued in any state for which a local acknowledgement is not pending. The LMS provider state at the time that the primitive was issued is indicated in the primitive.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
4.1.2 Information Reporting Service Primitives
These service primitives implement the information reporting service (see Information Reporting Service).
4.1.2.1 LMI_INFO_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive is issued by the LMS user to request that the LMS provider return information concerning the capabilities and state of the LMS provider.
Format
The primitive consists of one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_ulong lmi_primitive;
} lmi_info_req_t;
Parameters
This primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the primitive type. Always
LMI_INFO_REQ.
State
This primitive may be issued in any state but only when a local acknowledgement is not pending.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
Response
This primitive requires the LMS provider to acknowledge receipt of the primitive as follows:
- Successful:
The LMS provider is required to acknowledge receipt of the primitive and provide the requested
information using the
LMI_INFO_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
The LMS provider is required to negatively acknowledge the primitive using the
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive, and include the reason for failure in the primitive.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.2.2 LMI_INFO_ACK
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive acknowledges receipt and successful processing of the
LMI_INFO_REQ primitive and provides the request information concerning the LMS provider.
Format
This message is formatted a one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_version;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
lmi_ulong lmi_max_sdu;
lmi_ulong lmi_min_sdu;
lmi_ulong lmi_header_len;
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_style;
lmi_uchar lmi_ppa_addr[0];
} lmi_info_ack_t;
Parameters
The information acknowledgement service primitive has the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_INFO_ACK. lmi_version- Indicates the version of this specification that is being used by the LMS provider.
lmi_state- Indicates the state of the LMS provider at the time that the information acknowledgement service
primitive was issued. This field can be one of the following values:
LMI_UNATTACHED- No PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ATTACH_REQ. LMI_ATTACH_PENDING- Waiting for attach.
LMI_UNUSABLE- Device cannot be used, STREAM in hung state.
LMI_DISABLED- PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ENABLE_REQ. LMI_ENABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_ENABLE_CON. LMI_ENABLED- Ready for use, awaiting primitive exchange.
LMI_DISABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_DISABLE_CON. LMI_DETACH_PENDING- Waiting for detach.
lmi_max_sdu- Indicates the maximum size of a Service Data Unit.
lmi_min_sdu- Indicates the minimum size of a Service Data Unit.
lmi_header_len- Indicates the amount of header space that should be reserved for placing LMS provider headers.
lmi_ppa_style- Indicates the PPA style of the LMS provider. This value can be one of the following values:
LMI_STYLE1- PPA is implicitly attached by
open(2). LMI_STYLE2- PPA must be explicitly attached using
LMI_ATTACH_REQ.
lmi_ppa_addr- This is a variable length field. The length of the field is determined by the length of the
M_PROTOorM_PCPROTOmessage block.For a Style 2 driver, when
lmi_ppa_styleisLMI_STYLE2, and when in an attached state, this field providers the current PPA associated with the stream; the length is typically 4 bytes.For a Style 1 driver, when
lmi_ppa_styleisLMI_STYLE1, the length it 0 bytes.
State
This primitive can be issued in any state where a local acknowledgement is not pending.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
4.1.3 Physical Point of Attachment Service Primitives
These service primitives implement the physical point of attachment service (see Physical Point of Attachment Service).
4.1.3.1 LMI_ATTACH_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive requests that the stream upon which the primitive is issued by
associated with the specified Physical Point of Attachment (PPA). This primitive is only applicable
to Style 2 LMS provider streams, that is, streams that return LMI_STYLE2 in the
lmi_ppa_style field of the LMI_INFO_ACK.
Format
This primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_uchar lmi_ppa[0];
} lmi_attach_req_t;
Parameters
The attach request primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
LMI_ATTACH_REQ. lmi_ppa- Specifies the Physical Point of Attachment (PPA) to which to associated the Style 2 stream.
This is a variable length identifier whose length is determined by the length of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
State
This primitive is only valid in state LMI_UNATTACHED and when a local acknowledgement is not
pending.
New State
Upon success, the new state is LMI_ATTACH_PENDING. Upon failure, the state remains unchanged.
Response
The attach request service primitive requires that the LMS provider respond as follows:
- Successful:
The LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the primitive and successful outcome of the attach service
with a
LMI_OK_ACKprimitive. The new state isLMI_DISABLED. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
The LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the primitive and failure of the attach service with a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the reason for failure. The new state remains unchanged.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.3.2 LMI_DETACH_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive request that the stream upon which the primitive is issued be
disassociated from the Physical Point of Appearance (PPA) to which it is currently attached. This
primitive is only applicable to Style 2 LMS provider streams, that is, streams that return
LMI_STYLE2 in the lmi_ppa_style field of the LMI_INFO_ACK.
Format
The detach request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
} lmi_detach_req_t;
Parameters
The detach request service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
LMI_DETACH_REQ.
State
This primitive is valid in the LMI_DISABLED state and when no local acknowledgement is pending.
New State
Upon success, the new state is LMI_DETACH_PENDING. Upon failure, the state remains unchanged.
Response
The detach request service primitive requires that the LMS provider respond as follows:
- Successful:
The LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the primitive and successful outcome of the detach service
with a
LMI_OK_ACKprimitive. The new state isLMI_UNATTACHED. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
The LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the primitive and failure of the detach service with a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the reason for failure. The new state remains unchanged.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.4 Initialization Service Primitives
Initialization service primitives allow the LMS user to enable or disable the protocol service interface. Enabling the protocol service interface may require that some action be taken to prepare the protocol service interface for use or to remove it from use. For example, where the PPA corresponds to a signalling data link identifier as defined in Q.704, it may be necessary to perform switching to connect or disconnect the circuit identification code associated with the signalling data link identifier.
These service primitives implement the initialization service (see Initialization Service).
4.1.4.1 LMI_ENABLE_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive request that the LMS provider perform the actions necessary to enable the protocol service interface and confirm that it is enabled. This primitive is applicable to both styles of PPA.
Format
The enable request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_uchar lmi_rem[0];
} lmi_enable_req_t;
Parameters
The enable request service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
LMI_ENABLE_REQ. lmi_rem- Specifies a remote address to which to connect the PPA. The need for and form of this address is
provider-specific. The length of the field is determined by the length of the
M_PROTOmessage block. This remote address could be a circuit identification code, an IP address, or some other form of circuit or channel identifier.
State
This primitive is valid in the LMI_DISABLED state and when no local acknowledgement is pending.
New State
Upon success the new state is LMI_ENABLE_PENDING. Upon failure, the state remains unchanged.
Response
The enable request service primitive requires that the LMS provider acknowledge receipt of the primitive as follows:
- Successful:
When successful, the LMS provider acknowledges successful completion of the enable service with an
LMI_ENABLE_CONprimitive. The new state isLMI_ENABLED. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure of the enable service wtih an
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error. The new state remains unchanged.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.4.2 LMI_ENABLE_CON
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive is issued by the LMS provider to confirm the successful completion of the enable service.
Format
The enable confirmation service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as
follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_enable_con_t;
Parameters
The enable confirmation service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_ENABLE_CON. lmi_state- Indicates the state following issuing the enable confirmation primitive. This field can take on one
of the following values:
LMI_ENABLED- Ready for use, awaiting primitive exchange.
State
This primitive is issued by the LMS provider in the LMI_ENABLE_PENDING state.
New State
The new state is LMI_ENABLED.
4.1.4.3 LMI_DISABLE_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive requests that the LMS provider perform the actions necessary to disable the protocol service interface and confirm that it is disabled. The primitive is applicable to both styles of PPA.
Format
The disable request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
} lmi_disable_req_t;
Parameters
The disable request service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
LMI_DISABLE_REQ.
State
The disable request service primitive is valid in the LMI_ENABLED state and when no local
acknowledgement is pending.
New State
Upon success, the new state is LMI_DISABLE_PENDING. Upon failure, the state remains unchanged.
Response
The disable request service primitive requires the LMS provider to acknowledge receipt of the primitive as follows:
- Successful:
When successful, the LMS provider acknowledges successful completion of the disable service with an
LMI_DISABLE_CONprimitive. The new state isLMI_DISABLED. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the LMS provider acknowledges the failure of the disable service with an
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error. The new state remains unchanged.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.4.4 LMI_DISABLE_CON
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive is issued by the LMS provider to confirm the successful completion of the disable service.
Format
The disable confirmation service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as
follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_disable_con_t;
Parameters
The disable confirmation service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_DISABLE_CON. lmi_state- Indicates the state following issuing the disable confirmation primitive. This field can take on one
of the following values:
LMI_DISABLED- PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ENABLE_REQ.
State
This primitive is issued by the LMS provider in the LMI_DISABLE_PENDING state.
New State
The new state is LMI_DISABLED.
4.1.5 Options Management Service Primitives
The options management service primitives allow the LMS user to negotiate options with the LMS provider, retrieve the current and default values of options, and check that values specified for options are correct.
The options management service primitive implement the options management service (see Options Management Service).
4.1.5.1 LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ
Description
This LMS user originated primitive requests that LMS provider options be managed.
Format
The option management request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_offset;
lmi_ulong lmi_mgmt_flags;
} lmi_optmgmt_req_t;
Parameters
The option management request service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ. lmi_opt_length- Specifies the length of the options.
lmi_opt_offset- Specifies the offset, from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block, of the start of the options. lmi_mgmt_flags- Specifies the management flags which determine what operation the LMS provider is expected to
perform on the specified options. This field can assume one of the following values:
LMI_NEGOTIATE- Negotiate the specified value of each specified option and return the negotiated value.
LMI_CHECK- Check the validity of the specified value of each specified option and return the result. Do not
alter the current value assumed by the LMS provider.
LMI_DEFAULT- Return the default value for the specified options (or all options). Do not alter the current value
assumed by the LMS provider.
LMI_CURRENT- Return the current value for the specified options (or all options). Do not alter the current value assumed by the LMS provider.
State
This primitive is valid in any state where a local acknowledgement is not pending.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
Response
The option management request service primitive requires the LMS provider to acknowledge receipt of the primitive as follows:
- Successful:
Upon success, the LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the service primitive and successful
completion of the options management service with an
LMI_OPTMGMT_ACKprimitive containing the options management result. The state remains unchanged. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
Upon failure, the LMS provider acknowledges receipt of the service primitive and failure to
complete the options management service with an
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error. The state remains unchanged.
Reasons for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.1.5.2 LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive is issued by the LMS provider upon successful completion of
the options management service. It indicates the outcome of the options management operation
requested by the LMS user in a LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ primitive.
Format
The option management acknowledgement service primitive consists of one M_PCPROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_offset;
lmi_ulong lmi_mgmt_flags;
} lmi_optmgmt_ack_t;
Parameters
The option management acknowledgement service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK. lmi_opt_length- Indicates the length of the returned options.
lmi_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the returned options from the start of the
M_PCPROTOmessage block. lmi_mgmt_flags- Indicates the returned management flags. These flags indicate the overall success of the options
management service. This field can assume one of the following values:
LMI_SUCCESS- The LMS provider succeeded in negotiating or returning all of the options specified by the LMS
user in the
LMI_OPTMGMT_REQprimitive. LMI_FAILURE- The LMS provider failed to negotiate one or more of the options specified by the LMS user.
LMI_PARTSUCCESS- The LMS provider negotiated a value of lower quality for one or more of the options specified by
the LMS user.
LMI_READONLY- The LMS provider failed to negotiate one ore more of the options specified by the LMS user because
the option is treated as read-only by the LMS provider.
LMI_NOTSUPPORT- The LMS provider failed to recognize one or more of the options specified by the LMS user.
State
This primitive is issued by the LMS provider in direct response to an LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ primitive.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
Rules
The LMS provider follows the following rules when processing option management service requests:
- When the
lmi_mgmt_flagsfield in theLMI_OPTMGMT_REQprimitive is set toLMI_NEGOTIATE, the LMS provider will attempt to negotiate a value for each of the options specified in the request. - When the flags are
LMI_DEFAULT, the LMS provider will return the default values of the specified options, or the default values of all options known to the LMS provider if no options were specified. - When the flags are
LMI_CURRENT, the LMS provider will return the current values of the specified options, or all options. - When the flags are
LMI_CHECK, the LMS provider will attempt to negotiate a value for each of the options specified in the request and return the resulg of the negotiation, but will not affect the current value of the option.
4.1.6 Event Reporting Service Primitives
The event reporting service primitives allow the LMS provider to indicate asynchronous errors, events and statistics collection to the LMS user.
These service primitives implement the event reporting service (see Event Reporting Service).
4.1.6.1 LMI_ERROR_IND
Description
This LMS provider originated service primitive is issued by the LMS provider when it detects and asynchronous error event. The service primitive is applicable to all styles of PPA.
Format
The error indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_errno;
lmi_ulong lmi_reason;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_error_ind_t;
Parameters
The error indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_ERROR_IND. lmi_errno- Indicates the LMI error number describing the error. This field can have one of the following
values:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADADDRESS- Address was invalid.
LMI_BADADDRTYPE- Invalid address type.
LMI_BADDIAL- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDIALTYPE- (Not used.)
LMI_BADDISPOSAL- Invalid disposal parameter.
LMI_BADFRAME- Defective SDU received.
LMI_BADPPA- Invalid PPA identifier.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_WRITEFAIL- Unitdata request failed.
LMI_CRCERR- CRC or FCS error.
LMI_DLE_EOT- DLE EOT detected.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_HDLC_ABORT- Aborted frame detected.
LMI_OVERRUN- Input overrun.
LMI_TOOSHORT- Frame too short.
LMI_INCOMPLETE- Partial frame received.
LMI_BUSY- Telephone was busy.
LMI_NOANSWER- Connection went unanswered.
LMI_CALLREJECT- Connection rejected.
LMI_HDLC_IDLE- HDLC line went idle.
LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE- HDLC link no longer idle.
LMI_QUIESCENT- Line being reassigned.
LMI_RESUMED- Line has been reassigned.
LMI_DSRTIMEOUT- Did not see DSR in time.
LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS- LAN excessive collisions.
LMI_LAN_REFUSED- LAN message refused.
LMI_LAN_NOSTATION- LAN no such station.
LMI_LOSTCTS- Lost Clear to Send signal.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
lmi_reason-
Indicates the reason for failure. This field is protocol-specific. When the
lmi_errnofield isLMI_SYSERR, thelmi_reasonfield is the UNIX error number as described inerrno(3). lmi_state-
Indicates the state of the LMS provider at the time that the primitive was issued.
This field can have one of the following values:
LMI_UNATTACHED- No PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ATTACH_REQ. LMI_ATTACH_PENDING- Waiting for attach.
LMI_UNUSABLE- Device cannot be used, STREAM in hung state.
LMI_DISABLED- PPA attached, awaiting
LMI_ENABLE_REQ. LMI_ENABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_ENABLE_CON. LMI_ENABLED- Ready for use, awaiting primitive exchange.
LMI_DISABLE_PENDING- Waiting to send
LMI_DISABLE_CON. LMI_DETACH_PENDING- Waiting for detach.
State
This primitive can be issued in any state for which a local acknowledgement is not pending. The LMS provider state at the time that the primitive was issued is indicated in the primitive.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
4.1.6.2 LMI_STATS_IND
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive is issued by the LMS provider to indicate a periodic statistics collection event. The service primitive is applicable to all styles of PPA.
Format
The statistics indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as
follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_interval;
lmi_ulong lmi_timestamp;
} lmi_stats_ind_t;
Following this structure within the M_PROTO message block is the provider-specific statistics.
Parameters
The statistics indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_STATS_IND. lmi_interval- Indicates the statistics collection interval to which the statistics apply. This interval is
specified in milliseconds.
lmi_timestamp- Indicates the UNIX time (from epoch) at which statistics were collected. The timestamp is given in milliseconds from epoch.
State
This service primitive may be issued by the LMS provider in any state in which a local acknowledgement is not pending.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
4.1.6.3 LMI_EVENT_IND
Description
This LMS provider originated primitive is issued by the LMS provider to indicate an asynchronous event. The service primitive is applicable to all styles of PPA.
Format
The event indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_objectid;
lmi_ulong lmi_timestamp;
lmi_ulong lmi_severity;
} lmi_event_ind_t;
Following this structure within the M_PROTO message block is the provider-specific event
information.
Parameters
THe event indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
lmi_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
LMI_EVENT_IND. lmi_objectid- Indicates the provider-specific object identifier that identifies the managed object to which the
event is associated.
lmi_timestamp- Indicates the UNIX time from epoch (in milliseconds).
lmi_severity- Indicates the provider-specific severity of the event.
State
This service primitive can be issued by the LMS provider in any state where a local
acknowledgement is not pending. Normally the LMS provider must be in the LMI_ENABLED state for
event reporting to occur.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
4.2 Protocol Service Primitives
The protocol service primitives implement the services of the DAEDT, DAEDR, AERM, SUERM/EIM and a provider specific receive congestion function, including power on, initial alignment support, error rate monitoring, receive cnogestion detection, and data transfer.
These service primitives implement the protocol services (see Protocol Services).
4.2.1 Power On Service Primitives
The power on service primitives provide the ability for the SDTS user to power on the DAEDR and DAEDT functions within the SDTS provider.
These service primitives implement the power on service (see Power On Service).
4.2.1.1 SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ
Description
The DAEDT start request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user when it wishes to start the transmitters as part of a power-on sequence. Once started, the transmitters cannot be stopped under protocol control.
Format
The DAEDT start request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, formatted as
follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_daedt_start_req_t;
Parameters
The DAEDT start request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state and is valid when the DAEDT
is in the IDLE state.
New State
The new DAEDT state is the IN-SERVICE state.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful: When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The link state is unchanged.
- Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
When the terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state and the DAEDT is already in the
IN-SERVICE state, this primitive should be ignored and the SDTS provider should not
generate a non-fatal error.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.1.2 SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ
Description
The DAEDR start request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user when it wishes to start the receivers as part of a power-on sequence. Once started, the receivers cannot be stopped under protocol control. This primitive is a request from the Reception Control (RC) function in the SDTS user to the DAEDR function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The DAEDR start request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, formatted as
follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_daedr_start_req_t;
Parameters
The DAEDR start request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state and is valid when the DAEDR
is in the IDLE state.
New State
The new DAEDR state is the IN-SERVICE state.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful: When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The link state is unchanged.
- Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
When the terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state and the DAEDR is already in the
IN-SERVICE state, this primitive should be ignored and the SDTS provider should not
generate a non-fatal error.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.2 Data Transfer Service Primitives
The data transfer service primitives provide the means for transfering data between SDTS users across a signalling data link. Data is sent and received in signal units. Signal units are the data contained in frames that occur between flags on the line excluding the checksum octets. These are packets of data that contain an integer number of octets (a multiple of 8 bits). When performing data transfer, signal units that are correctly received on the signalling data link are delivered to the SDTS user as they arrive. Signal units for transmission are delivered to the SDTS provider on demand, however, during quiescent periods it is sometimes advantageous from the point of view of synchronous driver design to request trasnmission of additional signal units in a pull arrangement rather than a push arrangement. Therefore there is a primitive to allow the SDTS provider to request additional data for trasnsmission.
These service primitives implement the data transfer service (see Data Transfer Service).
4.2.2.1 SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ
Description
The DAEDT transmission request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user to request that the SDTS provider trasnmit a signal unit on the medium. A signal unit is a self-contained packet of data containing an integer number of octets of information. This primitive is a request from the Transmission Control (TXC) function in the SDTS user to the DAEDT function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The DAEDT transmission request service primitive consists of zero or one M_PROTO message
block, followed by one or more M_DATA message blocks containing the signal unit to transmit.
The M_PROTO mesage block, when present, is structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_daedt_transmission_req_t;
Parameters
The DAEDT transmission request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state with the DAEDT in the
IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The new state is unchanged.
Rules
The SDTS user must observe the following rules when issuing the DAEDT transmission request service primitive:
- This primitive should only be issued by the SDTS provider after the transmitters have been enabled
with a
SDT_DAEDT_START_REQand the DAEDT is in theIN-SERVICEstate. - After the transmitter have been enabled while in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state, the DAEDT state is always appropriate for the SDTS user to issue this primitive. - The
M_PROTOmessage block is optional. The SDTS provider will be prepared to acceptM_DATAmessage blocks from the SDTS user, without anyM_PROTOmessage block, as service primitive of this type. - Most narrowband SS7 SDTS providers peform what is known as SU repetition. When SUs that correspond
to FISUs (Fill-In Signal Units) or LSSUs (Link Status Signal Units) which are sent continuously on
the signalling link, the SDTS user need only send the first such signal unit. The SDTS provider
will continuously repeat a FISU or LSSU, when appropriate,1 until the next signal unit is presented for transmission. To
perform this function, a narrowband SS7 SDTS provider must know the protocol options associated with
the signalling link (i.e. the size of the sequence numbers and length indicator).
Activate or deactivation of SU Repeating is a provider-specific function.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful: When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The link state is unchanged.
- Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
When the terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state, but the DAEDT is still in the
IDLE state, the primitive should be ignored and the corresponding data discarded without
generating a non-fatal error.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.2.2 SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND
Description
The RC signal unit indication service primitive is issued by the SDTS provider when a signal unit arrives on the signalling data link and passes error detection. The primitive is named the ‘RC’ signal unit indication because this signal is normally sent to reception control (RC) within the SS7 Level 2 state machine. This primitive is an indication from the DAEDR function in the SDTS provider to the Reception Control (RC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The RC signal unit indication service primtive consists of one optional M_PROTO message block
followed by one or more M_DATA message blocks containing the receive signal unit. The
M_PROTO message block, when present, is structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
sdt_ulong sdt_count;
} sdt_rc_signal_unit_ind_t;
Parameters
The RC signal unit indication service primtive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND. sdt_count- When signal unit compression is in effect, this field contains a count of the number of compressed identical signal units (not counting the original). When signal unit compression is not in effect, or the signal unit was not compressed (it was not repeated on the line), this field is set to the value 0.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state.
New State
The state remains unchanged.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when generating the RC signal unit indication primitive:
- The primitive is only issued when the signalling data terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state. - Received signal units are indicated only after the receivers have been enabled using the
SDT_DAEDR_START_REQcommand and the DAEDR is in theIN-SERVICEstate. - Once the SDTS user is receiving signal units, it will continue to do so until a fatal error occurs,
the stream is closed, or the signalling data terminal is disabled with the
LMI_DISABLE_REQprimitive. - The
M_PROTOmessage block is optional and is only really required for indicating the count of compressed signal units. When signal unit compression is not in effect, or when a signal unit is not compressed (i.e. has asdt_countof zero), theM_PROTOmessage block is unnecessary and SDTS providers are encouraged to not include it. When theM_PROTOmessage block is not included, the signal unit is delivered simply as a chain of one or moreM_DATAmessage blocks to the SDTS user. The SDTS user must be prepared to receive RC signal unit indications consisting of onlyM_DATAmessage blocks. - Most narrowband SS7 SDTS providers provider for signal unit compression. Under this scheme, the
first non-identical signal unit is indicated with a
sdt_countof zero. Should additional identical signal units be received, the will be counted until another non-identical signal unit is received. At that point, an RC signal unit indication with asdt_countindicating the number of compressed signal units is indicated followed by an indication of the new non-identical signal unit with asdt_countof zero. And the cycle repeats.To support this feature, SDTS users must be prepared to accept a compressed frame representing all of the contiguous identical signalling units in this fashion. For example, the SDTS user cannot rely by its design on the third identical signal unit causing a state transsition in a timely manner.
- Invocation and applicability of a signal unit compression feature is provider-specific. So, for example, Q.703 drivers use FISU and LSSU compression techniques, whereas, M2PA (RFC 4165) does not require them.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
4.2.2.3 SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND
Description
The TXC transmission request indication service primitive is originated by the SDTS provider to indicate that if a signal unit is not available for transmission that the signalling terminal will idle the signalling data link. Depending on the specific SDTS provider, idling the signalling data link may consist of idling continuous flags, FISUs or LSSUs. This indication provides timing ques to the SDTS user. This primitive is an indication from the DAEDT function in the SDTS provider to the Transmission Control (TXC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The TXC transmission request indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message
block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_txc_transmission_request_ind_t;
Parameters
The TXC transmission request indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state and when the DAEDT is
in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The new state is unchanged.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the TXC transmission request indication service primitive:
- This service primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state. - This service primitive is only issued when the DAEDT is in the
IN-SERVICEstate; that is, aSDT_DAEDT_START_REQprimitive has been received by the SDTS provider for the signalling terminal. - This service primitive is only issued by the SDTS provider when its transmission queue is empty.
- This service primitive is only issued by the SDTS provider when the provider is configured to generate these indications. Configuration of the SDTS provider is a provider-specific matter.
Response
This primitive does not require a specific response from the SDTS user. Upon receiving this
primitive, if the SDTS user does not wish the signalling data link to idle flags, FISUs or LSSUs, it
should generate another trasnmission request using the SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ
primitive.
4.2.3 Initial Alignment Service Primitives
The initial alignment service primitives peform the functions of the Alignment Error Rate Monitor (AERM). They provide the SDTS user with the ability to start and stop the AERM, set normal or emergency proving periods, and receive correct signal unit indications and indications that the error rate has exceeded the threshold.
Not all SDTS providers implement nor require an AERM function. For example, broadband signalling links can be configured to not perform proving, in which case the AERM function is not necessary. Regardless of whether the AERM function is necessary or not, each SDTS provider should be prepared to handle requests and generate appropriate indications as though an AERM function existed, and without generating non-fatal errors.
Note that some designs do no permit the AERM function and the SUERM or EIM function to be active simultaneously.
These service primitives implement the initial alignment service (see Initial Alignment Service).
4.2.3.1 SDT_AERM_START_REQ
Description
The AERM start request service primitive is originated by the SDTS use to request that the Alignment Error Rate Monitor be started. This primitive is a request from the Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user to the AERM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The AERM start request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured
as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_aerm_start_req_t;
Parameters
The AERM start request service primitive containst the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_AERM_START_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state and valid when the DAEDR
function is in the IN-SERVICE state and the AERM function is in the IDLE state.
New State
The new state of the AERM function is the IN-SERVICE state.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful:
When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The AERM function is moved
to the
IN-SERVICEstate. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
When the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state, the DAEDR is in the
IN-SERIVCE state and the AERM is already in the IN-SERVICE state, this service
primitive should be ignored without generating a non-fatal error. Some STDS providers may generate
a non-fatal error when the SUERM/EIM function is not in the IDLE state.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.3.2 SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ
Description
The AERM set Ti to Tin request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user to request that the normal proving period be used for the current or next initial alignment error rate monitoring. This primitive is a request from the Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user to the AERM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The AERM set Ti to Tin request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req_t;
Parameters
The AERM set Ti to Tin request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state but may be issued in any
signalling terminal state.
New State
The new state remains unchanged and normal proving is asserted.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful: When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The link state is unchanged.
- Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.3.3 SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ
Description
The AERM set Ti to Tie request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user to request that the emergency proving period be used for the current or next initial alignment error rate monitoring. This primitive is a request from the Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user to the AERM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The AERM set Ti to Tie request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req_t;
Parameters
The AERM set Ti to Tie request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state but may be issued in any
signalling terminal state.
New State
The new state is unchanged and emergency proving is asserted.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful: When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The link state is unchanged.
- Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.3.4 SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND
Description
The IAC correct SU indication service primitive is issued by the SDTS provider during the intial
alignment phase to indicate that a correct signal unit has been received. Some STDS user state
machines require this primitive; others can use the SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND primitive
in its stead. This primitive is an indication from the AERM function in the SDTS provider to the
Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The IAC correct SU indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_iac_correct_su_ind_t;
Parameters
The IAC correct SU indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state and when the DAEDR
function is in the IN-SERVICE state and the AERM function is in the IN-SERVICE state.
It is only issued for the first correct signal unit received in this total state.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the IAC correct SU indication service primitive:
- The primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state. - The primitive is only issued when the DEADR function is in the
IN-SERVICEstate. - The primitive is only issued when the AERM function is in the
IN-SERVICEstate. - The primitive is only issued for the first correct signal unit that is received in the appropriate states.
- Whether the primitive is issued in the appropriate state is SDTS provider-specific. Some SDTS
providers may need configuration options set before this primitive will be issued. The SDTS user
should be prepared to use a
SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_INDprimitive in its stead.
Response
This primitive does not require a specific response from the SDTS user.
4.2.3.5 SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND
Description
The IAC abort proving indication service primitive is issued by the SDTS provider to indicate that the error rate experience on the signalling data link has exceeded the operating threshold. This primitive is an indication from the AERM function in the SDTS provider to the Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The IAC abort proving indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_iac_abort_proving_ind_t;
Parameters
The IAC abort proving indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state with the DAEDR function
in the IN-SERIVCE state and the AERM function in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The new AERM state is IDLE.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the IAC abort proving indication service primitive:
- The primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state. - The primitive is only issued when the DAEDR function is in the
IN-SERVICEstate. - The primitive is only issued when the AERM function is in the
IN-SERVICEstate. After issuing the primitive the AERM is placed into theIDLEstate. - The primitive is only issued from the appropriate state when the error rate is detected as exceeding the operating threshold. The setting of the operating threshold is a SDTS provider-specific configuration matter.
- Not all SDTS providers have a fully functional AERM. Some providers may never issue this primitive.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
4.2.3.6 SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ
Description
The AERM stop request service primitive is originated by the SDTS user to request that the AERM
function be stopped (moved to the IDLE state).
This primitive is a request from the Initial Alignment Control (IAC) function in the SDTS user to
the AERM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The AERM stop request service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block, structured as
follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_aerm_stop_req_t;
Parameters
The AERM stop request service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state with the DAEDR function in
the IN-SERVICE state and the AERM function in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The new state of the AERM function is the IDLE state.
Response
This primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement.
- Successful:
When successful, the primitive does not require receipt acknowledgement. The AERM state is moved to
the
IDLEstate. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider negatively acknowledges the primitive using a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error and reason for failure. The state remains unchanged.
When the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state and the AERM function
is already in the IDLE state, this primitive should be ignored and no non-fatal error
generated.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event occurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_INITFAILED- Link initialization failed.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.4 Error Rate Monitoring Service Primitives
The error rate monitoring service primitives perform the functions of the Signal Unit Error Rate Monitor (SUERM) or Errored Interval Monitor (EIM). They provide the SDTS user with the ability to start and stop the SUERM/EIM, and receive indications that the error rate has exceeded the operating threshold.
Not all SDTS providers implement nor require a SUERM/EIM function. Regardless of whether the SUERM/EIM function is necessary or not, each SDTS provider should be prepared to handle requests and generate appropriate indications as though a SUERM or EIM function existed, and without generating non-fatal errors.
Note that some designs do no permit the AERM function and the SUERM or EIM function to be active simultaneously.
These service primitives implement the error rate monitoring service (see Error Rate Monitoring Service).
4.2.4.1 SDT_SUERM_START_REQ
Description
This SDTS user originated primitive is used to start the Signal Unit Error Rate Monitor (SUERM) or Errorred Interval Monitor (EIM) service. This primitive is a request from the Link State Control (LSC) function in the SDTS user to the SUERM/EIM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The SUERM start service primitive consists of one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_suerm_start_req_t;
Parameters
The SUERM start service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_SUERM_START_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state, when the DAEDR is in the
IN-SERVICE state, when the AERM is in the IDLE state and when the SUERM/EIM is in the
IDLE state.
New State
The new management state remains unchanged. The state of the SUERM is moved to IN-SERVICE
state.
Response
This service primitive is not acknowledged, but can cause a non-fatal error as follows:
- Successful:
When successful, the primitive is not acknowledged. The SUERM/EIM function is moved to the
IN-SERVICEstate. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider responds with a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error.
When the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED state and the SUERM/EIM function is
already in the IN-SERVICE state, this primitive should be ignored without generating a
non-fatal error.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event ocurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.4.2 SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND
Description
This SDTS provider originated primitive is issued by the SDTS provider while the SUERM/EIM service is active to indicate that the error rate monitor has detected errors that exceed the configured threshold and that the link should be failed for execessive errors. This primitive is an indication from the SUERM/EIM function in the SDTS provider to the Link State Control (LSC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The link failure indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
message block, structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_lsc_link_failure_ind_t;
Parameters
The link failure service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND.
State
This primitive will only be issued when the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED
management state and the SUERM/EIM is in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The new state for the SUERM is the IDLE state.
Rules
The following rules apply to the link failure indication service primitive:
- The SDTS provider will only issue an
SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_INDprimitive while the SUERM or EIM is in theIN-SERVICEstate and the monitored error rate exceeds the operating threshold configured for the error monitor. After issuing the primitive, the SUERM is placed in theIDLEstate. - Not all STDS providers have a fully functional SUERM/EIM. Some providers may never issue this primitive.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
4.2.4.3 SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ
Description
This SDTS user originated primitive is used to stop the Signal Unit Error Rate Monitor (SUERM) or Errorred Interval Monitor (EIM) service. This primitive is a request from the Link State Control (LSC) function in the SDTS user to the SUERM/EIM function in the SDTS provider.
Format
The SUERM stop service primitive consists of one M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_suerm_stop_req_t;
Parameters
The SUERM stop service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Specifies the service primitive type. Always
SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ.
State
This primitive is only valid in the LMI_ENABLED management state, and when the SUERM/EIM is
in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The state of the SUERM/EIM is moved to IDLE state.
Response
This service primitive is not acknowledged, but can cause a non-fatal error as follows:
- Successful:
When successful, the primitive is not acknowledged. The SUERM function is moved to the
IDLEstate. - Unsuccessful (non-fatal errors):
When unsuccessful, the SDTS provider responds with a
LMI_ERROR_ACKprimitive containing the error. The state remains unchanged.
When the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management state and the SUERM/EIM is
already in the IDLE state, this primitive should be ignored without generating a non-fatal
error.
Reason for Failure
Non-Fatal Errors: applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
LMI_UNSPEC- Unknown or unspecified.
LMI_BADPRIM- Unrecognized primitive.
LMI_DISC- Disconnected.
LMI_EVENT- Protocol-specific event ocurred.
LMI_FATALERR- Device has become unusable.
LMI_NOTSUPP- Primitive not supported by this device.
LMI_OUTSTATE- Primitive was issued from invalid state.
LMI_PROTOSHORTM_PROTOblock too short.LMI_SYSERR- UNIX system error.
LMI_FORMAT- Format error detected.
LMI_DEVERR- Start of device-specific error codes.
4.2.5 Receive Congestion Service Primitives
The receive congestion service primitives provide the SDTS user with the ability to be informed by the SDTS provider when it detects receive congestion conditions and can determine a receive congestion policy. Receive congestion is a provider-specific matter. The SDTS user is also capable of detecting receive congestion without the assistance of these primitives. They are used to indicate receive congestion to the SDTS user that can only be detected within the SDTS provider.
These service primitives implement the receive congestion service (see Receive Congestion Service).
4.2.5.1 SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND
Description
The RC convestion accept indication service primitive is indicated by the SDTS provider when it is experiencing receive congestion but signal units continue to be delivered by the SDTS provider. This primitive is an indication from a provider-specific function in the SDTS provider to the Reception Control (RC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The RC congestion accept indication service primtive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_rc_congestion_accept_ind_t;
Parameters
The RC congestion accept indication service primtive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the LMI_ENABLED management
state and the DAEDR function is in the IN-SERVICE state.
New State
The receive congestion state is moved to CONGESTION-ACCEPT.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the RC congestion accept service primitive:
- This primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state, the DAEDR function is in theIN-SERVICEstate, and the SDTS provider has detected receive congestion but is not discarding signal units. - Not all SDTS providers have a fully functional receive congestion function. Some SDTS providers may never generate this primitive.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
4.2.5.2 SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND
Description
The RC convestion discard indication service primitive is indicated by the SDTS provider when it is experiencing receive congestion and signal units are being discarded by the SDTS provider. This primitive is an indication from a provider-specific function in the SDTS provider to the Reception Control (RC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The RC congestion discard indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_rc_congestion_discard_ind_t;
Parameters
The RC congestion discard indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state.
New State
The receive congestion state is moved to CONGESTION-DISCARD.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the RC congestion discard service primitive:
- This primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state, the DAEDR function is in theIN-SERVICEstate, and the SDTS provider has detected receive congestion and is discarding signal units. - Not all SDTS providers have a fully functional receive congestion function. Some SDTS providers may never generate this primitive.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
4.2.5.3 SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND
Description
This SDTS provider originated primitive This primitive is an indication from a provider-specific function in the SDTS provider to the Reception Control (RC) function in the SDTS user.
Format
The RC no congestion indication service primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block,
structured as follows:
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
} sdt_rc_no_congestion_ind_t;
Parameters
The RC no congestion indication service primitive contains the following parameters:
sdt_primitive- Indicates the service primitive type. Always
SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND.
State
This primitive is only issued from the LMI_ENABLED management state.
New State
The receive congestion state is moved to NO-CONGESTION.
Rules
The SDTS provider observes the following rules when issuing the RC no congestion service primitive:
- This primitive is only issued when the signalling terminal is in the
LMI_ENABLEDmanagement state, the DAEDR function is in theIN-SERVICEstate, and the SDTS provider has detected that receive congestion has abated. - Not all SDTS providers have a fully functional receive congestion function. Some SDTS providers may never generate this primitive.
Response
This primitive does not require a response from the SDTS user.
5 Diagnostics Requirements
Two error handling facilities should be provided to the SDTS user: one to handle non-fatal errors, and the other to handle fatal errors.
5.1 Non-Fatal Error Handling Facility
These are errors that do not change the state of the SDTS interface as seen by the SDTS user and
provide the user with the option of reissuing the SDT primitive with the corrected options
specification. The non-fatal error handling is provided only to those primitives that require
acknowledgements, and uses the LMI_ERROR_ACK to report these errors. These errors retain the
state of the SDTS interface the same as it was before the SDT provider received the primitive that
was in error. Syntax errors and rule violations are reported via the non-fatal error handling
facility.
5.2 Fatal Error Handling Facility
These errors are issued by the SDT provider when it detects errors that are not correctable by the
SDT user, or if it is unable to report a correctible error to the SDTS user. Fatal errors are
indicated via the STREAMS message type M_ERROR with the UNIX system error EPROTO. The
M_ERROR STREAMS message type will result in the failure of all the UNIX system calls on the
stream. The SDTS user can recover from a fatal error by having all the processes close the files
associated with the stream, and then reopening them for processing.
Appendix A LMI Header File Listing
#define LMI_PROTO_BASE 16L
#define LMI_DSTR_FIRST ( 1L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_INFO_REQ ( 1L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_ATTACH_REQ ( 2L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_DETACH_REQ ( 3L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_ENABLE_REQ ( 4L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_DISABLE_REQ ( 5L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ ( 6L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_DSTR_LAST ( 6L + LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_USTR_LAST (-1L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_INFO_ACK (-1L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_OK_ACK (-2L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_ERROR_ACK (-3L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_ENABLE_CON (-4L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_DISABLE_CON (-5L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK (-6L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_ERROR_IND (-7L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_STATS_IND (-8L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_EVENT_IND (-9L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_USTR_FIRST (-9L - LMI_PROTO_BASE )
#define LMI_UNATTACHED 1L /* No PPA attached, awating LMI_ATTACH_REQ */
#define LMI_ATTACH_PENDING 2L /* Waiting for attach */
#define LMI_UNUSABLE 3L /* Device cannot be used, STREAM in hung state */
#define LMI_DISABLED 4L /* PPA attached, awaiting LMI_ENABLE_REQ */
#define LMI_ENABLE_PENDING 5L /* Waiting to send LMI_ENABLE_CON */
#define LMI_ENABLED 6L /* Ready for use, awaiting primtiive exchange */
#define LMI_DISABLE_PENDING 7L /* Waiting to send LMI_DISABLE_CON */
#define LMI_DETACH_PENDING 8L /* Waiting for detach */
/*
* LMI_ERROR_ACK and LMI_ERROR_IND reason codes
*/
#define LMI_UNSPEC 0x00000000 /* Unknown or unspecified */
#define LMI_BADADDRESS 0x00010000 /* Address was invalid */
#define LMI_BADADDRTYPE 0x00020000 /* Invalid address type */
#define LMI_BADDIAL 0x00030000 /* (not used) */
#define LMI_BADDIALTYPE 0x00040000 /* (not used) */
#define LMI_BADDISPOSAL 0x00050000 /* Invalid disposal parameter */
#define LMI_BADFRAME 0x00060000 /* Defective SDU received */
#define LMI_BADPPA 0x00070000 /* Invalid PPA identifier */
#define LMI_BADPRIM 0x00080000 /* Unregognized primitive */
#define LMI_DISC 0x00090000 /* Disconnected */
#define LMI_EVENT 0x000a0000 /* Protocol-specific event ocurred */
#define LMI_FATALERR 0x000b0000 /* Device has become unusable */
#define LMI_INITFAILED 0x000c0000 /* Link initialization failed */
#define LMI_NOTSUPP 0x000d0000 /* Primitive not supported by this device
*/
#define LMI_OUTSTATE 0x000e0000 /* Primitive was issued from invalid
state */
#define LMI_PROTOSHORT 0x000f0000 /* M_PROTO block too short */
#define LMI_SYSERR 0x00100000 /* UNIX system error */
#define LMI_WRITEFAIL 0x00110000 /* Unitdata request failed */
#define LMI_CRCERR 0x00120000 /* CRC or FCS error */
#define LMI_DLE_EOT 0x00130000 /* DLE EOT detected */
#define LMI_FORMAT 0x00140000 /* Format error detected */
#define LMI_HDLC_ABORT 0x00150000 /* Aborted frame detected */
#define LMI_OVERRUN 0x00160000 /* Input overrun */
#define LMI_TOOSHORT 0x00170000 /* Frame too short */
#define LMI_INCOMPLETE 0x00180000 /* Partial frame received */
#define LMI_BUSY 0x00190000 /* Telephone was busy */
#define LMI_NOANSWER 0x001a0000 /* Connection went unanswered */
#define LMI_CALLREJECT 0x001b0000 /* Connection rejected */
#define LMI_HDLC_IDLE 0x001c0000 /* HDLC line went idle */
#define LMI_HDLC_NOTIDLE 0x001d0000 /* HDLC link no longer idle */
#define LMI_QUIESCENT 0x001e0000 /* Line being reassigned */
#define LMI_RESUMED 0x001f0000 /* Line has been reassigned */
#define LMI_DSRTIMEOUT 0x00200000 /* Did not see DSR in time */
#define LMI_LAN_COLLISIONS 0x00210000 /* LAN excessive collisions */
#define LMI_LAN_REFUSED 0x00220000 /* LAN message refused */
#define LMI_LAN_NOSTATION 0x00230000 /* LAN no such station */
#define LMI_LOSTCTS 0x00240000 /* Lost Clear to Send signal */
#define LMI_DEVERR 0x00250000 /* Start of device-specific error codes */
typedef signed int lmi_long;
typedef unsigned int lmi_ulong;
typedef unsigned short lmi_ushort;
typedef unsigned char lmi_uchar;
/*
* LOCAL MANAGEMENT PRIMITIVES
*/
/*
LMI_INFO_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_INFO_REQ */
} lmi_info_req_t;
/*
LMI_INFO_ACK, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_INFO_ACK */
lmi_ulong lmi_version;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
lmi_ulong lmi_max_sdu;
lmi_ulong lmi_min_sdu;
lmi_ulong lmi_header_len;
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_style;
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_offset;
lmi_ulong lmi_prov_flags; /* provider specific flags */
lmi_ulong lmi_prov_state; /* provider specific state */
lmi_uchar lmi_ppa_addr[0];
} lmi_info_ack_t;
#define LMI_VERSION_1 1
#define LMI_VERSION_2 2
#define LMI_CURRENT_VERSION LMI_VERSION_2
/*
* LMI provider style.
*
* The LMI provider style which determines whether a provider requires an
* LMI_ATTACH_REQ to inform the provider which PPA user messages should be
* sent/received on.
*/
#define LMI_STYLE1 0x00 /* PPA is implicitly bound by open(2) */
#define LMI_STYLE2 0x01 /* PPA must be explicitly bound via STD_ATTACH_REQ */
/*
LMI_ATTACH_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_ATTACH_REQ */
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_ppa_offset;
lmi_uchar lmi_ppa[0];
} lmi_attach_req_t;
/*
LMI_DETACH_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_DETACH_REQ */
} lmi_detach_req_t;
/*
LMI_ENABLE_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_ENABLE_REQ */
lmi_ulong lmi_rem_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_rem_offset;
lmi_uchar lmi_rem[0];
} lmi_enable_req_t;
/*
LMI_DISABLE_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_DISABLE_REQ */
} lmi_disable_req_t;
/*
LMI_OK_ACK, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_OK_ACK */
lmi_long lmi_correct_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_ok_ack_t;
/*
LMI_ERROR_ACK, M_CTL
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_ERROR_ACK */
lmi_ulong lmi_errno;
lmi_ulong lmi_reason;
lmi_long lmi_error_primitive;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_error_ack_t;
/*
LMI_ENABLE_CON, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_ENABLE_CON */
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_enable_con_t;
/*
LMI_DISABLE_CON, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_DISABLE_CON */
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_disable_con_t;
/*
LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ, M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_OPTMGMT_REQ */
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_offset;
lmi_ulong lmi_mgmt_flags;
} lmi_optmgmt_req_t;
/*
LMI_OPTMGMT_ACK, M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_OPMGMT_ACK */
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_length;
lmi_ulong lmi_opt_offset;
lmi_ulong lmi_mgmt_flags;
} lmi_optmgmt_ack_t;
#undef LMI_DEFAULT
#define LMI_NEGOTIATE 0x0004
#define LMI_CHECK 0x0008
#define LMI_DEFAULT 0x0010
#define LMI_SUCCESS 0x0020
#define LMI_FAILURE 0x0040
#define LMI_CURRENT 0x0080
#define LMI_PARTSUCCESS 0x0100
#define LMI_READONLY 0x0200
#define LMI_NOTSUPPORT 0x0400
/*
LMI_ERROR_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_ERROR_IND */
lmi_ulong lmi_errno;
lmi_ulong lmi_reason;
lmi_ulong lmi_state;
} lmi_error_ind_t;
/*
LMI_STATS_IND, M_PROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_STATS_IND */
lmi_ulong lmi_interval;
lmi_ulong lmi_timestamp;
} lmi_stats_ind_t;
/*
LMI_EVENT_IND, M_PROTO
*/
typedef struct {
lmi_long lmi_primitive; /* LMI_EVENT_IND */
lmi_ulong lmi_objectid;
lmi_ulong lmi_timestamp;
lmi_ulong lmi_severity;
} lmi_event_ind_t;
union LMI_primitive {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_ok_ack_t ok_ack;
lmi_error_ack_t error_ack;
lmi_error_ind_t error_ind;
lmi_stats_ind_t stats_ind;
lmi_event_ind_t event_ind;
};
union LMI_primitives {
lmi_long lmi_primitive;
lmi_info_req_t info_req;
lmi_info_ack_t info_ack;
lmi_attach_req_t attach_req;
lmi_detach_req_t detach_req;
lmi_enable_req_t enable_req;
lmi_disable_req_t disable_req;
lmi_ok_ack_t ok_ack;
lmi_error_ack_t error_ack;
lmi_enable_con_t enable_con;
lmi_disable_con_t disable_con;
lmi_error_ind_t error_ind;
lmi_stats_ind_t stats_ind;
lmi_event_ind_t event_ind;
};
#define LMI_INFO_REQ_SIZE sizeof(lmi_info_req_t)
#define LMI_INFO_ACK_SIZE sizeof(lmi_info_ack_t)
#define LMI_ATTACH_REQ_SIZE sizeof(lmi_attach_req_t)
#define LMI_DETACH_REQ_SIZE sizeof(lmi_detach_req_t)
#define LMI_ENABLE_REQ_SIZE sizeof(lmi_enable_req_t)
#define LMI_DISABLE_REQ_SIZE sizeof(lmi_disable_req_t)
#define LMI_OK_ACK_SIZE sizeof(lmi_ok_ack_t)
#define LMI_ERROR_ACK_SIZE sizeof(lmi_error_ack_t)
#define LMI_ENABLE_CON_SIZE sizeof(lmi_enable_con_t)
#define LMI_DISABLE_CON_SIZE sizeof(lmi_disable_con_t)
#define LMI_ERROR_IND_SIZE sizeof(lmi_error_ind_t)
#define LMI_STATS_IND_SIZE sizeof(lmi_stats_ind_t)
#define LMI_EVENT_IND_SIZE sizeof(lmi_event_ind_t)
typedef struct lmi_opthdr {
lmi_ulong level;
lmi_ulong name;
lmi_ulong length;
lmi_ulong status;
lmi_uchar value[0];
/*
followed by option value */
} lmi_opthdr_t;
#define LMI_LEVEL_COMMON '\0'
#define LMI_LEVEL_SDL 'd'
#define LMI_LEVEL_SDT 't'
#define LMI_LEVEL_SL 'l'
#define LMI_LEVEL_SLS 's'
#define LMI_LEVEL_MTP 'M'
#define LMI_LEVEL_SCCP 'S'
#define LMI_LEVEL_ISUP 'I'
#define LMI_LEVEL_TCAP 'T'
#define LMI_OPT_PROTOCOL 1 /* use struct lmi_option */
#define LMI_OPT_STATISTICS 2 /* use struct lmi_sta */
Appendix B SDTI Header File Listing
/*
* The purpose of the SDT interface is to provide a separation between
* the SL (Signalling Link) interface which provides SS7 Level 2 (LINK)
* state machine services and the underlying driver which provides
* essentially HDLC capablities. In SS7 the entity providing HDLC
* services is called the Signalling Data Terminal (SDT). An SDTI
* implements the AERM/SUERM/EIM and DAEDR/DAEDT capabilities and
* communicates upstream to the Signalling Link using the primitives
* provided here.
*
* The SDT interface also recognizes Local Management Interface (LMI)
* primitives defined elsewhere <sys/ss7/lmi.h>.
*/
typedef lmi_long sdt_long;
typedef lmi_ulong sdt_ulong;
typedef lmi_ushort sdt_ushort;
typedef lmi_uchar sdt_uchar;
#define SDT_PROTO_BASE 48L
#define SDT_DSTR_FIRST ( 1L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ ( 1L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ ( 2L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ ( 3L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_AERM_START_REQ ( 4L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ ( 5L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ ( 6L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ ( 7L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_SUERM_START_REQ ( 8L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ ( 9L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_DSTR_LAST ( 9L + SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_USTR_LAST (-1L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND (-1L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND (-2L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND (-3L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND (-4L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND (-5L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND (-6L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND (-7L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND (-8L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
#define SDT_USTR_FIRST (-8L - SDT_PROTO_BASE)
/*
* STATE
*/
#define SDTS_POWER_OFF 0
#define SDTS_IDLE 1
#define SDTS_ABORTED_PROVING 2
#define SDTS_NORMAL_PROVING 3
#define SDTS_EMERGENCY_PROVING 4
#define SDTS_MONITORING_ERRORS 5
#define SDTS_MONITORING 6
/*
* FLAGS
*/
#define SDTF_DAEDT_ACTIVE (1<<0)
#define SDTF_DAEDR_ACTIVE (1<<1)
#define SDTF_AERM_ACTIVE (1<<2)
#define SDTF_SUERM_ACTIVE (1<<3)
/*
* SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND, M_DATA or M_PROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND */
sdt_ulong sdt_count;
} sdt_rc_signal_unit_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ, M_DATA or M_PROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ */
} sdt_daedt_transmission_req_t;
/*
* SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ */
} sdt_daedt_start_req_t;
/*
* SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ */
} sdt_daedr_start_req_t;
/*
* SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND */
} sdt_iac_correct_su_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_AERM_START_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_AERM_START_REQ */
} sdt_aerm_start_req_t;
/*
* SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ */
} sdt_aerm_stop_req_t;
/*
* SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ */
} sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req_t;
/*
* SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ */
} sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req_t;
/*
* SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND */
} sdt_iac_abort_proving_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_SUERM_START_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_SUERM_START_REQ */
} sdt_suerm_start_req_t;
/*
* SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ */
} sdt_suerm_stop_req_t;
/*
* SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND */
} sdt_lsc_link_failure_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND */
} sdt_rc_congestion_accept_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND */
} sdt_rc_congestion_discard_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND */
} sdt_rc_no_congestion_ind_t;
/*
* SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND, M_PROTO or M_PCPROTO
*/
typedef struct {
sdt_long sdt_primitive; /* SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND */
} sdt_txc_transmission_request_ind_t;
union SDT_primitives {
sdt_long sdt_primitive;
sdt_daedt_transmission_req_t daedt_transmission_req;
sdt_daedt_start_req_t daedt_start_req;
sdt_daedr_start_req_t daedr_start_req;
sdt_aerm_start_req_t aerm_start_req;
sdt_aerm_stop_req_t aerm_stop_req;
sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req_t aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req;
sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req_t aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req;
sdt_suerm_start_req_t suerm_start_req;
sdt_suerm_stop_req_t suerm_stop_req;
sdt_rc_signal_unit_ind_t rc_signal_unit_ind;
sdt_rc_congestion_accept_ind_t rc_congestion_accept_ind;
sdt_rc_congestion_discard_ind_t rc_congestion_discard_ind;
sdt_rc_no_congestion_ind_t rc_no_congestion_ind;
sdt_iac_correct_su_ind_t iac_correct_su_ind;
sdt_iac_abort_proving_ind_t iac_abort_proving_ind;
sdt_lsc_link_failure_ind_t lsc_link_failure_ind;
sdt_txc_transmission_request_ind_t txc_transmission_request_ind;
};
#define SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_daedt_transmission_req_t)
#define SDT_DAEDR_START_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_daedr_start_req_t)
#define SDT_DAEDT_START_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_daedt_start_req_t)
#define SDT_AERM_START_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_aerm_start_req_t)
#define SDT_AERM_STOP_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_aerm_stop_req_t)
#define SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req_t)
#define SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req_t)
#define SDT_SUERM_START_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_suerm_start_req_t)
#define SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQ_SIZE sizeof(sdt_suerm_stop_req_t)
#define SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_rc_signal_unit_ind_t)
#define SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_rc_congestion_accept_ind_t)
#define SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_rc_congestion_discard_ind_t)
#define SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_rc_no_congestion_ind_t)
#define SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_iac_correct_su_ind_t)
#define SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_iac_abort_proving_ind_t)
#define SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_lsc_link_failure_ind_t)
#define SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND_SIZE sizeof(sdt_txc_transmission_request_ind_t)
License
GNU Free Documentation License
Copyright © 2000 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
Preamble
The purpose of this License is to make a manual, textbook, or other written document free in the sense of freedom: to assure everyone the effective freedom to copy and redistribute it, with or without modifying it, either commercially or noncommercially. Secondarily, this License preserves for the author and publisher a way to get credit for their work, while not being considered responsible for modifications made by others.
This License is a kind of “copyleft”, which means that derivative works of the document must themselves be free in the same sense. It complements the GNU General Public License, which is a copyleft license designed for free software.
We have designed this License in order to use it for manuals for free software, because free software needs free documentation: a free program should come with manuals providing the same freedoms that the software does. But this License is not limited to software manuals; it can be used for any textual work, regardless of subject matter or whether it is published as a printed book. We recommend this License principally for works whose purpose is instruction or reference.
- APPLICABILITY AND DEFINITIONS
This License applies to any manual or other work that contains a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it can be distributed under the terms of this License. The “Document”, below, refers to any such manual or work. Any member of the public is a licensee, and is addressed as “you”.
A “Modified Version” of the Document means any work containing the Document or a portion of it, either copied verbatim, or with modifications and/or translated into another language.
A “Secondary Section” is a named appendix or a front-matter section of the Document that deals exclusively with the relationship of the publishers or authors of the Document to the Document's overall subject (or to related matters) and contains nothing that could fall directly within that overall subject. (For example, if the Document is in part a textbook of mathematics, a Secondary Section may not explain any mathematics.) The relationship could be a matter of historical connection with the subject or with related matters, or of legal, commercial, philosophical, ethical or political position regarding them.
The “Invariant Sections” are certain Secondary Sections whose titles are designated, as being those of Invariant Sections, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License.
The “Cover Texts” are certain short passages of text that are listed, as Front-Cover Texts or Back-Cover Texts, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License.
A “Transparent” copy of the Document means a machine-readable copy, represented in a format whose specification is available to the general public, whose contents can be viewed and edited directly and straightforwardly with generic text editors or (for images composed of pixels) generic paint programs or (for drawings) some widely available drawing editor, and that is suitable for input to text formatters or for automatic translation to a variety of formats suitable for input to text formatters. A copy made in an otherwise Transparent file format whose markup has been designed to thwart or discourage subsequent modification by readers is not Transparent. A copy that is not “Transparent” is called “Opaque”.
Examples of suitable formats for Transparent copies include plain ascii without markup, Texinfo input format, LaTeX input format, SGML or XML using a publicly available DTD, and standard-conforming simple HTML designed for human modification. Opaque formats include PostScript, PDF, proprietary formats that can be read and edited only by proprietary word processors, SGML or XML for which the DTD and/or processing tools are not generally available, and the machine-generated HTML produced by some word processors for output purposes only.
The “Title Page” means, for a printed book, the title page itself, plus such following pages as are needed to hold, legibly, the material this License requires to appear in the title page. For works in formats which do not have any title page as such, “Title Page” means the text near the most prominent appearance of the work's title, preceding the beginning of the body of the text.
- VERBATIM COPYING
You may copy and distribute the Document in any medium, either commercially or noncommercially, provided that this License, the copyright notices, and the license notice saying this License applies to the Document are reproduced in all copies, and that you add no other conditions whatsoever to those of this License. You may not use technical measures to obstruct or control the reading or further copying of the copies you make or distribute. However, you may accept compensation in exchange for copies. If you distribute a large enough number of copies you must also follow the conditions in section 3.
You may also lend copies, under the same conditions stated above, and you may publicly display copies.
- COPYING IN QUANTITY
If you publish printed copies of the Document numbering more than 100, and the Document's license notice requires Cover Texts, you must enclose the copies in covers that carry, clearly and legibly, all these Cover Texts: Front-Cover Texts on the front cover, and Back-Cover Texts on the back cover. Both covers must also clearly and legibly identify you as the publisher of these copies. The front cover must present the full title with all words of the title equally prominent and visible. You may add other material on the covers in addition. Copying with changes limited to the covers, as long as they preserve the title of the Document and satisfy these conditions, can be treated as verbatim copying in other respects.
If the required texts for either cover are too voluminous to fit legibly, you should put the first ones listed (as many as fit reasonably) on the actual cover, and continue the rest onto adjacent pages.
If you publish or distribute Opaque copies of the Document numbering more than 100, you must either include a machine-readable Transparent copy along with each Opaque copy, or state in or with each Opaque copy a publicly-accessible computer-network location containing a complete Transparent copy of the Document, free of added material, which the general network-using public has access to download anonymously at no charge using public-standard network protocols. If you use the latter option, you must take reasonably prudent steps, when you begin distribution of Opaque copies in quantity, to ensure that this Transparent copy will remain thus accessible at the stated location until at least one year after the last time you distribute an Opaque copy (directly or through your agents or retailers) of that edition to the public.
It is requested, but not required, that you contact the authors of the Document well before redistributing any large number of copies, to give them a chance to provide you with an updated version of the Document.
- MODIFICATIONS
You may copy and distribute a Modified Version of the Document under the conditions of sections 2 and 3 above, provided that you release the Modified Version under precisely this License, with the Modified Version filling the role of the Document, thus licensing distribution and modification of the Modified Version to whoever possesses a copy of it. In addition, you must do these things in the Modified Version:
- Use in the Title Page (and on the covers, if any) a title distinct from that of the Document, and from those of previous versions (which should, if there were any, be listed in the History section of the Document). You may use the same title as a previous version if the original publisher of that version gives permission.
- List on the Title Page, as authors, one or more persons or entities responsible for authorship of the modifications in the Modified Version, together with at least five of the principal authors of the Document (all of its principal authors, if it has less than five).
- State on the Title page the name of the publisher of the Modified Version, as the publisher.
- Preserve all the copyright notices of the Document.
- Add an appropriate copyright notice for your modifications adjacent to the other copyright notices.
- Include, immediately after the copyright notices, a license notice giving the public permission to use the Modified Version under the terms of this License, in the form shown in the Addendum below.
- Preserve in that license notice the full lists of Invariant Sections and required Cover Texts given in the Document's license notice.
- Include an unaltered copy of this License.
- Preserve the section entitled “History”, and its title, and add to it an item stating at least the title, year, new authors, and publisher of the Modified Version as given on the Title Page. If there is no section entitled “History” in the Document, create one stating the title, year, authors, and publisher of the Document as given on its Title Page, then add an item describing the Modified Version as stated in the previous sentence.
- Preserve the network location, if any, given in the Document for public access to a Transparent copy of the Document, and likewise the network locations given in the Document for previous versions it was based on. These may be placed in the “History” section. You may omit a network location for a work that was published at least four years before the Document itself, or if the original publisher of the version it refers to gives permission.
- In any section entitled “Acknowledgments” or “Dedications”, preserve the section's title, and preserve in the section all the substance and tone of each of the contributor acknowledgments and/or dedications given therein.
- Preserve all the Invariant Sections of the Document, unaltered in their text and in their titles. Section numbers or the equivalent are not considered part of the section titles.
- Delete any section entitled “Endorsements”. Such a section may not be included in the Modified Version.
- Do not retitle any existing section as “Endorsements” or to conflict in title with any Invariant Section.
If the Modified Version includes new front-matter sections or appendices that qualify as Secondary Sections and contain no material copied from the Document, you may at your option designate some or all of these sections as invariant. To do this, add their titles to the list of Invariant Sections in the Modified Version's license notice. These titles must be distinct from any other section titles.
You may add a section entitled “Endorsements”, provided it contains nothing but endorsements of your Modified Version by various parties—for example, statements of peer review or that the text has been approved by an organization as the authoritative definition of a standard.
You may add a passage of up to five words as a Front-Cover Text, and a passage of up to 25 words as a Back-Cover Text, to the end of the list of Cover Texts in the Modified Version. Only one passage of Front-Cover Text and one of Back-Cover Text may be added by (or through arrangements made by) any one entity. If the Document already includes a cover text for the same cover, previously added by you or by arrangement made by the same entity you are acting on behalf of, you may not add another; but you may replace the old one, on explicit permission from the previous publisher that added the old one.
The author(s) and publisher(s) of the Document do not by this License give permission to use their names for publicity for or to assert or imply endorsement of any Modified Version.
- COMBINING DOCUMENTS
You may combine the Document with other documents released under this License, under the terms defined in section 4 above for modified versions, provided that you include in the combination all of the Invariant Sections of all of the original documents, unmodified, and list them all as Invariant Sections of your combined work in its license notice.
The combined work need only contain one copy of this License, and multiple identical Invariant Sections may be replaced with a single copy. If there are multiple Invariant Sections with the same name but different contents, make the title of each such section unique by adding at the end of it, in parentheses, the name of the original author or publisher of that section if known, or else a unique number. Make the same adjustment to the section titles in the list of Invariant Sections in the license notice of the combined work.
In the combination, you must combine any sections entitled “History” in the various original documents, forming one section entitled “History”; likewise combine any sections entitled “Acknowledgments”, and any sections entitled “Dedications”. You must delete all sections entitled “Endorsements.”
- COLLECTIONS OF DOCUMENTS
You may make a collection consisting of the Document and other documents released under this License, and replace the individual copies of this License in the various documents with a single copy that is included in the collection, provided that you follow the rules of this License for verbatim copying of each of the documents in all other respects.
You may extract a single document from such a collection, and distribute it individually under this License, provided you insert a copy of this License into the extracted document, and follow this License in all other respects regarding verbatim copying of that document.
- AGGREGATION WITH INDEPENDENT WORKS
A compilation of the Document or its derivatives with other separate and independent documents or works, in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, does not as a whole count as a Modified Version of the Document, provided no compilation copyright is claimed for the compilation. Such a compilation is called an “aggregate”, and this License does not apply to the other self-contained works thus compiled with the Document, on account of their being thus compiled, if they are not themselves derivative works of the Document.
If the Cover Text requirement of section 3 is applicable to these copies of the Document, then if the Document is less than one quarter of the entire aggregate, the Document's Cover Texts may be placed on covers that surround only the Document within the aggregate. Otherwise they must appear on covers around the whole aggregate.
- TRANSLATION
Translation is considered a kind of modification, so you may distribute translations of the Document under the terms of section 4. Replacing Invariant Sections with translations requires special permission from their copyright holders, but you may include translations of some or all Invariant Sections in addition to the original versions of these Invariant Sections. You may include a translation of this License provided that you also include the original English version of this License. In case of a disagreement between the translation and the original English version of this License, the original English version will prevail.
- TERMINATION
You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Document except as expressly provided for under this License. Any other attempt to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Document is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such parties remain in full compliance.
- FUTURE REVISIONS OF THIS LICENSE
The Free Software Foundation may publish new, revised versions of the GNU Free Documentation License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns. See http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/.
Each version of the License is given a distinguishing version number. If the Document specifies that a particular numbered version of this License “or any later version” applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and conditions either of that specified version or of any later version that has been published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation. If the Document does not specify a version number of this License, you may choose any version ever published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation.
How to use this License for your documents
To use this License in a document you have written, include a copy of the License in the document and put the following copyright and license notices just after the title page:
Copyright (C) year your name.
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document
under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.1
or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation;
with the Invariant Sections being list their titles, with the
Front-Cover Texts being list, and with the Back-Cover Texts being list.
A copy of the license is included in the section entitled ``GNU
Free Documentation License''.
If you have no Invariant Sections, write “with no Invariant Sections” instead of saying which ones are invariant. If you have no Front-Cover Texts, write “no Front-Cover Texts” instead of “Front-Cover Texts being list”; likewise for Back-Cover Texts.
If your document contains nontrivial examples of program code, we recommend releasing these examples in parallel under your choice of free software license, such as the GNU General Public License, to permit their use in free software.
Glossary
- Signalling Data Terminal Service Data Unit
-
A grouping of SDT user data whose boundaries are preserved from one end of the signalling data terminal
connection to the other.
- Data transfer
-
The phase in connection and connectionless modes that supports the transfer of data between to
signalling data terminal users.
- SDT provider
-
The signalling data terminal layer protocol that provides the services of the signalling data terminal
interface.
- SDT user
-
The user-level application or user-level or kernel-level protocol that accesses the services of the
signalling data terminal layer.
- Local management
-
The phase in connection and connectionless modes in which a SDT user initializes a stream and
attaches a PPA address to the stream. Primitives in this phase generate local operations only.
- PPA
-
The point at which a system attaches itself to a physical communications medium.
- PPA identifier
- An identifier of a particular physical medium over which communication transpires.
Acronyms
| AERM | Alignment Error Rate Monitor
|
| CC | Congestion Control
|
| DAEDR | Delimitation Alignment and Error Detection (Receive)
|
| DAEDT | Delimitation Alignment and Error Detection (Transmit)
|
| EIM | Errored Interval Monitor
|
| IAC | Initial Alignment Control
|
| ITU-T | International Telecommunications Union - Telecom Sector
|
| LMS Provider | A provider of Local Management Services
|
| LMS | Local Management Service
|
| LMS User | A user of Local Management Services
|
| LM | Local Management
|
| LSC | Link State Control
|
| PPA | Physical Point of Attachment
|
| RC | Reception Control
|
| SDLI | Signalling Data Link Interface
|
| SDL SDU | Signalling Data Link Service Data Unit
|
| SDLS | Signalling Data Link Service
|
| SDL | Signalling Data Link
|
| SDTI | Signalling Data Terminal Interface
|
| SDTS | Signalling Data Terminal Service
|
| SDT | Signalling Data Terminal
|
| SLI | Signalling Link Interface
|
| SLS | Signalling Link Service
|
| SL | Signalling Link
|
| SL | Signalling Link
|
| SS7 | Signalling System No. 7
|
| TXC | Transmission Control
|
References
| [1] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.700,
Introduction to CCITT Signalling System No. 7,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
| [2] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.701,
Functional Description of the Message Transfer Part (MTP) of Signalling System No. 7,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
| [3] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.702,
Signalling System No. 7—Signalling Data Link,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
| [4] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.703,
Signalling System No. 7—Signalling Link,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
| [5] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.704,
Message Transfer Part—Signalling Network Functions and Messages,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
| [6] |
Geoffrey Gerrietts; Dave Grothe, Mikel Matthews, Dave Healy,
CDI—Application Program Interface Guide,
March 1999,
(Savoy, IL),
GCOM, Inc.
|
| [7] | ITU-T Recommendation Q.771,
Signalling System No. 7—Functional Description of Transaction Capabilities,
March 1993, (Geneva), ITU,
ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU,
(Previously “CCITT Recommendation”).
|
Index
close(2): Physical Point of Attachment Serviceerrno(3): LMI_ERROR_INDerrno(3): LMI_ERROR_ACK- license, FDL: GNU Free Documentation License
- license, GNU Free Documentation License: GNU Free Documentation License
lmi_attach_req_t: LMI_ATTACH_REQlmi_detach_req_t: LMI_DETACH_REQlmi_disable_con_t: LMI_DISABLE_CONlmi_disable_req_t: LMI_DISABLE_REQlmi_enable_con_t: LMI_ENABLE_CONlmi_enable_req_t: LMI_ENABLE_REQlmi_error_ack_t: LMI_ERROR_ACKlmi_error_ind_t: LMI_ERROR_INDlmi_event_ind_t: LMI_EVENT_INDlmi_info_ack_t: LMI_INFO_ACKlmi_info_req_t: LMI_INFO_REQlmi_ok_ack_t: LMI_OK_ACKlmi_optmgmt_ack_t: LMI_OPTMGMT_ACKlmi_optmgmt_req_t: LMI_OPTMGMT_REQlmi_stats_ind_t: LMI_STATS_INDopen(2): LMI_INFO_ACKopen(2): Physical Point of Attachment Servicesdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tie_req_t: SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIE_REQsdt_aerm_set_ti_to_tin_req_t: SDT_AERM_SET_TI_TO_TIN_REQsdt_aerm_start_req_t: SDT_AERM_START_REQsdt_aerm_stop_req_t: SDT_AERM_STOP_REQsdt_daedr_start_req_t: SDT_DAEDR_START_REQsdt_daedt_start_req_t: SDT_DAEDT_START_REQsdt_daedt_transmission_req_t: SDT_DAEDT_TRANSMISSION_REQsdt_iac_abort_proving_ind_t: SDT_IAC_ABORT_PROVING_INDsdt_iac_correct_su_ind_t: SDT_IAC_CORRECT_SU_INDsdt_lsc_link_failure_ind_t: SDT_LSC_LINK_FAILURE_INDsdt_rc_congestion_accept_ind_t: SDT_RC_CONGESTION_ACCEPT_INDsdt_rc_congestion_discard_ind_t: SDT_RC_CONGESTION_DISCARD_INDsdt_rc_no_congestion_ind_t: SDT_RC_NO_CONGESTION_INDsdt_rc_signal_unit_ind_t: SDT_RC_SIGNAL_UNIT_INDsdt_suerm_start_req_t: SDT_SUERM_START_REQsdt_suerm_stop_req_t: SDT_SUERM_STOP_REQsdt_txc_transmission_request_ind_t: SDT_TXC_TRANSMISSION_REQUEST_IND- STREAMS: Model of the SDTI
- STREAMS: Introduction
- STREAMS: Preface
Short Contents
Table of Contents
- Signalling Data Terminal Interface
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The Signalling Data Terminal Layer
- 3 SDTI Services Definition
- 3.1 Local Management Services
- 3.2 Protocol Services
- 4 SDTI Primitives
- 4.1 Local Management Service Primitives
- 4.2 Protocol Service Primitives
- 5 Diagnostics Requirements
- Appendix A LMI Header File Listing
- Appendix B SDTI Header File Listing
- License
- Glossary
- Acronyms
- References
- Index
SS7 for the
Common Man
| Home |
© Copyright 1997-2007 OpenSS7 Corporation All Rights Reserved.