SS7 for the
Common Man
Last modified: Sat, 01 Nov 2008 14:12:37 GMT
| Home |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
ISUPI Technical Specification
Description: OpenSS7 Resources Library.
A PDF version of this document is available here.
Call Control Interface (CCI)
Call Control Interface
Preface
Security Warning
Permission to use, copy and distribute this documentation without modification, for any purpose and without fee or royalty is hereby granted, provided that both the above copyright notice and this permission notice appears in all copies and that the name of OpenSS7 Corporation not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to distribution of this documentation or its contents without specific, written prior permission. OpenSS7 Corporation makes no representation about the suitability of this documentation for any purpose. It is provided “as is” without express or implied warranty.
OpenSS7 Corporation disclaims all warranties with regard to this documentation including all implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, or title; that the contents of the document are suitable for any purpose, or that the implementation of such contents will not infringe on any third party patents, copyrights, trademarks or other rights. In no event shall OpenSS7 Corporation be liable for any direct, indirect, special or consequential damages or any damages whatsoever resulting from loss of use, data or profits, whether in an action of contract, negligence or other tortious action, arising out of or in connection with any use of this document or the performance or implementation of the contents thereof.
OpenSS7 Corporation is making this documentation available as a reference point for the industry. While OpenSS7 Corporation believes that these interfaces are well defined in this release of the document, minor changes may be made prior to products conforming to the interfaces being made available.
Abstract
This document is a Specification containing technical details concerning the implementation of the Call Control Interface (CCI) for OpenSS7. It contains recommendations on software architecture as well as platform and system applicability of the Call Control Interface (CCI).
This document specifies a Call Control Interface (CCI) Specification in support of the OpenSS7 Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) and ISDN User Part (ISUP) protocol stacks.1 It provides abstraction of the call control interface to these components as well as providing a basis for call control for other call control signalling protocols.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to provide technical documentation of the Call Control Interface (CCI). This document is intended to be included with the OpenSS7 STREAMS software package released by OpenSS7 Corporation. It is intended to assist software developers, maintainers and users of the Call Control Interface (CCI) with understanding the software architecture and technical interfaces that are made available in the software package.
Intent
It is the intent of this document that it act as the primary source of information concerning the Call Control Interface (CCI). This document is intended to provide information for writers of OpenSS7 Call Control Interface (CCI) applications as well as writers of OpenSS7 Call Control Interface (CCI) Users.
Audience
The audience for this document is software developers, maintainers and users and integrators of the Call Control Interface (CCI). The target audience is developers and users of the OpenSS7 SS7 and ISDN stack.
Disclaimer
Although the author has attempted to ensure that the information in this document is complete and correct, neither the Author nor OpenSS7 Corporation will take any responsibility in it.
Revision History
Take care that you are working with a current version of this documentation: you will not be notified of updates. To ensure that you are working with a current version, check the OpenSS7 Project website for a current version.
Only the texinfo or roff source is controlled. A printed (or postscript) version of this document is an UNCONTROLLED VERSION.
cci.texi,v
Revision 0.9.2.14 2008-09-20 11:04:27 brian
- added package patchlevel
Revision 0.9.2.13 2008-08-03 06:03:29 brian
- protected agains texinfo commands in log entries
Revision 0.9.2.12 2008-08-03 05:05:13 brian
- conditional @syncodeindex frags out automake, fails distcheck
Revision 0.9.2.11 2008-07-11 09:36:11 brian
- updated documentation
Revision 0.9.2.10 2008-04-29 07:10:36 brian
- updating headers for release
Revision 0.9.2.9 2007/08/14 12:16:57 brian
- GPLv3 header updates
Revision 0.9.2.8 2007/06/27 08:42:05 brian
- added MTPI spec document
Revision 0.9.2.7 2007/06/17 01:55:58 brian
- updates for release, remove any later language
Revision 0.9.2.6 2006/08/26 09:17:03 brian
- better release file generation
Revision 0.9.2.5 2006/08/23 11:02:50 brian
- corrections
Revision 0.9.2.4 2006/08/22 12:44:12 brian
- documentation updates
Revision 0.9.2.3 2006/01/04 08:04:11 brian
- corrected documentation
Revision 0.9.2.2 2006/01/03 12:00:35 brian
- documentation updates
Revision 0.9.2.1 2006/01/02 11:51:36 brian
- new CCI texinfo file
Revision 0.8.2.3 2003/07/12 19:12:29 brian
Update draft revision 4.
Revision 0.8.2.2 2003/03/23 19:56:50 brian
Finalizing isdn.
Revision 0.8.2.1 2003/02/21 12:00:35 brian
Updated primitive interface and Q.764 conformance.
Revision 0.8 2002/11/17 15:06:36 brian
Added initial documentation for call control interface.
1 Introduction
This document specifies a STREAMS-based kernel-level instantiation of the ITU-T Call Control Interface (CCI) definition. The Call Control Interface (CCI) enables the user of a call control service to access and use any of a variety of conforming call control service providers without specific knowledge of the provider's protocol. The service interface is designed to support any network call control protocol and user call control protocol. This interface only specifies access to call control service providers, and does not address issues concerning call control and circuit management, protocol performance, and performance analysis tools.
This specification assumes that the reader is familiar with ITU-T state machines and call control interfaces (e.g., Q.764, Q.931), and STREAMS.
1.1 Related Documentation
- 1993 ITU-T Q.764 Recommendation
- 1993 ITU-T Q.931 Recommendation
- System V Interface Definition, Issue 2 - Volume 3
1.1.1 Role
This document specifies an interface that supports the services provided by the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and ISDN User Part (ISUP) for ITU-T applications as described in ITU-T Recommendation Q.931 and ITU-T Recommendation Q.764.2 These specifications are targeted for use by developers and testers of protocol modules that require call control service.
1.2 Definitions, Acronyms, Abbreviations
- Application Context
- Object Identifier
- Calling Party
- Object Identifier
- The Calling Party.
- Called Party
- The Called Party.
- Operations Class
- One of 5 ISO/OSI Transport Protocol Classes.
- MAP
- Mobile Applications Part
- TCAP
- Transaction Capabilities Application Part
- SCCP
- Service Connection Control Part
- MTP
- Message Transfer Part
- TR
- Transaction Sub-Layer
- TC
- Component Sub-Layer
- IMSI
- International Mobile Station Identifier
- MSISDN
- Mobile Station ISDN Directory Number (E.164)
- ITU
- International Telecommunications Union
- ITU-T
- International Telecommunications Union – Telecom Sector
- OSI
- Open Systems Interconnect
- ISO
- International Organization for Standardization
- MAP User
- A user of the Mobile Application Part (MAP) Interface.
- MAP Provider
- A provider of the Mobile Application Part (MAP) Interface.
- MAPI
- The Mobile Application Part (MAP) Interface.
- MS
- Mobile Station.
- Components
- Transaction components as defined in ITU-T Recommendation Q.771.
- QoS
- Quality of Service
- STREAMS
- A communication services development facility first available with UNIX System V Release 3.
2 The Call Control Layer
The Call Control Layer provides the means to manage the connection and disconnection of calls. It is responsible for the routing and management of call control signalling between call control-user entities.
2.1 Model of the CCI
The CCI defines the services provided by the call control layer to the call control-user at the boundary between the call control provider and the call control user entity. The interface consists of a set of primitives defined as STREAMS messages that provide access to the call control layer services, and are transferred between the CCS user entity and the CCS provider. These primitives are of two types; ones that originate from the CCS user, and others that originate from the CCS provider. The primitives that originate from the CCS user make requests to the CCS provider, or respond to an indication of an event of the CCS provider. The primitives that originate from the CCS provider are either confirmations of a request or are indications to the CCS user that an event has occurred. Figure 1 shows the model of the CCI.
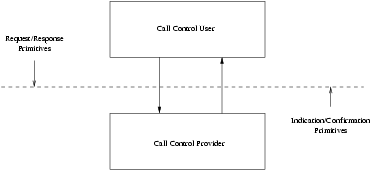
The CCI allows the CCS provider to be configured with any call control layer user (such as an ISDN
user call control application) that also conforms to the CCI. A call control layer user can also be
a user program that conforms to the CCI and accesses the CCS provider via putmsg(2s) and
getmsg(2s) system calls.
2.2 CCI Services
The features of the CCI are defined in terms of the services provided by the CCS provider, and the individual primitives that may flow between the CCS user and the CCS provider.
The services supported by the CCI are based on three distinct modes of communication, user-network interface (UNI) User mode, user-network interface (UNI) Network mode, and network-network interface (NNI). In addition, the CCI supports services for local management.
2.2.1 UNI
The main features of the User-Network Interface mode of communication are:
- It is call oriented.
- It employs facility associated signalling in that the signalling interface and circuits that are controlled by that signalling interface are bound by physical configuration. (For example, 23B+D, 2B+D).
- The protocol has two aspects to the interface: one side of the interface follows the User protocol whereas the other side of the interface follows the Network protocol.
- The user side of the protocol has no formal maintenance or monitoring procedures and therefore reports most if not all system events to the user.
- The network side of the protocol has formal maintenance and monitoring procedures and therefore reports most if not all system events to maintenance.
2.2.1.1 Address Formats
Addresses specifying all the calls and channels known to the provider are specified with scope ISDN_SCOPE_DF and
identifier zero (0).
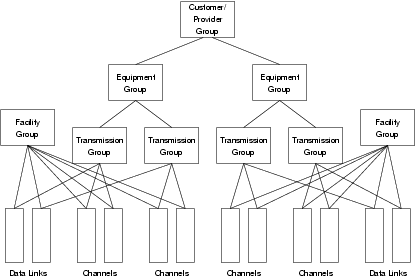
Customer/Provider Group
A customer/provider group has a different interpretation on the User and Network side of the call control interface. In User mode, the provider group is a group of all equipment groups that are serviced by the same network provider. In Network mode, the customer group is a group of all equipment groups to which the same service is provided to the same customer by the network.
Customer/provider groups are identifier using a unique customer/provider group identifier within the
CCS provider. Addresses specifying all of the equipment groups in a customer/provider group and
specified with scope ISDN_SCOPE_XG and the customer/provider group identifier.
Equipment Group
An equipment group is a group of all transmission groups (B- and D-channels) terminating at the same location. For User mode this corresponds to all the B- and D-channels terminating on the same network provider exchange. For Network mode this corresponds to all the B- and D-channels terminating on the same customer site.
Equipment groups are identified using a unique equipment group identifier within the CCS provider.
Addresses specifying all of the B- and D-channels making up an equipment group are specified with
scope ISDN_SCOPE_EG and the equipment group identifier.
Facility Group
A facility group is a group of D-channels (data links) controlling a set of B-channels. This corresponds to the signalling interface. For regular interfaces, a signalling relation consists of a single signalling interface. Where multiple signalling interfaces are used to control the same range of channels (e.g. primary and backup interfaces), all signalling interfaces belong to the same facility group.
The B-channels that make up a facility group are channels that share the same dial plan and routing characteristics for telephone calls. A facility group is associated with an equipment group.
Facility groups are identified using a unique facility group identifier within the CCS provider.
Addresses specifying all of the channels in a facility group are specified with scope
ISDN_SCOPE_FG and the facility group identifier.
An ISDN Channel Identifier is only unique within a facility group.
Transmission Group
A transmission group is the group of all D- and B-Channels associated with a given Q.931 signalling interface. For example, a typical PRI interface would consist of 23B+D, where there is one signalling interface (the D-Channel) with 23 B-Channels associated with the D-Channel. The 1 D-Channel and 23 B-Channels form a single transmission group associated with the physical interface. Every D- or B-Channel belongs to one transmission group and occupies a single time slot within that transmission group.
Transmission groups are identified using a unique transmission group identifier within the CCS
provider. Addresses specifying all of the channels in a transmission group are specified with scope
ISDN_SCOPE_TG and the transmission group identifier. Transmission groups can also be
specified using scope ISDN_SCOPE_FG and the Channel Identifier of one of the channels in the
facility group.
Channel
A channel refers to a specific B-Channel within a transmission and facility group.
Channels are identified using a unique channel identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses
specifying a specific channel are specified with scope ISDN_SCOPE_CH and the channel
identifier. Channels can also be specified using scope ISDN_SCOPE_FG, the facility group
identifier, and the Channel Identity of the channel within the facility group.
Data Link
A data link corresponds to a specific D-channel used for the control of channels. Data links can be grouped into facility groups.
Data links are identified using a unique data link identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses
specifying all of the channels controlled by a data link are specified with scope
ISDN_SCOPE_DL and the data link identifier.
2.2.2 NNI
The main features of the Network-Network Interface mode of communication are:
- It is circuit oriented.
- It employs quasi-associated signalling in that the path taken by signalling and the path taken by the circuits are not necessarily related.
- The protocol has one aspect and is peer-to-peer: that is, both sides of a signalling interface follow the same protocol in the same way.
- The network side of the protocol has formal maintenance and monitoring procedures and therefore reports most if not all system events to maintenance.
2.2.2.1 Address Formats
Addresses specifying all of the circuits known to the provider are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_DF and
identifier zero (0).
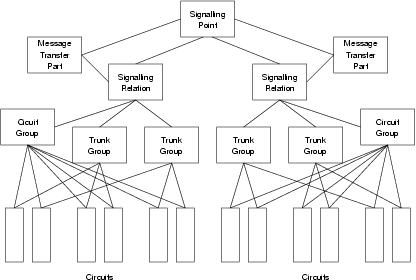
Signalling Points
A signalling point is the SS7 signalling point (central office) that the provider represents. A CCS provider can represent more than one signalling point.
A signalling point is identifier using a unique signalling point identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses
specifying all of the circuits in signalling point are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_SP and the signalling
point identifier.
Signalling Relations
A signalling relation is a relationship between a local signalling point and a remote signalling point. A signalling relation consists of a single signalling interface.
Signalling relations are identified using a unique signalling relation identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses
specifying all of the circuits in a signalling relation are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_SR and the signalling
relation identifier.
An ISUP Circuit Identification Code is only unique within a signalling relation.
Trunk Groups
A trunk group is a group of circuits that share the same routing characteristics for telephone calls. A trunk group is associated with a signalling relation. For the NNI, a signalling relation is the combination of local MTP Point Code and remote MTP Point Code.
A trunk group is identified using a unique trunk group identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses specifying all of
the circuits in a trunk group are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_TG and the trunk group identifier.
Circuit Groups
A circuit group is a group of circuits that share the same common transmission facility (e.g, E1 span) and is therefore impacted by any failure of the transmission facility. All of the individual channels of an E1 span that are used to carry calls are members of the circuit group.
Circuits groups are identified using a unique circuit group identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses specifying
all of the circuits within a circuit group are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_CG and the circuit group
identifier. Circuit groups can also be specified using scope ISUP_SCOPE_SR and the Circuit Identification Code
of one of the circuits within the circuit group.
Circuits
A circuit refers to a specific time slot within a digital facility.
Circuits are identified using a unique circuit identifier within the CCS provider. Addresses specifying a specific
circuit are specified with scope ISUP_SCOPE_CT and the circuit identifier. Circuits can also be specified using
scope ISUP_SCOPE_CG, the circuit group identifier, and the Circuit Identification Code of the circuit within the
group. Circuits can also be specified using scope ISUP_SCOPE_SR, the signalling relation identifier, and the
Circuit Identification Code of the circuit within the signalling relation.
2.2.3 Local Management
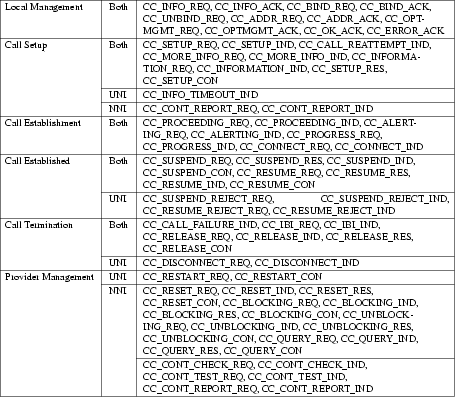
The CCI specifications also define a set of local management functions that apply to UNI and NNI modes of communication. These services have local significance only. Tables 1, 2 and 3 summarizes the CCI service primitives by their state and service.
3 CCI Services Definition
This section describes the services of the CCI primitives. Time-sequence diagrams that illustrate the sequence of primitives are included. (Conventions for the time-sequence diagrams are defined in ITU-T X.210.) The format of the primitives will be defined later in this document.
3.1 Local Management Services Definition
The services defined in this section are outside the scope of international standards. These services apply to UNI (User and Network), and NNI modes of communication. They are invoked for the initialization/de-initialization of a stream connected to the CCS provider. They are also used to manage options supported by the CCS provider and to report information on the supported parameter values.
3.1.1 Call Control Information Reporting Service
This service provides information on the options supported by the CCS provider.
CC_INFO_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider return the values of all the supported protocol parameters. This request may be invoked during any phase.CC_INFO_ACK: This primitive is in response to the N_INFO_REQ primitive and returns the values of the supported protocol parameters to the CCS user.
The sequence of primitive for call control information management is shown in Figure 4.

3.1.2 CCS Address Service
This service allows a CCS user to determine the bound call control address and the connected call control address for a given call reference associated with a stream. It permits the CCS user to not necessarily retain this information locally, and allows the CCS user to determine this information from the CCS provider at any time.
CC_ADDR_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider return information concerning which call control address the CCS user is bound as well as the call control address upon which the CCS user is currently engaged in a call for the specified call reference.CC_ADDR_ACK: This primitive is in response to theCC_ADDR_REQprimitive and indicates to the CCS user the requested information.
The sequence of primitives is shown in Figure 5.

3.1.3 CCS User Bind Service
This service allows a call control address to be associated with a stream. It allows the CCS user to negotiate the number of setup indications that can remain unacknowledged for that CCS user (a setup indication is considered unacknowledged while it is awaiting a corresponding setup response or release request from the CCS user). This service also defines a mechanism that allows a stream (bound to a call control address of the CCS user) to be reserved to handle incoming calls only. This stream is referred to as the listener stream.
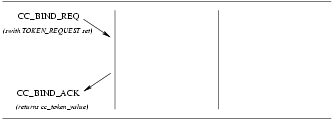
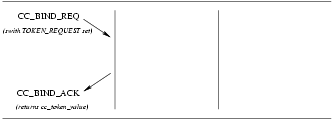
CC_BIND_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS user be bound to a particular call control address and negotiate the number of allowable outstanding setup indications for that address.CC_BIND_ACK: This primitive is in response to theCC_BIND_REQprimitive and indicates to the user that the specified CCS user has been bound to a call control address.
The sequence of primitives is shown in Figure 6 .

3.1.4 CCS User Unbind Service
This service allows the CCS user to be unbound from a call control address.
CC_UNBIND_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS user be unbound from the call control address that it had previously been bound to.
The sequence of primitives is shown in Figure 7.

3.1.5 Receipt Acknowledgement Service
CC_OK_ACK: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the previous (indicated) CCS user originated primitive was received successfully by the CCS provider.
An example showing the sequence of primitives for successful receipt acknowledgement is depicted in Figure 8.

3.1.6 Options Management Service
This service allows the CCS user to manage options parameter values associated with the CCS provider.
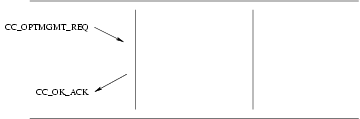
CC_OPTMGMT_REQ: This primitive allows the CCS user to select default values for options parameters within the range supported by the CCS provider.
Figure 9 shows the sequence of primitives for call control options management.
3.1.7 Error Acknowledgement Service
CC_ERROR_ACK: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a non-fatal error has occurred in the last CCS user originated request or response primitive (listed in Figure 10), on the stream.
Figure 10 shows the sequence or primitives for the error management primitive.

3.2 User-Network Interface Services Definition
This section describes the required call control service primitives that define the UNI interface.
The queue model for UNI is discussed in more detail in ITU-T Q.931. For Q.931 specific conformance considerations, see Addendum for Q.931 Conformance.
The queue model represents the operation of a call control connection in the abstract by a pair of queues linking the two call control addresses. There is one queue for each direction of signalling transfer. The ability of a user to add objects to a queue will be determined by the behaviour of the user removing objects from that queue, and the state of the queue. The pair of queues is considered to be available for each potential call. Objects that are entered or removed from the queue are either as a result of interactions at the two call control addresses, or as the result of CCS provider initiatives.
- A queue is empty until a setup object has been entered and can be returned to this state, with loss of its contents, by the CCS provider.
- Objects may be entered into a queue as a result of the action of the source CCS user, subject to control by the CCS provider.
- Objects may also be entered into a queue by the CCS provider.
- Objects are removed from the queue under the control of the receiving CCS user.
- Objects are normally removed under the control of the CCS user in the same order as they were entered except:
- if the object is of a type defined to be able to advance ahead of the preceding object, or
- if the following object is defined to be destructive with respect to the preceding object on the queue. If necessary, the last object on the queue will be deleted to allow a destructive object to be entered \- they will therefore always be added to the queue. For example, "release" objects are defined to be destructive with respect to all other objects.
Table 3 shows the ordering relationship among the queue model objects.
3.2.1 Call Setup Phase
A pair of queues is associated with a call between two call control addresses (facility group and channel(s)) when the
CCS provider receives a CC_SETUP_REQ primitive at one of the call control addresses resulting in a setup object
being entered into the queue. The queues will remain associated with the call until a CC_RELEASE_REQ or
CC_RELEASE_IND (resulting in a release object) is either entered into or removed from a queue. Similarly, in the
queue from the called CCS user, objects can be entered into the queue only after the setup object associated with the
CC_SETUP_RES has been entered into the queue. Alternatively, the called CCS user can enter a release object into
the queue instead of the setup object to terminate the call.
The call establishment procedure will fail if the CCS provider is unable to establish the call, or if the destination
CCS user is unable to accept the CC_SETUP_IND (see call failure and call reject primitive definitions).
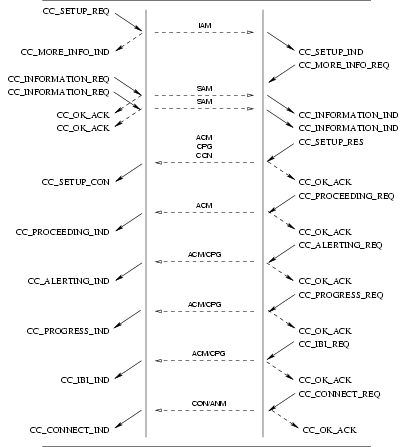
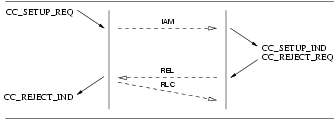
3.2.1.1 User Primitives for Successful Call Setup
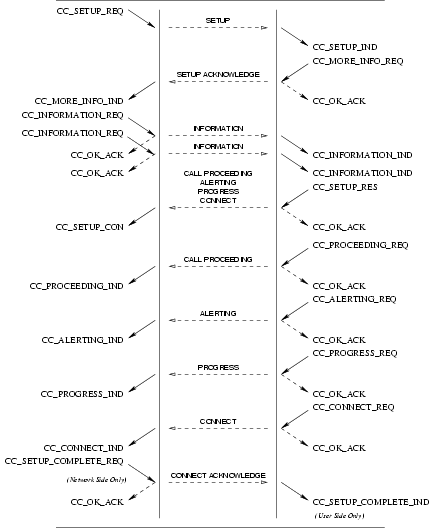
CC_SETUP_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider setup a call to the specified destination (called party number).CC_MORE_INFO_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider provide more information to establish the call. This primitive is not issued for en bloc signalling mode.CC_INFORMATION_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider provide more information (digits) in addition to the destination (called party number) already specified in theCC_SETUP_REQand subsequentCC_INFORMATION_REQprimitives. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_SETUP_RES: This primitive requests that the CCS provider accept a previous call setup indication on the specified stream.
3.2.1.2 Provider Primitives for Successful Call Setup
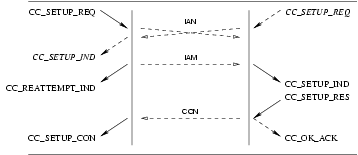
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that an event has caused call setup to fail on the selected address and that a reattempt should be made (or has been made) on another call control address (facility group and channel(s)). This primitive is only issued by the CCS provider if the CCS user is bound at the channel level rather than the facility group or equipment group levels.CC_SETUP_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a call setup request has been made by a user at the specified call control address (facility group and channel(s)).CC_MORE_INFO_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that more information is required to establish the call. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_INFORMATION_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user more information (digits) in addition to the destination (called party number) already indicated in theCC_SETUP_INDand subsequentCC_INFORMATION_INDprimitives. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: This primitive indicates to the called CCS user that a timeout occurred while waiting for additional information (called party number). The receiving CCS User should determine whether sufficient address digits have been received and either disconnect the call with theCC_DISCONNECT_REQprimitive or continue the call withCC_SETUP_RES. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_SETUP_CON: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a call setup request has been confirmed on the indicated call control address (channel(s)).
If the CCS provider is unable to establish a call, it indicates this to the request by a CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND.
This is shown in Figure 14.

The sequence of primitives for call reattempt on dual seizure are shown in Figure 15.
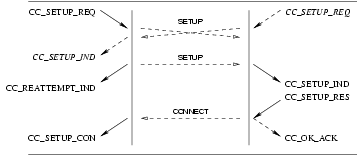
3.2.2 Call Establishment Phase
During the call establishment phase, a pair of queues has already been associated with the call between the selected call control addresses (facility group and channel(s)) during the setup phase.
3.2.2.1 User Primitives for Successful Call Establishment
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the call is proceeding and that all necessary information has been received.CC_ALERTING_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the terminating user is being alerted.CC_PROGRESS_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the specified progress event has occurred.CC_IBI_REQ(CC_DISCONNECT_REQ): This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that in-band information is now available. This will also invite the peer to release the call.CC_CONNECT_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the call has been connected.CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider complete the call setup.
3.2.2.2 Provider Primitives for Successful Call Establishment
CC_PROCEEDING_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call control peer is proceeding and that all necessary information has been received.CC_ALERTING_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the terminating user is being alerted.CC_PROGRESS_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the specified progress event has occurred.CC_IBI_IND(CC_DISCONNECT_IND): This primitive indicates to the CCS user that in-band information is now available. It also invites the CCS user to release the call.CC_CONNECT_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call has been connected.CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call has completed setup.
3.2.2.3 Provider Primitives for Successful Call Setup
The sequence of primitives in a successful call establishment is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 16.
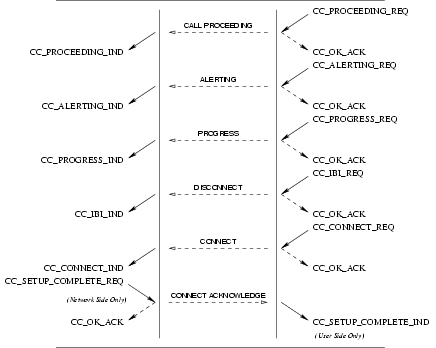
3.2.3 Call Established Phase
Flow control of the call is done by management of the queue capacity, and by allowing objects of certain types to be inserted to the queues, as shown in Table X.
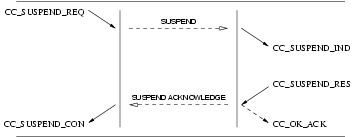
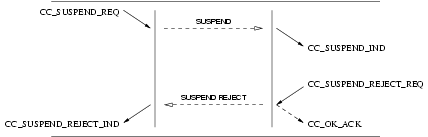
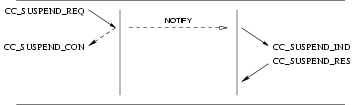
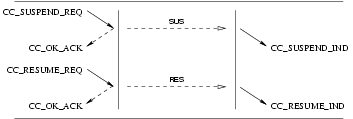
3.2.3.1 Suspend Service
User Primitives for Suspend Service
CC_SUSPEND_REQ: This primitives requests that the CCS provider temporarily suspend a call at the network, or indicate user suspension of a call.CC_SUSPEND_RES: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user (Network) is accepting the request for suspension of the call.CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user (Network) is rejecting the request for suspension of the call, and the cause for rejection.
Provider Primitives for Suspend Service
CC_SUSPEND_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that an established call has been temporarily suspended at the network, or by the remote user.CC_SUSPEND_CON: This primitive confirms to the requesting CCS user (User) that the call has been temporarily suspended at the network.CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND: This primitive indicates to the requesting CCS user (User) that the request to suspend the call has been rejected by the network, and the cause for rejection.
Figure 17 and Figure 18 show the sequence of primitives for suspend service. The sequence of primitives may remain
incomplete if a CC_RESET or a CC_RELEASE primitive occurs.
The sequence of primitives to suspend a call is defined in the time sequence diagram as shown in Figure 17 and Figure 18.
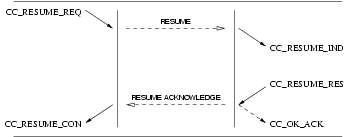
3.2.3.2 Resume Service
User Primitives for Resume Service
CC_RESUME_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider resume a previously network suspended call, or indicates that the user has resumed a call.CC_RESUME_RES: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user (Network) is accepting the request for resumption of the call.CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user (Network) is rejecting the request for resumption of the call, and the cause for rejection.
Provider Primitives for Resume Service
CC_RESUME_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a previously suspended call has been resumed at the network, or by the remote user.CC_RESUME_CON: This primitive confirms to the requesting CCS user (User) that the call has been resumed at the network.CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND: This primitive indicates to the requesting CCS user (User) that the request to resume the call has been rejected by the network, and the cause for rejection.
Figure 20 and Figure 21 show the sequence of primitives for resume service. The sequence of primitives may remain
incomplete if a CC_RESET or a CC_RELEASE primitive occurs.
The sequence of primitives to resume a call is defined in the time sequence diagram as shown in Figure 20 and Figure 21.
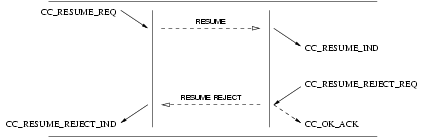
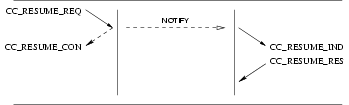
The sequence of primitives as shown above may remain incomplete if a CC_RESET or CC_RELEASE primitive
occurs (see Table 3). A CCS user must not issue a CC_RESUME_REQ primitive if no CC_SUSPEND_REQ has been
sent previously. Following a reset procedure (CC_RESET_REQ or CC_RESET_IND), a CCS user may not issue a
CC_RESUME_REQ to resume a call suspended before the reset procedure was signalled.
3.2.4 Call Termination Phase
3.2.4.1 Call Reject Service
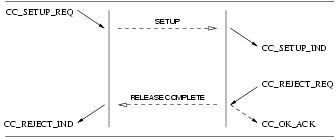
User Primitives for Call Reject Service
CC_REJECT_REQ: This primitive indicates that the CCS user receiving the specifiedCC_SETUP_INDrequests that the specified call indication be rejected.
Provider Primitives for Call Reject Service
The sequence of events for rejecting a call setup attempt at the UNI is defined in the time sequence diagram shown in Figure 23.
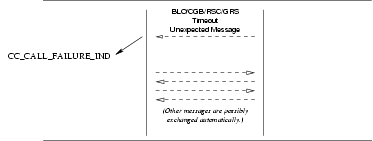
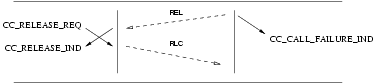
3.2.4.2 Call Failure Service
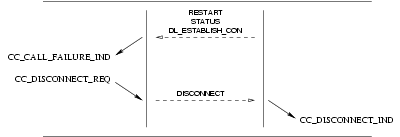
Provider Primitives for Call Failure Service
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: This primitive indicates to the called CCS user that an event has caused the call to fail and indicates the reason for the failure and the cause value associated with the failure. The CCS user is required to release the call using the indicated cause value in aCC_DISCONNECT_REQprimitive.
The sequence of events for error indications is described in the time sequence diagram shown in Figure 24.
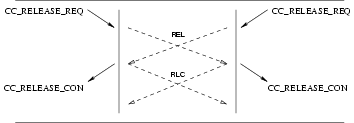
3.2.4.3 Call Release Service
The call release procedure is initialized by the insertion of a release object (associated with a
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ, CC_RELEASE_REQ, or CC_REJECT_REQ) in the queue. As shown in Table 3, the
release procedure is destructive with respect to other objects in the queue, and eventually results in the emptying of
queues and termination of the call.
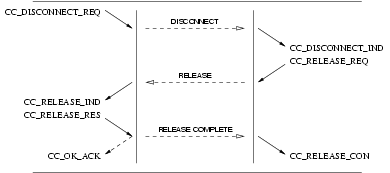
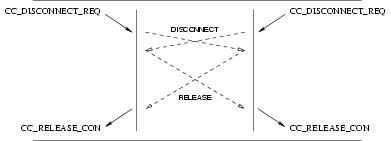
The Release procedure invokes the following interactions:
- A
CC_DISCONNECT_REQfrom the CCS user, followed by aCC_RELEASE_INDfrom the CCS provider and a subsequentCC_RELEASE_RESfrom the CCS user; or - A
CC_DISCONNECT_INDfrom the CCS provider, followed by aCC_RELEASE_REQfrom the CCS user and a subsequentCC_RELEASE_CONfrom the CCS provider.
The sequence of primitive depends on the origin of the release action. The sequence may be:
- invoked by the CCS user, with a request from that CCS user, leading to interaction (A) with that CCS user and interaction (B) with the peer CCS user;
- invoked by both CCS users, with a request from each of the CCS users, leading to interaction (A) with both CCS users;
- invoked by the CCS provider, leading to interaction (B) with both CCS users.
- invoked independently by one CCS user and the CCS provider, leading to interaction (A) with the originating CCS user and (B) with the peer CCS user.
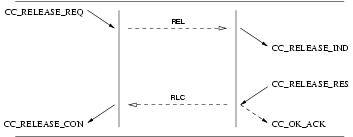
User Primitives for Release Service
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider disconnect the B-Channel or indicate tones and announcements present. Tones and announcements should be requested in theCC_IBI_REQprimitive rather than theCC_DISCONNECT_REQprimitive.CC_RELEASE_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider disconnect the B-Channel (if not already disconnected) and release the call reference.CC_RELEASE_RES: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user has accepted a release indication and has released the call reference.
Provider Primitives for Release Service
CC_DISCONNECT_IND: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user or provider has disconnected the B-Channel or has made tones and announcements available. The CCS provider should indicate tones and announcements present only with theCC_IBI_INDprimitive rather than theCC_DISCONNECT_INDprimitive.CC_RELEASE_IND: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS has disconnected the B-Channel and released the call reference.CC_RELEASE_CON: This primitive confirms that the remove CCS has disconnected the B-Channel and released the call reference.
The sequence of primitives as shown in Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, and Figure 28 may remain incomplete if a
CC_RESTART primitive occurs.
A CCS user can release a call establishment attempt by issuing a CC_DISCONNECT_REQ. The sequence of events is
shown in Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, and Figure 28.
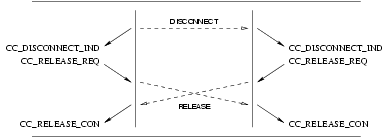
3.2.5 Call Management
3.2.5.1 User Primitives for Call Management
CC_RESTART_REQ: This primitive requests the CCS provider to restart all the call control addresses (signalling interface and channels) for the UNI interface.
3.2.5.2 Provider Primitives for Call Management
CC_RESTART_CON: This primitive confirms to the requesting CCS user that all call control addresses (signalling interface and channels) for the UNI interface have been restarted and all calls are in theCCS_IDLEstate.CC_MAINT_IND: This primitive indicates to CCS user that various events have occurred requiring maintenance notification (e.g., restart indication).
3.3 Network-Network Interface Services Definition
This section describes the required call control service primitives that define the NNI interface.
The queue model for NNI is discussed in more detail in ITU-T Q.764. For Q.764 specific conformance considerations, see Addendum for Q.764 Conformance. For ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 specific conformance considerations, see Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformance.
3.3.1 Call Setup Phase
A pair of queues is associated with a call between the two call control addresses when the CCS provider receives a
CC_SETUP_REQ primitive at one of the call control addresses resulting in a setup object being entered into the
queue. The queues will remain associated with the call until a CC_RELEASE_REQ (resulting in a release object) is
either entered into or removed from a queue. Similarly, in the queue from the called CCS user, objects can be entered
into the queue only after the setup object associated with the CC_SETUP_RES has been entered into the queue.
Alternatively, the called CCS user can enter a release object into the queue instead of the setup object to terminate
the call.
The call establishment procedure will fail if the CCS provider is unable to establish the call, or if the destination
CCS user is unable to accept the CC_SETUP_IND (see call release primitive definition).
3.3.1.1 User Primitives for Successful Call Setup
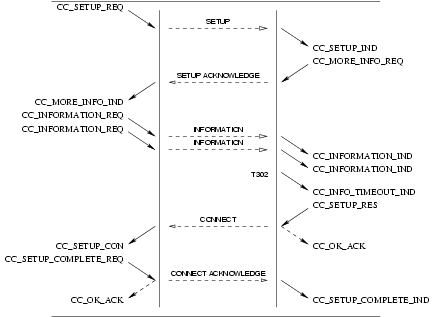
CC_SETUP_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider setup a call to the specified destination (called party address).CC_MORE_INFO_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider provide more information to establish the call. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_INFORMATION_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider provide more information (digits) in addition to the destination (called party number) already specified in theCC_SETUP_REQand subsequentCC_INFORMATION_REQprimitives. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_SETUP_RES: This primitive requests that the CCS provider accept a previous call setup indication on the specified stream.
3.3.1.2 Provider Primitives for Successful Call Setup
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that an event has caused call setup to fail on the selected address and that a reattempt should be made (or has been made) on another call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). This primitive is only issued by the CCS provider if the CCS user is bound at the circuit level rather than the circuit group or trunk group level.CC_SETUP_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a call setup request has been made by a user at the specified call control address (circuit(s)).CC_MORE_INFO_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that more information is required to establish the call. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_INFORMATION_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user more information (digits) in addition to the destination (called party number) already indicated in theCC_SETUP_INDand subsequentCC_INFORMATION_INDprimitives. This primitive is not issued for en block signalling mode.CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: This primitive indicates to the called CCS user that a timeout occurred while waiting for additional information (called party number). The receiving CCS User should determine whether sufficient address digits have been received and either disconnect the call with theCC_DISCONNECT_REQprimitive or continue the call withCC_SETUP_RES.CC_SETUP_CON: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a call setup request has been confirmed on the indicated call control address (circuits(s)).
The sequence of primitives in a successful call setup is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 30 and Figure 31.
The sequence of primitives for the call response token value determination is shown in Figure 32 (procedures for call response token value determination are discussed in section 4.1.3 and 4.1.4.)
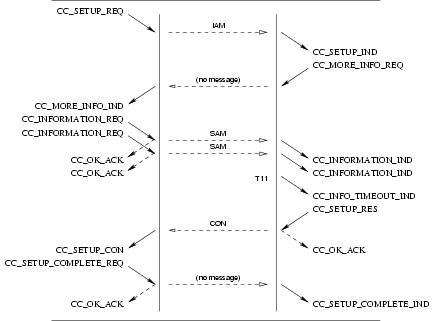
If the CCS provider is unable to establish a call, it indicates this to the request by a CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND.
This is shown in Figure 33.

The sequence of primitives for call reattempt on dual seizure are shown in Figure 34.
3.3.2 Continuity Test Phase
The continuity test service is only applicable to the NNI.
During the continuity test phase, a pair of queues has already been associated with the call between the selected call
control addresses (signalling interface and circuit(s)) during the setup phase. The continuity test phase begins when
the CCS provider returns a CC_CONT_TEST_IND primitive in response to a CC_SETUP_REQ primitive that had the
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED flag set in the call flags. The continuity test phase also begins when the CCS user
responds with a CC_CONT_TEST_REQ primitive in response to a CC_SETUP_IND primitive that had the
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED flag set in the call flags.
Upon entering the continuity test phase, it is the responsibility of the CCS user to establish a loop back on the call
control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)) or to attach tone generation and detection devices to the call
control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)).
3.3.2.1 Continuity Test Successful
User Primitives for Successful Continuity Test
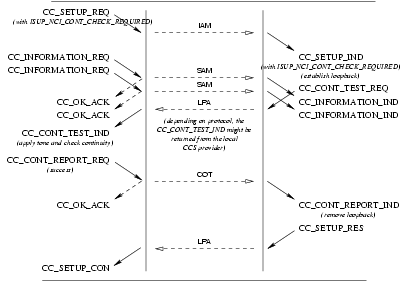
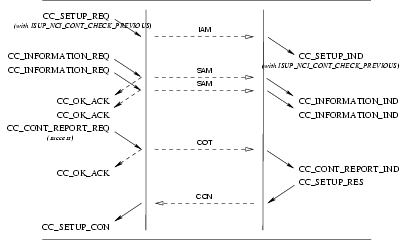
CC_SETUP_REQ: This primitive, with theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, requests that the CCS provider setup a call and include a continuity check before the call is established.CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider perform a continuity check on the specified call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). This primitive is only necessary for performing continuity checks that are not in conjunction with a call.CC_CONT_TEST_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider accept an outstanding call setup indication. When theCC_SETUP_INDhad theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, it indicates to the CCS provider that the necessary loop back device has been install on the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)).CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the remote CCS user that the continuity test has succeeded (cc_result is set toISUP_COT_SUCCESS).
Provider Primitives for Successful Continuity Test
CC_SETUP_IND: This primitive, with theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, indicates to the CCS user that a call setup including a continuity check is requested.CC_CONT_CHECK_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a continuity check was requested on the specified call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). This primitive is only necessary for performing continuity checks that are not in conjunction with a call.CC_CONT_TEST_IND: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user has accepted a call setup indication on the specified call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). When theCC_SETUP_INDprimitive had theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, it indicates to the CCS user that the necessary loop back device has been installed on the remote end of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). The CCS user receiving this primitive must attach the necessary tone generation and detection devices to the circuit(s) and perform the continuity test.CC_CONT_REPORT_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the continuity test was successful.
The sequence of primitives in a successful continuity test associated with call setup when continuity check is required on the circuit(s) is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 35.
The sequence of primitives in a successful continuity test associated with call setup when continuity check is being performed on a previous circuit is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 36.
The sequence of primitives in a successful continuity test not associated with call setup is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 37.
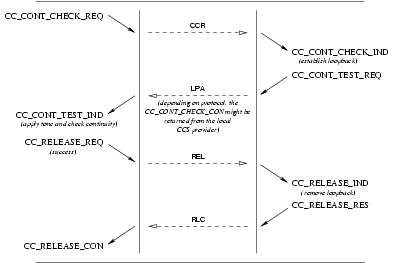
3.3.2.2 Continuity Test Unsuccessful
User Primitives for Unsuccessful Continuity Test
CC_SETUP_REQ: This primitive, with theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, requests that the CCS provider setup a call and include a continuity check before the call is established.CC_CONT_TEST_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider accept an outstanding call setup indication. When theCC_SETUP_INDhad theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, it also indicates to the CCS provider that the necessary loop back device has been install on the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)).CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the remote CCS user that the continuity test has failed (cc_result is set toISUP_COT_FAILURE).
Provider Primitives for Unsuccessful Continuity Test
CC_SETUP_IND: This primitive, with theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, indicates to the CCS user that a call setup including a continuity check is requested.CC_CONT_TEST_IND: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user has accepted a call setup indication on the specified call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). When theCC_SETUP_INDprimitive had theISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDflag set, it indicates to the CCS user that the necessary loop back device hass been installed on the remote end of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). The CCS user receiving this primitive must attach the necessary tone generation and detection devices to the circuit(s) and perform the continuity test.CC_CONT_REPORT_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the continuity test failed.CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the continuity test failed and that a reattempt should be made (or has been made) on another call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)). This primitive is only issued by the CCS provider if the CCS user is bound at the circuit level rather than the circuit group or trunk group level.
The sequence of primitives for an unsuccessful continuity test associated with a call setup is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 38.
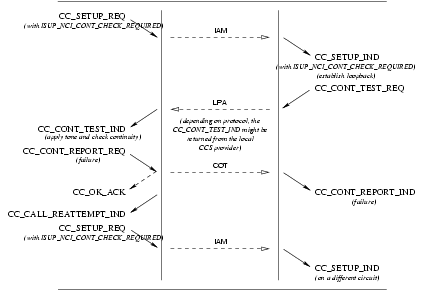
The sequence of primitives for an unsuccessful continuity test not associated with a call setup is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 39.
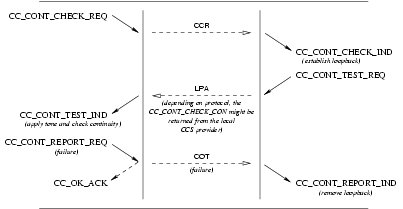
3.3.3 Call Establishment Phase
During the call establishment phase, a pair of queues has already been associated with the call between the selected
call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit(s)) during the setup phase. The call establishment phase
begins when the CCS provider returns a CC_SETUP_CON
primitive (or receives a CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ
primitive) in response to a CC_SETUP_REQ
primitive (that had the ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED flag set). The call establishment phase also begins when the CCS
user responds with a CC_SETUP_RES
primitive (or receives a CC_CONT_REPORT_IND
primitive) in response to a CC_SETUP_IND
primitive (that had the ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED flag set).
Upon entering the call establishment phase, it is the responsibility of the CCS user to remove any loop back from the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)) or to remove tone generation and detection devices from the call control address (signalling interface and circuit(s)).
3.3.3.1 User Primitives for Successful Call Establishment
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the call is proceeding.CC_ALERTING_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the terminating user is being alerted.CC_PROGRESS_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the specified progress event has occurred.CC_IBI_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that interworking has been encountered and in-band information is now available. This will also inform the peer CCS user that no connect indication is pending.CC_CONNECT_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the call control peer that the call has been connected.CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider complete the call setup. This primitive is used in NNI mode for interworking with UNI mode.
3.3.3.2 Provider Primitives for Successful Call Establishment
CC_PROCEEDING_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call control peer is proceeding.CC_ALERTING_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the terminating user is being alerted.CC_PROGRESS_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the specified progress event has occurred.CC_IBI_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that interworking has been encountered and in-band information is now available. It also indicates to the CCS user that no connect indication is pending.CC_CONNECT_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call has been connected.CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call has completed setup. This primitive is used in NNI mode for interworking with UNI mode.
The sequence of primitives in a successful call establishment is defined by the time sequence diagrams as shown in Figure 40.
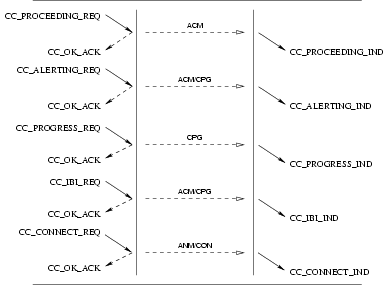
3.3.4 Call Established Phase
Flow control of the call is done by management of the queue capacity, and by allowing objects of certain types to be inserted to the queues, as shown in Table X.
3.3.4.1 User Primitives for Established Calls
CC_SUSPEND_REQ: This primitives requests that the CCS provider temporarily suspend a call.CC_RESUME_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider resume a previously suspended call.
3.3.4.2 Provider Primitives for Established Calls
CC_SUSPEND_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that an established call has been temporarily suspended.CC_RESUME_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a previously suspended call has been resumed.
Figure 41 shows the sequence of primitives for suspension and resumption of established calls. The sequence of
primitives may remain incomplete if a CC_RESET or a CC_RELEASE primitive occurs. The sequence of primitives to
successfully suspend and resume a call is defined in the time sequence diagram as shown in Figure 41.
The sequence of primitives as shown above may remain incomplete if a CC_RESET or CC_RELEASE primitive
occurs (see Table 3). A CCS user must not issue a CC_RESUME_REQ primitive if no CC_SUSPEND_REQ has been
sent previously. Following a reset procedure (CC_RESET_REQ or CC_RESET_IND), a CCS user may not issue a
CC_RESUME_REQ to resume a call suspended before the reset procedure was signalled.
3.3.5 Call Termination Phase
3.3.5.1 Call Reject Service
User Primitives for Call Reject Service
CC_REJECT_REQ: This primitive indicates that the CCS user receiving the specifiedCC_SETUP_INDrequests that the specified call indication be rejected.
Provider Primitives for Call Reject Service
The sequence of events for rejecting a call setup attempt at the NNI is defined in the time sequence diagram shown Figure 42.
3.3.5.2 Call Failure Service
The call error procedure is indicated by the removal of a reattempt or failure object (associated with a local event) from the queue. The error procedure is destructive with respect to other objects in the queue, and eventually results in the emptying of queues and termination of the call.
Provider primitives for the Call Failure Service
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that an event has caused the call to fail and indicates the reason for the failure and the cause value associated with the failure. The CCS user is required to immediately disconnect the circuit(s) and release the call on any previous legs using the indicated cause value in the primitive.
The sequence of primitives for call failure are shown in Figure 43.
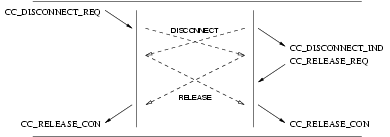
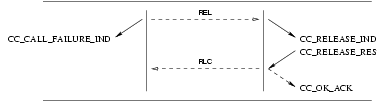
3.3.5.3 Call Release Service
The call release procedure is initialized by the insertion of a release object (associated with a CC_RELEASE_REQ)
into the queue. As shown in Table 3, the release procedure is destructive with respect to other objects in the queue,
and eventually results in the emptying of queues and termination of the call.
The release procedure invokes the following interactions:
- a
CC_RELEASE_REQfrom the CCS user, followed by aCC_RELEASE_CONfrom the CCS provider; or - A
CC_RELEASE_INDfrom the CCS provider, followed by aCC_RELEASE_REQfrom the CCS user.
The sequence of primitives depends on the origin of the release action. The sequence may be:
- invoked by one CCS user, with a request from that CCS user, leading to interaction (A) with that CCS user and interaction (B) with the peer CCS user;
- invoked by both CCS users, with a request from each of the CCS users, leading to interaction (A) with both CCS users;
- invoked by the CCS provider, leading to interaction (B) with both CCS users;
- invoked independently by on CCS user and the CCS provider, leading to interaction (A) with the originating CCS user and (B) with the peer CCS user.
User primitives for the Release Service
CC_RELEASE_REQ: This primitive request that the CCS provider release the call.CC_RELEASE_RES: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user has accepted a release indication.
Provider primitives for the Release Service
CC_RELEASE_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call has been released.CC_RELEASE_CON: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the release request has been confirmed.
The sequence of primitives as shown in Figure 44, Figure 45, Figure 46, and Figure 47, may remain incomplete if
a CC_RESET primitive occurs.
A CCS user can release a call establishment attempt by issuing a CC_RELEASE_REQ. The sequence of events is shown
in Figure 44, Figure 45, Figure 46, and Figure 47.
3.3.6 Circuit Management Services
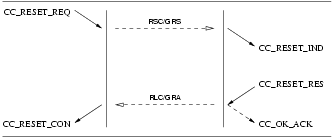
3.3.6.1 Reset Service
The reset service is used by the CCS user or management to resynchronize the use of the call, or by the CCS provider to report detected loss of a unrecoverable call.
The reset service is only applicable to the NNI.
The reset procedure invokes the following interactions:
- a
CC_RESET_REQfrom the CCS user, followed by aCC_RESET_CONfrom the CCS provider; or - a
CC_RESET_INDfrom the CCS provider, followed by aCC_RESET_RESfrom the CCS user.
The complete sequence of primitives depends upon the origin of the reset action. The reset service may be:
- invoked by one CCS user, leading to interaction (A) with that CCS user and interaction (B) with the peer CCS user.
- invoked by both CCS users, leading to interaction (A) with both CCS users;
- invoked by the CCS provider, leading to interaction (B) with both CCS users;
- invoked by one CCS user and the CCS provider, leading to interaction (A) with the originating CCS user and (B) with the peer CCS user.
User Primitives for Reset Service
CC_RESET_REQ: This primitive requests that the CCS provider reset the specified call control address (circuit or circuit group).CC_RESET_RES: This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the CCS user has accepted a reset indication and has performed local reset of the specified call control address (circuit or circuit group).3
Provider Primitives for Reset Service
CC_RESET_IND: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the user should reset the specified call control address (circuit or circuit group).CC_RESET_CON: This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the specified call control address (circuit or circuit group) has been successfully reset by the peer.
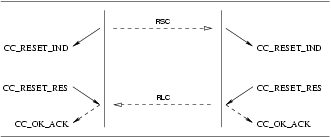
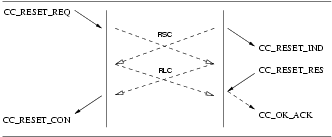
The sequence of primitives are shown in Figure 48, Figure 49, Figure 50, and Figure 51.
4
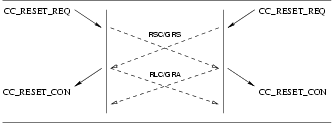
5
6
7
3.3.6.2 Blocking Service
The blocking service is used by the CCS user or management to effect local maintenance or hardware blocking on circuits, or by the CCS provider to indicate to CCS user or management the remote maintenance or hardware blocking of circuits.
The blocking service is only applicable to the NNI.
The blocking service provides for the local and remote blocking of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.
Blocking should only be invoked from streams that are listening on a circuit group that includes the circuits for which
blocking is requested, or the CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER. Maintenance blocking will also only be indicated on streams
that are listening on circuit group that includes the circuits for which blocking is requested, or in the absence of
such a stream, the CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER. When no stream is available to report maintenance blocking indications,
the indication should be responded to by the CCS provider without user or management indication.
User Primitives for Blocking Service
CC_BLOCKING_REQ: This primitive requests that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) be locally blocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.CC_BLOCKING_RES: This primitive accepts a request and indicates the call control address(es) (circuit or circuit group) that were remotely blocked for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.8
Provider Primitives for Blocking Service
CC_BLOCKING_IND: This primitive indicates that the CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) be remotely blocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.CC_BLOCKING_CON: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user has confirmed the specified call control address(es) (signalling interfaces and circuit or circuit group) as locally blocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes
The sequence of primitives are shown in Figure 51.
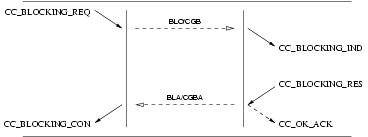
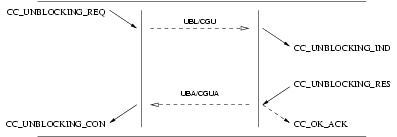
3.3.6.3 Unblocking Service
The unblocking service is only applicable to the NNI.
The unblocking service provides for the local and remote unblocking of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.
User Primitives for Unblocking Service
CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ: This primitive requests that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interfaces and circuit or circuit groups) be locally unblocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.CC_UNBLOCKING_RES: This primitive accepts a request and indicates the call control address(es) (circuit or circuit group) that were remotely unblocked for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.9
Provider Primitives for Unblocking Service
CC_UNBLOCKING_IND: This primitive indicates that the CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) be remotely blocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.CC_UNBLOCKING_CON: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user has confirmed the specified call control address(es) (signalling interfaces and circuit or circuit group) as locally unblocked either for maintenance oriented or hardware failure purposes.
The sequence of primitives are shown in Figure 52.
3.3.6.4 Query Service
The query service is only applicable to the NNI.
The query service provides for the query of the remote state and blocking level of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit group).
User Primitives for Query Service
CC_QUERY_REQ: This primitive request that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interfaces and circuit group) be queried for remote state and blocking level.CC_QUERY_RES: This primitive accepts a request and indicates the local state and blocking level for the previously requested specified call control addresses (circuit group).10
Provider Primitives for Query Service
CC_QUERY_IND: This primitive indicates that the CCS user has requested that the local state and blocking level for the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit group).CC_QUERY_CON: This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user has confirmed the specified call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit group) and has returned the remote state and blocking level for each address.
The sequence of primitives are shown in Figure 53.
4 CCI Primitives
This section describes the format and parameters of the CCI primitives (Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931 and Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764. shows the mapping of CCI primitives of the primitives defined in Q.931 and Q.764). In addition, it discusses the states the primitive is valid in, the resulting state, and the acknowledgement that the primitive expects. (The state/event tables for these primitives are shown in State/Event Tables. The precedence tables for the CCI primitives are shown in Primitive Precedence Tables.) Rules for ITU-T conformance are described in Addendum for Q.931 Conformance and Addendum for Q.764 Conformance to this document.
Tables 5, 6, and 7 provide a summary of the CCS primitives and their parameters.
4.1 Management Primitives
These primitives apply to UNI (User and Network) and NNI.
4.1.1 Call Control Information Request
CC_INFO_REQ
This primitive request the CCS provider to return the values of all supported protocol parameters (see under
CC_INFO_ACK), and also the current state of the CCS provider (as defined in State/Event Tables). This
primitive does not affect the state of the CCS provider and does not appear in the state tables.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PCPROTO message block and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_info_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_REQ */
} CC_info_req_t;
Parameters
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state where a local acknowledgement is not pending.
New State
The new state remains unchanged.
Acknowledgements
This primitive requires the CCS provider to generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of the primitive:
- Successful: Acknowledgement of the primitive via the
CC_INFO_ACKprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: There are no errors associated with the issuance of this primitive.
4.1.2 Call Control Information Acknowledgement
CC_INFO_ACK
This primitive indicates to the CCS user any relevant protocol-dependent parameters. It should be initiated in
response to the CC_INFO_REQ primitive described above.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PCPROTO message block and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_info_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_ACK */
/* FIXME ... more ... */
} CC_info_ack_t;
Parameters
The above fields have the following meaning:
Flags
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state in response to a CC_INFO_REQ primitive.
New State
The state remains the same.
4.1.3 Protocol Address Request
CC_ADDR_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider return information concerning the call control addresses upon which the CCS user is bound or engage in a call.
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_addr_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ADDR_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_addr_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference for which to obtain the connected address.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state.
New State
The new state is CCS_WACK_AREQ.
Rules
- If the call reference is specified as zero (0), then no connected address information will be returned in the
CC_ADDR_ACK.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider will generate on of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of the CC_ADDR_REQ
primitive:
- Successful: Correct acknowledgement of the primitive is indicated via the
CC_ADDR_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): These errors will be indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
4.1.4 Protocol Address Acknowledgement
CC_ADDR_ACK
This primitive acknowledges the corresponding request primitive and is used by the CCS provider to return information concerning the bound and connected protocol addresses for the stream.
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_addr_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ADDR_ACK */
ulong cc_bind_length; /* length of bound address */
ulong cc_bind_offset; /* offset of bound address */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_conn_length; /* length of connected address */
ulong cc_conn_offset; /* offset of connected address */
} CC_addr_ack_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_bind_length- Indicates the length of the bound call control address.
cc_bind_offset- Indicates the offset of the bound call control address.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference for the connected call control address.
cc_conn_length- Indicates the length of the connected call control address.
cc_conn_offset- Indicates the offset of the connected call control address.
Valid State
This primitive is valid in state CC_WACK_AREQ.
New State
The new state is the state previous to the CC_ADDR_REQ.
Rules
- If the requesting stream is not bound to a call control address, the CCS provider will code the
cc_bind_lengthandcc_bind_offsetfields to zero. Otherwise, the CCS provider will return the same call control address that was returned in theCC_BIND_ACK. - If the requesting stream is not connected to a call, the CCS provider will code the
cc_conn_lengthandcc_conn_offsetfields to zero. Otherwise, the CCS provider will indicate the call control address (circuit) upon which the call is connected.
4.1.5 Bind Protocol Address Request
CC_BIND_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider bind a CCS user entity to a call control address (circuit, circuit group) and negotiate the number of setup indications allowed to be outstanding by the CCS provider for the specified CCS user entity being bound.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_bind_req { ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BIND_REQ */ ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */ ulong cc_addr_offset; /* offset of address */ ulong cc_setup_ind; /* req # of setup inds to be queued */ ulong cc_bind_flags; /* bind options flags */ } CC_bind_req_t;/* Flags associated with CC_BIND_REQ */ #define CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER 0x000000001UL #define CC_TOKEN_REQUEST 0x000000002UL #define CC_MANAGEMENT 0x000000004UL #define CC_TEST 0x000000008UL #define CC_MAINTENANCE 0x000000010UL #define CC_MONITOR 0x000000020UL
Parameters
cc_primitive- Is the primitive type.
cc_addr_length- Is the length in bytes of the call control (circuit, circuit group) address to be bound to the stream.
cc_addr_offset- Is the offset from the beginning of the
M_PROTOblock where the call control (circuit, circuit group) address begins. cc_setup_ind- Is the requested number of setup indications (simultaneous incoming calls) allowed to be outstanding by the CCS
provider for the specified protocol address. (If the number of outstanding setup indications equals cc_setup_ind,
the CCS provider need not discard further incoming setup indications, but may choose to queue them internally until
the number of outstanding setup indications drops below the cc_setup_ind number.) Only one stream per call control
address is allowed to have a cc_setup_ind number value greater than zero. This indicates to the CCS provider that
this stream is the listener stream for the CCS user. This stream will be used by the CCS provider for setup
indications for that call control address.
if a stream is bound as a listener stream, it is still able to initiate outgoing call setup requests.
cc_bind_flags- See "Flags" below.
Flags
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER- When set, this flag specifies that this stream is the "default listener stream." This stream is used to pass setup
indications (or continuity check requests) for all incoming calls that contain protocol identifiers that are not
bound to any other listener, or when a listener stream with cc_setup_ind value of greater than zero is not found.
Also, the default listener will receive all incoming call indications that contain no user data (i.e., test calls)
and all maintenance indications (i.e.,
CC_MAINT_IND). Only one default listener stream is allowed per occurrence of CCI. An attempt to bind a default listener stream when one is already bound should result in an error (of typeCCADDRBUSY). CC_TOKEN_REQUEST- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that the CCS user has requested that a "token" be assigned to the
stream (to be used in the call response message), and the token value be returned to the CCS user via the
CC_BIND_ACKprimitive. The token assigned by the CCS provider can then be used by the CCS user in a subsequentCC_SETUP_RESprimitive to identify the stream on which the call is to be established. CC_MANAGEMENT- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for circuit management indications
for the specified addresses.
CC_TEST- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for continuity and test call
indications for the specified addresses.
CC_MAINTENANCE- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for maintenance indications for the specified addresses.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_UNBND (see State/Event Tables).
New State
The new state is CCS_WACK_BREQ.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider will generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of the CC_BIND_REQ
primitive:
- Successful: Correct acknowledgement of the primitive is indicated via the
CC_BIND_ACKprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: These errors will be indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADADDR- The call control address was in an incorrect format or the address contained illegal information. It is not
intended to indicate protocol errors.
CCNOADDR- The CCS user did not provide a call control address and the CCS provider could not allocate an address to the user.
CCADDRBUSY- The CCS user attempted to bind a second stream to a call control address with the cc_setup_ind number set to a
non-zero value, or attempted to bind a second stream with the
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERflag value set to non-zero. CCBADFLAG- The flags were invalid or unsupported, or the combination of flags was invalid. This error is returned if more than
one of
CC_TEST,CC_MANAGEMENT, orCC_MAINTENANCEflags are set. CCBADPRIM-
The primitive format was incorrect (i.e. too short).
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions.
4.1.6 Bind Protocol Address Acknowledgement
CC_BIND_ACK
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the specified call control user entity has been bound to the requested call control address and that the specified number of connect indications are allowed to be queued by the CCS provider for the specified network address.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PCPROTO message block, and its structure is the following:
typedef struct CC_bind_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BIND_ACK */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* offset of address */
ulong cc_setup_ind; /* setup indications */
ulong cc_token_value; /* setup response token value */
} CC_bind_ack_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_addr_length- Is the length of the call control address that was bound.
cc_addr_offset- Is the offset from the beginning of the
M_PCPROTOblock where the call control address begins. cc_setup_ind- Is the accepted number of setup indications allowed to be outstanding by the CCS provider for the specified call control
address. If its value is zero, this stream cannot accept
CC_SETUP_INDmessages. If its value is greater than zero, then the CCS user can acceptCC_SETUP_INDmessages up to the value specified in this parameter before having to respond with aCC_SETUP_RESor aCC_DISCONNECT_REQmessage. cc_token_value- Conveys the value of the "token" assigned to this stream that can be used by the CCS user in a
CC_SETUP_RESprimitive to accept a call on this stream. It is a non-zero value, and is unique to all streams bound to the CCS provider.
The proper alignment of the address in the M_PCPROTO message block is not guaranteed.
Rules
The following rules apply to the binding of the specified call control address to the stream:
- If the
cc_addr_lengthfield in theCC_BIND_REQprimitive is zero, then the CCS provider is to assign a call control address to the user. - The CCS provider is to bind the call control address as specified in the
CC_BIND_REQprimitive. If the CCS provider cannot bind the specified address, it may assign another call control address to the user. It is the call control user's responsibility to check the call control address returned in theCC_BIND_ACKprimitive to see if it is the same as the one requested.
The following rules apply to negotiating cc_setup_ind argument:
- The
cc_setup_indnumber in theCC_BIND_ACKprimitive must be less than or equal to the corresponding requested number as indicated in theCC_BIND_REQprimitive. - Only one stream that is bound to the indicated call control address may have a negotiated accepted number of maximum
setup indications greater than zero. If a
CC_BIND_REQprimitive specifies a value greater than zero, but another stream has already bound itself to the given call control address with a value greater than zero, the CCS provider should assign another protocol address to the user. - If a stream with
cc_setup_indnumber greater than zero is used to accept a call, the stream will be found busy during the duration of that call and no other streams may be bound to that call control address with acc_setup_indnumber greater than zero. This will prevent more than one stream bound to the identical call control address from accepting setup indications. - A stream requesting a
cc_setup_indnumber of zero should always be legal. This indicates to the CCS provider that the stream is to be used to request call setup only. - A stream with a negotiated
cc_setup_indnumber greater than zero may generate setup requests or accept setup indications.
If the above rules result in an error condition, then the CCS provider must issue a CC_ERROR_ACK
primitive to the CCS user specifying the error as defined in the description of the CC_BIND_REQ
primitive.
Valid States
This primitive is in response to a CC_BIND_REQ primitive and is valid in the state CCS_WACK_BREQ.
New State
4.1.7 Unbind Protocol Address Request
CC_UNBIND_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider unbind the CCS user entity that was previously bound to the call control address.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PROTO block, and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_unbind_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBIND_REQ */
} CC_unbind_req_t;
Parameters
Valid States
This primitive is valid in the CCS_IDLE state.
New State
The new state is CCS_WACK_UREQ.
Acknowledgements
This primitive requires the CCS provider to generate the following acknowledgements upon receipt of the primitive:
- Successful: Correct acknowledgement of the primitive is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): These errors will be indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are as follows:
4.1.8 Call Processing Options Management Request
CC_OPTMGMT_REQ
This primitive allows the CCS user to manage the call processing parameter values associated with the stream.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block, and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_optmgmt_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OPTMGMT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* length of option values */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* offset of option values */
ulong cc_opt_flags; /* option flags */
} CC_optmgmt_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference for which to manage options.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the default values of the options parameters as selected by the CCS user. These values will
be used in subsequent
CC_SETUP_REQprimitives on the stream that do not specify values for these options. If the CCS user cannot determine the value of an option, it value should be set to CC_UNKNOWN. If the CCS user does not specify any option paramter values, the length of this field should be set to zero. cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the options parameters from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_opt_flags- See "Flags" below.
Flags
Valid States
This primitive is valid in the CCS_IDLE
state.
New State
The new state is CCS_WACK_OPTREQ.
Acknowledgements
The CC_OPTMGMT_REQ primitive requires the CCS provider to generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt
of the primitive:
- Successful: Acknowledgement is via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. At successful completions, the resulting state isCCS_IDLE. - Non-fatal errors: These errors are indicated in the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The resulting state remains unchanged. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADOPT- The option parameter values specified are outside the range supported by the
CCS provider.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The flags were invalid or unsupported, or the combination of flags was invalid.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive format was incorrect (i.e. too short).
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions.
4.1.9 Call Processing Options Management Acknowledgement
CC_OPTMGMT_ACK
This primitive allows the CCS user to manage the call processing parameter values associated with the stream.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PCPROTO message block, and it structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_optmgmt_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OPTMGMT_ACK */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* length of option values */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* offset of option values */
ulong cc_opt_flags; /* option flags */
} CC_optmgmt_ack_t;
Parameters
Flags
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state.
New State
The new state is unchanged.
Acknowledgements
4.1.10 Error Acknowledgement
CC_ERROR_ACK
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a non-fatal error has occurred in the last CCS user originated primitive. This may only be initiated as an acknowledgement for those primitives that require one. It also indicates to the user that no action was taken on the primitive that caused the error.
Format
The format of the mssage is one M_PCPROTO message block, and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_error_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ERROR_ACK */
ulong cc_error_primitive; /* primitive in error */
ulong cc_error_type; /* CCI error code */
ulong cc_unix_error; /* UNIX system error code */
ulong cc_state; /* current state */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_error_ack_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Identifies the primitive type.
cc_error_primitive- Identifies the primitive type that cause the error.
cc_error_type- Contains the Call Control Interface error code.
cc_unix_error- Contains the UNIX system error code. This may only be non-zero if the cc_error_type is equal to
CCSYSERR. cc_state- Identifies the state of the interface at the time that the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive was issued by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Identifies the CCS provider or CCS user call reference associated with the request or response primitive that was in error. If no call reference is associated with the request or response primitive that caused the error, this field is coded zero (0) by the CCS provider.
Valid Error Codes
The following error codes are allows to be returned:
CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADADDR- The call control address as specified in the primitive was in an incorrect format, or the address contained illegal
information.
CCBADDIGS- The digits provided in the called party number or subsequent number specified in the primitive are of an incorrect
format or are invalid.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCNOADDR- The CCS provider could not allocate an address.
CCADDRBUSY- The CCS provider could not use the specified address because the specified address is already in use.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADTOK- Token used is not associated with an open stream.
CCBADFLAG- The flags specified in the primitive were incorrect or illegal.
CCNOTSUPP- Specified primitive type is not known to the CCS provider.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out of range).
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in all states that have a pending acknowledgement or confirmation.
New State
The new state is the same as the one from which the acknowledged request or response was issued.
4.1.11 Successful Receipt Acknowledgements
CC_OK_ACK
The primitive indicates to the CCS user that the previous call control user originated primitive was received
successfully by the call control provider. It does not indicate to the CCS user any call control protocol action taken
due to the issuance of the last primitive. The CC_OK_ACK primitive may only be initiated as an acknowledgement
for those user-originated primitives that have no other means of confirmation.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PCPROTO message block, and its structure is as follows:
typedef struct CC_ok_ack {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OK_ACK */
ulong cc_correct_prim; /* primitive being acknowledged */
ulong cc_state; /* current state */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_ok_ack_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Identifies the primitive.
cc_correct_prim- Identifies the successfully received primitive type.
cc_state- Identifies the state of the interface at the time that the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive was issued by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Identifies the CCS provider or CCS user call reference associated with the request or response primitive that was in error. If no call reference is associated with the request or response primitive that caused the error, this field is coded zero (0) by the CCS provider.
Valid States
This primitive is issued in states CCS_WACK_UREQ and CCS_WACK_OPTREQ.
New State
The resulting state depends on the current state (see State/Event Tables, Tables B-7 and B-8.).
4.2 Primitive Format and Rules
This section describes the format of the UNI (User and Newtork) and NNI primitives and the rules associated with
these primitives. The default values of the options parameters associated with a call may be selected via the
CC_OPTMGMT_REQ primitive.
4.2.1 Call Setup Phase
The following call control service primitives pertain to the setup of a call, provided the CCS users exist, and are known to the CCS provider.
4.2.1.1 Call Control Setup Request
CC_SETUP_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider make a call to the specified destination.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_REQ */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_type; /* call type */
ulong cc_call_flags; /* call flags */
ulong cc_cdpn_length; /* called party number length */
ulong cc_cdpn_offset; /* called party number offset */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameters length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameters offset */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* connect to address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connect to address offset */
} CC_setup_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies a reference number known to the CCS user that uniquely identifies the current setup request. When this
value is non-zero, it permits the CCS User to have multiple outstanding setup requests pending on the same stream.
Responses made by the CCS provider to the
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive will contain this CCS user call attempt reference. cc_call_type- Specifies the type of call to be set up. Call types supported are dependent upon the CCS provider and protocol, see
the addendum for call types for specific protocols.
cc_call_flags- Specifies a bit field of call options. Call flags supported are depeddent upon the CCS provider and protocol, see
the addendum for call flags for specific protocols.
cc_cdpn_length- Specifies the length of the called party number parameter that conveys an address identifying the CCS user to which
the call is to be established. This field will accommodate variable length numbers within a range supported by the
CCS provider. If no called party address is provided by the CCS user, this field must be coded to zero. The coding
of the called party number is protocol and provider-specific.
cc_cdpn_offset- Is the offset of the called party number from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of optional parameters to be conveyed in the call setup. This field will accomodate variable
length addresses within a range supported by the CCS provider. If no optional parameters are provided by the CCS
user, this field must be coded to zero. The format of optional parameters are protocol and provider-specific, see
the addendum for the format of optional parameters for specific protocols.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address parameter that conveys the call control address (circuit, circuit
group) of the CCS user entity to which the call is to be established. The semantics of the values in the
CC_SETUP_REQis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Rules
The following rules apply to the setup of calls to the specified addresses:
- If the cc_cdpn_length field in the
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive is zero, then the CCS provider is to select a called party number for the call. If the CCS provider cannot select a called party number for the call, the CCS provider responds with aCC_ERROR_ACKprimitive with errorCCNOADDR. - If the cc_cdpn_length field in the
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive is non-zero, the CCS provider is to setup the call to the specified number. If the CCS provider cannot setup a call of the specified call type to the specified number the call will fail and the CCS provider will return aCC_ERROR_ACKwith the appropriate error value (e.g.,CCBADADDR).
The following rules apply to the call control addresses (trunk groups and circuit identifiers):
- If the CCS user does not specify a call control address (i.e. cc_addr_length is set to zero), then the CCS provider may attempt to assign a call control address, assign it a call reference and associate it with the stream for the duration of the call.
The following rules apply to the CCS user call attempt reference:
- If the CCS user does not specify a call attempt reference (i.e. the cc_user_ref is set to zero), then the CCS
provider can only support one outstanding outgoing call attempt for the stream. If the CCS user specifies a call
attempt reference, all replies made by the CCS provider to this
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive will contain the CCS user specified call attempt reference until either the call fails or is released, or after the CCS provider sends aCC_SETUP_CONprimitive.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE.
New State
The new state depends upon the information provided in the CC_SETUP_REQ message as follows:
- If the setup request specifies that a continuity check was performed on a previous circuit, the new state is
CCS_WREQ_CCREP(awaiting report of the result of continuity test performed on the previous circuit). - If the setup request specifies that a continuity check is required on the circuit, the new state is
CCS_WIND_CTEST(awaiting indication of remote loop back on the circuit). - If the setup request specifies that no continuity test is required on this or a previous circuit and that the
called party address contains partial information, the new state is
CCS_WIND_MORE(awaiting the indication that more information is required). - If the setup request specifies that no continuity test is required on this or a previous circuit and that the called
party address contains complete information, the new state is
CCS_WCON_SREQ(awaiting confirmation of the setup request).
Acknowledgements
The following acknowledgements are valid for this primitive:
- Successful Call Establishment:
This is indicated via the
CC_SETUP_CONprimitive. This results in the Call Establishment state. ForCC_SETUP_REQprimitives whereISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDis set, or where the CCS provider otherwise determines that a continuity check is required on the circuit, success is still indicated via theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive. In this case, theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive is not sent by the CCS provider unless the continuity check is successful. ForCCS_SETUPprimitives whereISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUSis set, theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive is not sent by the CCS provider until the CCS user sends aCC_CONT_REPORT_REQprimitive indicating that continuity check on the previous circuit has been successful. Receipt of theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive always results in the Call Establishment state. - Unsuccessful Call Establishment:
This is indicated via the
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND,CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND, orCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives. For example, a call may be rejected because either the called CCS user cannot be reached, or the CCS provider and/or the called CCS user did not agree on the specified call type or options. This results in the Idle state. Where theCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives are sent before theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive, theCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives will contain the CCS user specified call attempt reference. - Non-fatal errors: These are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system eror is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADADDR- The call control address as specified in the primitive was in an incorrect format, or the address contained illegal
information.
CCBADDIGS- The called party number was in the incorrect format, or contained illegal information. This is used only to handle
coding errors of the number and is not intended to provide for protocol errors. Protocol errors should be conveyed
in the
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND,CC_CALL_FAILURE_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives. CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCNOADDR- The user did not provide a called party address field and one was required by the call type. The CCS provider could
not select a called party address.
CCADDRBUSY- The CCS provider could not use the specified address because the specified address is already in use.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal (not unique).
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out of range).
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
4.2.1.2 Call Control Setup Indication
CC_SETUP_IND
This primitive indicates to the destination CCS user that a call setup request has been made by the user at the specified source address.
Format
The format of the message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_call_type; /* call type */
ulong cc_call_flags; /* call flags */
ulong cc_cdpn_length; /* called party number length */
ulong cc_cdpn_offset; /* called party number offset */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameters length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameters offset */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* connecting address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connecting address offset */
} CC_setup_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Identifies the call reference that can be used by the CCS user to associate this message with the
CC_SETUP_RESorCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive that is to follow. This value must be unique among the outstandingCC_SETUP_INDmessages. cc_call_type- Indicates the type of call to be set up. Call types supported are dependent upon the CCS provider and protocol, see
the addendum for call types for specific protocols.
cc_call_flags- Indicates a bit field of call options. Call flags supported are dependent upon the CCS provider and protocol, see
the addendum for call flags for specific protocols.
cc_cdpn_length- Indicates the length of the called party number address parameter that conveys an address identifying the CCS user
to which the call is to be established. This field will accommodate variable length addresses within a range
supported by the CCS provider.
cc_cdpn_offset- Is the offset of the called party number address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters that were used in the call setup.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the connecting address parameter that conveys the call control address the CCS user entity
(circuit) on which the call is being established. The semantics of the values in the
CC_SETUP_INDis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_ACK. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the connecting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE
for the indicated call reference.
New State
The new state depends upon the information provided in the CC_SETUP_IND message as follows:
- If the setup indication indicates that a continuity check was performed on a previous circuit, the new state is
CCS_WIND_CCREP(awaiting the report of continuity test results). - If the setup indication indicates that a continuity check is required on the circuit, the new state is
CCS_WREQ_CTEST(awaiting confirmation of installation of loop back device on the circuit). - If the setup indication indicates that no continuity tests are required on this or a previous circuit and that the
called party number contains partial information, the new state is
CCS_WREQ_MORE(awaiting the request for more information to confirm the partial address). - If the setup indication indicates that no continuity tests are required on this or a previous circuit and that the
called party number contains complete information, the new state is
CCS_WRES_SIND(awaiting response to the setup indication).
In any event, the number of outstanding setup indications waiting for user response is incremented by one.
Rules
The rules for issuing the CC_SETUP_IND primitive are as follows:
- This primitive will only be issued to streams that have been bound with a non-zero negotiated maximum number of setup indications (i.e. on a listening stream), and where the number of outstanding setup indications (call references) for the stream is less than the negotiated maximum number of setup indications.
- If the call setup indicated is for a normal call, the stream upon which it is indicated was not bound with the
CC_TEST,CC_MANAGEMENTorCC_MAINTENANCEflags set. - If the call setup indicated is for an ISUP test call, the stream upon which it is indicated was bound with the
CC_TESTflag set and a non-zero number of negotiated maximum setup indications.
4.2.1.3 Call Control Setup Response
CC_SETUP_RES
This primitive allows the destination CCS user to request that the call control provider accept a previous setup
indication.
This primitive also indicates that overlap receiving is complete. The CCS use is still expected to
complete the setup process by issuing the CCS_PROCEED_REQ, CCS_ALERTING_REQ,
CCS_PROGRESS_REQ, CCS_IBI_REQ, CCS_CONNECT_REQ, or CCS_DISCONNECT_REQ
messages.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_RES */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_token_value; /* call response token value */
} CC_setup_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_RESmessage. It is used by the CCS provider to associated theCC_SETUP_RESmessage with an outstandingCC_SETUP_INDmessage. An invalid call reference should result in error with the error typeCCBADCLR. cc_token_value- Is used to identify the stream that the CCS user wants to establish the call on. (Its value is determined by the
CCS user by issuing a
CC_BIND_REQprimitive with theCC_TOKEN_REQflag set. The token value is returned in theCC_BIND_ACK.) The value of this field should be non-zero when the CCS user wants to establish the call on a stream other than the stream on which theCC_SETUP_INDarrived. If the CCS user wants to establish a call on the same stream that theCC_SETUP_INDarrived on, then the value of this field should be zero.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SIND.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_PROCEED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccesful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADTOK- The token specified is not associated with an open stream.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive format was incorrect (i.e. too short).
4.2.1.4 Call Control Setup Confirm
CC_SETUP_CON
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the call control setup request has been sent on the specified
call control address (circuit, circuit group). For calls that were requested setup with the
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED flag set in the CC_SETUP_REQ, or for which the CCS provider has otherwise decide to
perform continuity check, this also confirms that the continuity check was successful.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_CON */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* connecting address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connecting address offset */
} CC_setup_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitives type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the CCS user call attempt reference value which was provided by the CCS user in the
CC_SETUP_REQmessage. This permits the CCS user to associate thisCC_SETUP_CONprimitive with the previousCC_SETUP_REQprimitive and permits multiple outstandingCC_SETUP_REQprimitives. cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider assigned call reference. If the CCS user wishes to establish more than one simultaneous
call on a given stream, the CCS user must use this CCS provider indicated call reference in subsequent call control
primitives sent to the CCS provider. This permits the CCS provider to associate a CCS user primitive with one of
multiple simultaneous calls associated with a given stream.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the connecting address parameter that conveys the call control address of the CCS user
entity (circuit) on which the call is being established. The semantics of the values in the
CC_SETUP_CONis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the connecting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SREQ
and state CCS_WREQ_CCREP.
New State
The new state depends on whether an end-of-pulsing signal was present in the called party number in the associated
CC_SETUP_REQ
primitive. If an ST signal was present, the new state is CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
otherwise the new state is
CCS_WREQ_MORE.
In either case, the call enters the Call Establishment Phase.
4.2.1.5 Call Control Reattempt Indication
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the selected address (circuit) is unavailable and that a reattempt should be made on a new call control address (circuit).
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_call_reattempt_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_reason; /* reason for reattempt */
} CC_call_reattempt_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the CCS user call attempt reference value which was provided by the CCS user in the
CC_SETUP_REQmessage. This permits the CCS user to associate thisCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_INDprimitive with the previousCC_SETUP_REQprimitive and permits multiple outstandingCC_SETUP_REQprimitives. cc_reason- Indicates the cause of the reattempt. the cc_reason field is protocol and implementation specific. See the Addendum for protocol-specific values.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states
CCS_WCON_SREQ,
CCS_WREQ_CCREP,
CCS_WIND_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_INFO
and
CCS_WIND_PROCEED.
New State
Rules
- The
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_INDindicates that call repeat attempt should be made by the CCS user, and the reason for the reattempt. - If the
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_INDis issued before theCC_SETUP_CONprimitive, the user reference value will be the same value as appeared in the correspondingCC_SETUP_REQprimitive, and the call reference value will be zero. - If the CC_CALL_ATTEMPT_IND primitive is issued subsequent to the
CC_SETUP_CONprimitive, the user reference value will be zero, and the call reference value will be the same as appeared in the correspondingCC_SETUP_CONprimitive.
4.2.2 Continuity Check Phase
The following call control service primitives pertain to the continuity check phase of a call.
4.2.2.1 Call Control Continuity Check Request
CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider perform a continuity check procedure.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_check_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_check_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (circuit identifier) upon which the CCS user is requesting a
continuity check.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Rules
The following rules apply to the continuity check of call control addresses (circuit identifiers):
- If the CCS user does not specify a call control address (i.e, cc_addr_length is set to zero), then the CCS provider may attempt to assign a call control address and associate it with the stream for the duration of the continuitu test procedure. This can be useful for automated continuity testing.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE
for the selected circuit.
New State
The new state is CKS_WIND_CTEST for the selected address.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the
primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCNOADDR- The call control address was not provided (cc_addr_length coded zero).
CCBADADDR- The call control address contained in the primitive were poorly formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling address was provided in the call control
address or the address was issued to a UNI CCS provider.
CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to perform the operation on the specified call control addresses.
4.2.2.2 Call Control Continuity Check Indication
CC_CONT_CHECK_IND
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a continuity check is being requested by the CCS user peer on the
specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers). Upon receipt of this primitive,
the CCS user should establish a loop back device on the specified channel and issues the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ primitive
confirming the loop back. The CCS user should then wait for the CC_CONT_REPORT_IND indicating the success or
failure of the continuity check.
This primitive is only delivered to listening streams listening on the specified call control addresses or to a
stream bound as a default listener in the same manner as the CC_SETUP_IND. (A continuity test indication is treated
as a special form of call setup.)
This primitive is only issued to CCS users that successfully bound using the CC_BIND_REQ primitive with flag CC_TEST
set and a non-zero number of setup indications was provided in the CC_BIND_REQ and returned in the CC_BIND_ACK.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_check_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_check_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Identifies the call reference that can be used by the CCS user to associate this message with the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQorCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive that is to follow. This value must be unique among the outstandingCC_CONT_CHECK_INDmessages. cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (circuit identifier) upon which a continuity check is indicated.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the requesting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for addresses in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE
for the specified addresses.
New State
The new state is CKS_WREQ_CTEST for the specified addresses.
4.2.2.3 Call Control Continuity Test Request
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ
This message is used either to respond to a CC_SETUP_IND primitive which contains the
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED
flag, or to respond to a CC_CONT_CHECK_IND primitive. Before responding to either primitive, the CCS User should
install a loop back device on the requested channel and then respond with this response primitive to confirm the loop
back.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_test_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_token_value; /* token value */
} CC_cont_test_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQmessage. It is used by the CCS provider to associate theCC_CONT_TEST_REQmessage with an outstandingCC_SETUP_INDmessage. An invalid call reference should result in error with the error typeCCBADCLR. cc_token_value- Is used to identify the stream that the CCS user wants to establish the continuity check call on. (Its value is
determined by the CCS user by issuing a
CC_BIND_REQprimitive with theCC_TOKEN_REQflag set. The token value is returned in theCC_BIND_ACK.) The value of this field should be non-zero when the CCS user wants to establish the call on a stream other than the stream on which theCC_CONT_CHECK_INDarrived. If the CCS user wants to establish a call on the same stream that theCC_CONT_CHECK_INDarrived on, then the value of this field should be zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CKS_WREQ_CTEST.
New State
The new state is CKS_WIND_CCREP.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_REPORT_INDin the case that the primitive was issued in response to aCC_SETUP_IND, orCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive in the case that the primitive was issued in response to theCC_CONT_CHECK_INDprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_REPORT_INDprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the operation.
CCNOTSUPP- The CCS provider does not support the operation.
4.2.2.4 Call Control Continuity Test Indication
CC_CONT_TEST_IND
This message confirms to the testing CCS user that a loop back device has been (or will be) installed on the
specified call control address (circuit). Upon receiving this message, the testing CCS user should connect tone
generation and detection equipment to the specified circuit, perform the continuity test and issue a report using
the CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ primitive.
This primitive will only be issued to streams successfully bound with the CC_BIND_REQ primitive with a non-zero
number of setup indications and the CC_TEST bind flag set.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_test_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_test_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference associated with the continuity check call for the specified call control address
(circuit identifier).
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit identifier) upon which a
continuity check is confirmed. The semantics of the values in the
CC_CONT_TEST_INDis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the connecting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_CREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_WAIT_COR.
4.2.2.5 Call Control Continuity Report Request
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the called CCS user that the continuity check succeeded or failed. The CCS user should remove any continuity test tone generator/detection device from the circuit and verify silent code loop back before issuing this primitive.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_report_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the CCS user reference of the associated
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive. This value is non-zero when theCC_CONT_REPORT_REQprimitive is issued subsequent to aCC_SETUP_REQprimitive which had the flag ISUP_NCI_CONTINUITY_CHECK_PREVIOUS set to indicate the result of the continuity check on the previous circuit. Otherwise, this value is coded zero. cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the associated
CC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive for the continuity check call. This value is non-zero when theCC_CONT_REPORT_REQprimitive is issued in response to aCC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive. Otherwise, this value is coded zero. cc_result- Specifies the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. The value of the cc_result is protocol specific. For values representing success and values representing failure, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_CCREP.
New State
When issued in response to the CC_CONT_TEST_IND
primitive, the new state is CCS_IDLE.
When issued subsequent to a CC_SETUP_REQ
primitive, the new state is either CCS_WREQ_MORE
or CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
depending upon whether the sent address contain an ST pulse.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.2.2.6 Call Control Continuity Report Indication
CC_CONT_REPORT_IND
This primitive indicates to the called CCS user that the continuity check succeeded or failed. The called CCS user can remove the loop back or tone generation/detection devices from the circuit and the call either moves to the idle state or a call setup state.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_report_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference associated with the continuity check report as it appeared in the associated
CC_CONT_CHECK_INDprimitive. cc_result- Indicates the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. The value of the cc_result is protocol specific. For values representing success and values representing failure, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_CTEST or CCS_WIND_CCREP.
New State
If the primitive is issued subsequent to the CC_SETUP_REQ,
the new state is CCS_WCON_SREQ.
If the primitive is issued in response to the CC_CONT_TEST_IND
primitive, the new state is CCS_IDLE.
4.2.3 Collecting Information Phase
The following call control service primitive pertain to the collecting information phase of a call. During this phase requests for more information are issued and indicated, and additional information is provided.
4.2.3.1 Call Control More Information Request
CC_MORE_INFO_REQ
This message request more information (digits in the called party address, or optional parameters) from the calling CCS user. This specifies to the CCS provider that overlap receiving is in effect and the number of digits received are not sufficient to complete the call.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the
M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_more_info_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MORE_INFO_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_more_info_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference for the
CC_MORE_INFO_REQmessage. It is used by the CCS provider to associated theCC_MORE_INFO_REQmessage with an previousCC_SETUP_INDmessage and identify the incoming call. cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the nore information request.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User and Network) mode and for compatibility in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_MORE.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_INFO.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_INFORMATION_INDandCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_INDprimitives. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated by the
CC_CALL_FAILURE_INDprimitive with a protocol specific reason indicating that additional information was not provided within a sufficient period of time. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCNOTSUPP- The CCS provider does not support the operation.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the operation.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was incorrectly formatted (i.e. the
M_PROTOmessage block was too short).
4.2.3.2 Call Control More Information Indication
CC_MORE_INFO_IND
This message indicates that the calling CCS user needs to provide additional information (called party address
digits) to complete call processing. The CCS user should generate CC_INFORMATION_REQ primitives, if possible. This
is also an indication that overlap receiving is in effect. Appropriate protocol timers will be started.
In contrast to the the CC_INFORMATION_REQ primitive(s) which are sent by the CCS user in response to this message,
the CC_MORE_INFO_IND message is normally only issued once per call setup.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_more_info_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MORE_INFO_IND */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_more_info_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the user call reference of the
CC_MORE_INFO_INDmessage. It is used by the CCS user to associate theCC_MORE_INFO_INDmessage with an outstandingCC_SETUP_REQmessage. cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the more information indication. If no optional
parameters are associated with the more information indications, this parameter must be coded zero by the CCS
provider.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (Network and User) mode, and for compatibility in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WIND_MORE.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_INFO.
4.2.3.3 Call Control Information Request
CC_INFORMATION_REQ
This message request that the CCS provider include the subsequent number information in addition to the called party
number information previously supplied with a CC_SETUP_REQ primitive.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_information_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFORMATION_REQ */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_subn_length; /* subsequent number length */
ulong cc_subn_offset; /* subsequent number offset */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_information_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the user call reference. It is used by the CCS user to associate
the message with an outstanding
CC_SETUP_REQmessage. cc_subn_length- Specifies the length of the subsequent called party address parameter that conveys more of an address identifying
the CCS user to which the call is to be established. This field will accommodate variable length addresses within a
range supported by the CCS provider. If no subsequent called party address is provided by the CCS user, this field
must be coded to zero. The coding of the subsequent called party address is protocol and provider-specific.
cc_subn_offset- Is the offset of the subsequent called party address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the alerting indication.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (both User and Network) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WIND_MORE
and CCS_WREQ_INFO.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_MORE
if the subsequent number still does not contain complete address information or CCS_WIND_PROCEED
if it does.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCNOADDR- The user did not provide a subsequent called party address field and one was required by the call type. The CCS
provider could not select a called party address.
CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system eror is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The specified call reference was invalid.
CCBADADDR- The subsequent called party address was in the incorrect format, or contained illegal information. This is used
only to handle coding errors of the address and is not intended to provide for protocol errors. Protocol errors
should be conveyed in the
CC_CALL_FAILURE_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives. CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.3.4 Call Control Information Indication
CC_INFORMATION_IND
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_information_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFORMATION_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_subn_length; /* subsequent number length */
ulong cc_subn_offset; /* subsequent number offset */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_information_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the message. It is used by the CCS provider to associated the message with an
preceding
CC_SETUP_INDmessage. cc_subn_length- Indicates the length of the subsequent called party address parameter that conveys more of an address identifying
the CCS user to which the call is to be established. This field will accommodate variable length addresses within a
range supported by the CCS provider. If no subsequent called party address is provided by the CCS user, this field
must be coded to zero. The coding of the subsequent called party address is protocol and provider-specific.
cc_subn_offset- Is the offset of the subsequent called party address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block. cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the alerting indication.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (both User and Network) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_MORE
or CCS_WIND_INFO.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_MORE
if more information is still pending, or CCS_WREQ_PROCEED
if the information is complete.
4.2.3.5 Call Control Information Timeout Indication
CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND
This message indicates that a timeout has occurred while waiting for additional digits. It is up to the CCS user to
decide whether the digits collected are sufficient, in which case the call can proceed; or, to decide that the
digits collected are insufficient and begin tearing down the call with a CC_DISCONNECT_REQ or CC_RELEASE_REQ with
cause value CC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_info_timeout_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_info_timeout_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_INDprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid State
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WIND_INFO
or CCS_WREQ_INFO.
New State
The new state is unchanged.
4.2.4 Call Establishment Phase
The following call control service primitives pertain to the establishment of a call.
4.2.4.1 Call Control Proceeding Request
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the calling CCS user that the call is proceeding towards the called CCS user. This also means that there is sufficient called party address information to complete the call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_proceeding_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROCEEDING_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* proceeding flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_proceeding_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference for the request. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Specifies proceeding flags associated with the proceeding request. Proceeding flags are protocol specific (see the
Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the alerting indication.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_ICC_WAIT_ACM.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_MORE
or CCS_WIND_PROCEED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The specified flags were incorrect or unsupported.
CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.4.2 Call Control Proceeding Indication
CC_PROCEEDING_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the call is proceeding to the called CCS user. This also means that there is sufficient called party address information to complete the call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_proceeding_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROCEEDING_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* proceeding flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_proceeding_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. It is used by the CCS provider to indicate the call.
cc_flags- Indicates the proceeding flags associated with the proceeding indication. Proceeding flags are protocol specific
(see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the proceeding indication.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_MORE
or CCS_WIND_PROCEED.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_ALERTING.
4.2.4.3 Call Control Alerting Request
CC_ALERTING_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the calling CCS user that the called CCS user is being alerted.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_alerting_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ALERTING_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* alerting flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_alerting_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. It is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Specifies the alerting flags associated with the alerting request. Alerting flags are protocol specific (see
Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the alerting indication.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primiitve is valid in states CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_PROCEED
and CCS_WREQ_ALERTING
states.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The specified flags contained incorrect or unsupported information.
CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.4.4 Call Control Alerting Indication
CC_ALERTING_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the called CCS user is being alerted.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_alerting_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ALERTING_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* alerting flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_alerting_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Indicates the alerting flags.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the alerting indication. If no optional parameters
are associated with the alerting indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WIND_PROCEED
and CCS_WIND_ALERTING.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_PROGRESS.
4.2.4.5 Call Control Progress Request
CC_PROGRESS_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the calling CCS user that the call is progressing towards the called CCS user, with the specified event.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_progress_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROGRESS_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_event; /* progress event */
ulong cc_flags; /* progress flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_progress_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_event- Specifies the progress event. Progress events are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_flags- Indicates progress flags. Progress flags are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the progress request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the progress request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The specified flags contained incorrect or unsupported information.
CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.4.6 Call Control Progress Indication
CC_PROGRESS_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that the call is progressing towards the called CCS user with the specified progress event.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_progress_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROGRESS_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_event; /* progress event */
ulong cc_flags; /* progress flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_progress_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_event- Indicates the progress event. Progress events are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_flags- Indicates progress flags. Progress flags are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the progress request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the progress request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (User or Network) or NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid instates CCS_WIND_PROGRESS.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_PROGRESS.
4.2.4.7 Call Control In-Band Information Request
CC_IBI_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider indicate to the calling CCS user that the in-band information is now available.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_ibi_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_IBI_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* ibi flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_ibi_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Specifies the flags associated with the primitive. In band information flags are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the in-band information request. If no optional
parameters are associated with the in band information request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode and in UNI (User and Network) mode for compatibility with the NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
CCS_WREQ_ALERTING,
CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS
and CCS_WREQ_CONNECT.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_CONNECT.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The specified flags contained incorrect or unsupported information.
CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.4.8 Call Control In-Band Information Indication
CC_IBI_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that there is in-band information now available in the voice channel.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_ibi_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_IBI_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* ibi flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_ibi_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Indicates the flags associated with the primitive. In band information flags are provider and protocol specific
(see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the in-band information indication. If no optional
parameters are associated with the in band information request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode and in UNI (User and Network) mode for compatibility with the NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WIND_MORE,
CCS_WIND_PROCEED,
CCS_WIND_ALERTING
and CCS_WIND_PROGRESS.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_CONNECT.
4.2.4.9 Call Control Connect Request
CC_CONNECT_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provide indicate to the remote CCS user that the call control setup has complete and the called CCS use is connected on the call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_connect_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONNECT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* connect flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_connect_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call. The call
reference is the same value which was indicated in the corresponding
CC_SETUP_INDprimitive for the incoming call. cc_flags- Specifies the connect flags associated with the primitive. Connect flags are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the connect request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the connect request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode and in UNI (User) mode.
Valid States
This primitive is only valid for incoming calls in the CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
CCS_WREQ_ALERTING,
CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS,
CCS_WREQ_CONNECT
states.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_SCOMP (waiting for indication of setup complete).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_INDprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND,CC_DISCONNECT_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitives. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADFLAG- The specified flags contained incorrect or unsupported information.
CCBADOPT- The optional parameters were in an incorrect format, or contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the use of the requested address or options.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive is of an incorrect format or an offset exceeds the size of the
M_PROTOblock.
4.2.4.10 Call Control Connect Indication
CC_CONNECT_IND
This primitive indicates that the called CCS user has connected to the call. Upon receving this primitive the CCS
user operating in UNI (Network) mode should connect the calling CCS user to the call and acknowledge connection of
the calling CCS user by responding with the CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ primitive.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_connect_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONNECT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* connect flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_connect_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call. The call
reference is the same value which was indicated in the corresponding
CC_SETUP_CONprimitive for the outgoing call. cc_flags- Indicates the connect flags associated with the primitive. Connect flags are protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the connect indication. If no optional parameters
are associated with the connect indication, then this parameter is coded zero by the CCS provider.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode and in UNI (Network) mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WIND_SCOMP.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED.
4.2.4.11 Call Control Setup Complete Request
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider indicate to the remote CCS user that the call control setup has
completed (the calling CCS user is connected) by the requesting CCS user. It is used in response to the
CC_CONNECT_IND primitive.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_complete_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_setup_complete_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the setup complete request. If no optional
parameters are associated with the setup complete request, then this parameter must be coded zero. The CCS provider
may include additional protocol-specific optional parameters.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI mode (Network only) and NNI mode for compatibility.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_SCOMP.
For compatibility between NNI mode and UNI Network mode, the CCS provider in NNI mode should acknowledge this
primitive with a CC_OK_ACK
if it is issued in the CCS_CONNECTED
state.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out of range).
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.4.12 Call Control Setup Complete Indication
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND
This primitive indicates to the called CCS user, operating in UNI (User) mode, that the call control setup was completed (the call is answered and connected) by the calling CCS user. In UNI (User) mode, the CCS user may defer connecting the receive path to the called CCS user until this message is received. In response to this primitive, the CCS user should connect the receive path to the called CCS user and consider the call connected.
CCS users operating in UNI (Network) mode or NNI mode should ignore this primitive if issued by the CCS provider.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_setup_complete_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_setup_complete_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitives type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the setup complete indication. If no optional
parameters were associated with the setup complete indication, then this parameter must be coded zero. The CCS
provider may include additional optional protocol-specific optional parameters.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User only) mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WIND_SCOMP and CCS_CONNECTED.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED.
4.2.5 Call Established Phase
The following call control service primitives pertain to the Established phase of a call.
4.2.5.1 Forward Transfer Request
CC_FORWXFER_REQ
This message requests that the CCS provider forward transfer an established call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_forwxfer_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_FORWXFER_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_forwxfer_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the forward transfer request. If no optional
parameters were associated with the forward transfer request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_CONNECTED.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.2.5.2 Forward Transfer Indication
CC_FORWXFER_IND
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the peer CCS user has requested a forward transfer of an established call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_forwxfer_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_FORWXFER_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_forwxfer_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the forward transfer indication. If no optional
parameters were associated with the forward transfer indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode only.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_CONNECTED.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED.
4.2.5.3 Call Control Suspend Request
CC_SUSPEND_REQ
This message requests that the CCS provider suspend an established call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Specifies the suspend flags associated with the suspend request. Suspend flags specify whether the request is for a
user suspend or a network suspend. Suspend flags are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend request. If no optional parameters were
associated with the suspend request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_CONNECTED.
New State
The new state is CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_SUSPEND_CONprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive. The cause value in theCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_INDorCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive indicates the cause of failure. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.2.5.4 Call Control Suspend Indication
CC_SUSPEND_IND
This message indicates to the CCS user that the peer CCS user has requested the suspension of an establisehd call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Indicates the options associated with the suspend. Suspend flags are mode and protocol dependent, see the addendum.
Indicates the suspend flags associated with the suspend indication. Suspend flags indicate whether the request is
for a user suspend or a network suspend. Suspend flags are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend indication. If no optional parameters
were associated with the suspend indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_CONNECTED
or CCS_SUSPENDED.
New State
The new state is CCS_WRES_SUSIND for UNI and CCS_SUSPENDED for NNI.
4.2.5.5 Call Control Suspend Response
CC_SUSPEND_RES
This message requests that the CCS provider accept a previous suspend indication.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_RES */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend response. If no optional parameters
were associated with the suspend response, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SUSIND.
New State
The new state is CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.2.5.6 Call Control Suspend Confirmation
CC_SUSPEND_CON
This message indicates to the CCS user that the CCS provider has confirmed the CCS user request to suspend an established call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_CON */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend indication. If no optional parameters
were associated with the suspend indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SUSREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_SUSPENDED.
4.2.5.7 Call Control Suspend Reject Request
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ
This message request that the CCS provider reject a previous suspend indication with the specified cause.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_reject_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_reject_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS user to identify the call. Its value should be
the same as the value returned by the CCS provider in the
CC_SETUP_INDorCC_SETUP_CONprimitive. cc_cause- Indicates the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend reject request. If no optional
parameters are associated with the suspend reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the suspend reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SUSIND.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or another sense (network or user), otherwise the new state
remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.5.8 Call Control Suspend Reject Confirmation
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND
This message indicates to the requesting CCS user that a previous suspend request for an established call was rejected and the cause for rejection.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_suspend_reject_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_reject_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_cause- Indicates the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the suspend reject indication. If no optional
parameters are associated with the suspend reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the suspend reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SUSREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or another sense (network or user), otherwise the new state
remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
4.2.5.9 Call Control Resume Request
CC_RESUME_REQ
This message requests that the CCS provider resume a previously suspended call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS user to identify the call to the CCS provider.
The value should be the same as the value indicated by the CCS provider in a previous
CC_SETUP_INDorCC_SETUP_CONprimitive. cc_flags- Specifies the options associated with the resume. Resume flags are provider and protocol dependent (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the resume request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the resume request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_SUSPENDED.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or another sense (network or user), otherwise the new state
remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.5.10 Call Control Resume Indication
CC_RESUME_IND
This message indicates to the CCS user that the peer CCS user has requested that a previously suspended call be resumed.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_flags- Indicates the options associated with the resume. Resume flags are mode and protocol dependent, see the addendum.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume indication. If no optional parameters
are associated with the resume indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the resume indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network) and NNI.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_SUSPENDED.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or in another sense (network or user), otherwise the new
state remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
4.2.5.11 Call Control Resume Response
CC_RESUME_RES
This message requests that the CCS provider accept a previous request to resume a suspended call.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_RES */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS user to identify the call to the CCS provider.
Its value should be the same as the value indicated by a previous
CC_SETUP_INDorCC_SETUP_CONprimitive for the call. cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume response. If no optional parameters are
associated with the resume response, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the resume response, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network) and for compatibility in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SUSIND.
For compatibility with UNI, NNI should ignore, yet positively acknowledge, this primitive if received in the
CCS_CONNECTED
or CCS_SUSPENDED
states where the all is not suspended in the sense confirmed.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or another sense (network or user), otherwise the new state
remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.5.12 Call Control Resume Confirmation
CC_RESUME_CON
This message indicates to the requesting CCS user that a previous request to resume a suspended call has been confirmed.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_CON */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume confirmation. If no optional parameters
are associated with the resume confirmation, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameter are associated with the resume confirmation, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SUSREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_CONNECTED
if the call is not still suspended in the opposite direction or another sense (network or user), otherwise the new state
remains CCS_SUSPENDED.
4.2.5.13 Call Control Resume Reject Request
CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ
This message requests that the CCS provider reject a previous requst to resume a suspended call with the specified cause.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_reject_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_reject_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS user to identify the call to the CCS provider.
Its value should be the same as the value indicated in a previous
CC_SETUP_INDorCC_SETUP_CONprimitive by the CCS provider for the call. cc_cause- Indicates the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume reject request. If no optional
parameters are associated with the resume reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameters are associated with the resume reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (Network).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SUSIND.
New State
The new state is CCS_SUSPENDED.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.5.14 Call Control Resume Reject Indication
CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND
This message indicates to the requesting CCS user that a previous request to resume a suspended call has been rejected and the cause for rejection.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_resume_reject_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_reject_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_cause- Indicates the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the resume reject indication. If no optional
parameters are associated with the resume reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameters are associated with the resume reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in mode UNI (User).
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SUSREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_SUSPENDED.
4.2.6 Call Termination Phase
The following call control service primitives pertain to the Termination phase of a call.
4.2.6.1 Call Control Reject Request
CC_REJECT_REQ
This message is used to reject a call before any request for more information, or request for indication of proceeding, alerting, progress, or in-band information has been attempted. The message also includes the cause of the rejection.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reject_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_REJECT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_reject_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_REJECT_REQprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_cause- Specifies the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the reject request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameters are associated with the reject request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in the UNI mode (User or Network). (NNI users should use the CC_RELEASE_REQ primitive
in the same situation.)
Valid State
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_SIND.
New State
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.6.2 Call Control Reject Indication
CC_REJECT_IND
This message indicates to the CCS user that a previous setup request has been rejected by the peer CCS user and indicates the cause of the rejection.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reject_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_REJECT_IND */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_reject_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the CCS user reference of the associated
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive that was rejected. cc_cause- Indicates the cause for the rejection. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the reject indication. If no optional parameters
are associated with the reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameters are associated with the reject indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in the UNI mode (User or Network).
Valid State
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_SREQ.
New State
4.2.6.3 Call Control Call Failure Indication
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that the call on the selected address (circuit, circuit group) has failed.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_call_failure_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_reason; /* reason for failure */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause to use in release */
} CC_call_failure_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_reason- Indicates the reason for the failure. Reasons are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_cause- Indicates the cause value for the failure. Cause values are provider and protocol specific (see Addendum).
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the call failure indication. If no optional
parameters are associated with the call failure indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block. If no optional parameters are associated with the call failure indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in NNI mode only.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state other than CCS_IDLE,
CCS_WIND_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_INFO,
CCS_WCON_SREQ,
and CCS_WIND_PROCEED.
In the aforementioned states (other than CCS_IDLE),
a CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND
should be issued instead.
New State
4.2.6.4 Call Control Disconnect Request
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider indicate to the calling CCS user that in-band information may now be
available in the voice channel reflecting the specified cause. The CC_DISCONNECT_REQ primitive is an invitation to
the remote CCS user to release the call channel.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_disconnect_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_DISCONNECT_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_disconnect_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_DISCONNECT_REQmessage. It is used by the CCS provider to associated theCC_DISCONNECT_REQmessage with an outstandingCC_SETUP_INDmessage. An invalid call reference should result in error with the error typeCCBADCLR. cc_cause- Indicates the cause value for the disconnect.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the disconnect request. If no optional parameters
are associated with the disconnect request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in UNI (Network or User) mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
CCS_WREQ_ALERTING
and CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS.
New State
The new state is CCS_WREQ_CONNECT.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.6.5 Call Control Disconnect Indication
CC_DISCONNECT_IND
This primitive indicates to the calling CCS user that there is in-band information now available in the voice channel.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_disconnect_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_DISCONNECT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_disconnect_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_cause- Indicates the cause value for the disconnect.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the in-band information request. If no optional
parameters are associated with the in band information request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in states CCS_WIND_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_INFO,
CCS_WIND_PROCEED,
CCS_WIND_ALERTING,
CCS_WIND_PROGRESS
and CCS_WIND_CONNECT.
New State
The new state is CCS_WIND_CONNECT
4.2.6.6 Call Control Release Request
CC_RELEASE_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider release the call and provide the specified cause value to the remote CCS user.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_release_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_REQ */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the user call reference of the
CC_SETUP_REQwhen theCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_REQand before aCC_SETUP_CONis issued. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_cause- Specifies the cause of the release. Cause values are CCS provider and protocol specific. See the addendum for
protocol specific values.
cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the release request. If no optional parameters are
associated with the release request, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User or Network) and NNI modes.
Valid States
This primitive is valid from any call state other than CCS_IDLE
and CCS_WCON_RELREQ.
New State
If the current state is CCS_WRES_RELIND,
the new state is CCS_IDLE.
If the current state is other than CCS_WRES_RELIND,
the new state is CCS_WCON_RELREQ.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDorCC_RELEASE_CONprimitives. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCBADPRIM- The primitive was of an incorrect format (i.e. too small, or an offset it out
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCBADOPT- The options values as specified in the primitive were in an incorrect format, or they contained illegal information.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions to request the operation or to use the options specified.
CCNOTSUPP- The specified primitive type is not known to or not supported by the CCS provider.
4.2.6.7 Call Control Release Indication
CC_RELEASE_IND
This primitive indicates that the remote CCS user or CCS provider hsa released the call with the specified cause value.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_release_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_IND */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the user call reference of the
CC_SETUP_REQwhen theCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_REQand before aCC_SETUP_CONis issued. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_cause- Indicates the cause of the release. Cause values are CCS provider and protocol specific. See the addendum for
protocol specific values.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the release indication. If no optional parameters
are associated with the release indication, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User or Network) and NNI modes.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any setup or established call state other than CCS_IDLE
and CCS_WRES_RELIND.
New State
If the current state is CCS_WCON_RELREQ,
the new state is CCS_IDLE.
If the current state is other than CCS_WCON_RELREQ,
then new state is CCS_WRES_RELIND.
4.2.6.8 Call Control Release Response
CC_RELEASE_RES
This primitive indicates to the CCS provider that the release of the associated circuit is complete.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_release_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_RES */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the user call reference of the
CC_SETUP_REQwhen theCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_REQand before aCC_SETUP_CONis issued. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_opt_length- Specifies the length of the optional parameters associated with the release response. If no optional parameters are
associated with the release response, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User or Network) and NNI modes.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_RELIND.
New State
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.2.6.9 Call Control Release Confirmation
CC_RELEASE_CON
This primitive indicates to the releasing CCS user that the release of the associated circuit is complete.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_release_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_CON */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Indicates the user call reference of the
CC_SETUP_REQwhen theCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_REQand before aCC_SETUP_CONis issued. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDwhen theCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive is used in response to theCC_SETUP_INDon a listening stream. Otherwise, this parameter is coded zero and is ignored by the CCS provider. cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the release confirmation. If no optional parameters
are associated with the release confirmation, then this parameter must be coded zero.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the optional parameters from the start of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (User or Network) and NNI modes.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_RELREQ.
New State
4.3 Management Primitive Formats and Rules
This section describes the format of the UNI (Network and User) and NNI management primitives and rules associated with these primitives.
4.3.1 Interface Management Primitives
4.3.1.1 Interface Management Restart Request
CC_RESTART_REQ
This primitive request the CCS provider to restart all the call control addresses (signalling interface and channels) for the specified UNI interface.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_restart_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESTART_REQ */
ulong cc_flags; /* restart flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_restart_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which a restart
was requested. The semantics of the values in the
CC_RESET_REQis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the reporting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
4.3.1.2 Interface Management Restart Confirmation
CC_RESTART_CON
This primitive confirms to the requesting CCS user that the restart of the requested call control addresses (signalling interface and channels) for the specified UNI interface is complete.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_restart_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESTART_IND */
ulong cc_flags; /* restart flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_restart_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which a restart
was requested. The semantics of the values in the
CC_RESET_REQis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the reporting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
4.3.2 Circuit Management Primitives
4.3.2.1 Circuit Management Reset Request
CC_RESET_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider reset the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) with the CCS user peer. For the NNI this primitive supports both the Circuit Reset Service as well as the Circuit Group Reset Service.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reset_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_REQ */
ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which a reset
is requested. The semantics of the values in the
CC_RESET_REQis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the reporting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Rules
The following rules apply to the reset of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit identifiers):
- The call control address must contain a signalling interface identifier and one or more circuit identifiers.
- The signalling interface identifier must identify an NNI signalling interface.
- When the call control address contains one circuit identifier, a non-group reset will be performed.
- When the call control address contains more than one circuit identifier, the CCS provider may either issue individual circuit resets, or may issue one or more group circuit resets.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for call control address(es) in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the requested address(es).
New State
The new state is CCS_WCON_RESREQ for the specified address(es).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_RESET_CONprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to perform the operation on the specified call control addresses.
CCNOADDR- The call control address was not provided (cc_addr_length coded zero).
CCBADADDR- The call control address(es) contained in the primitive were poorly formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling interface identifier was provided in the
call control address.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state for the requested address(es).
CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
4.3.2.2 Circuit Management Reset Indication
CC_RESET_IND
This primitive indicates that the peer CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) be reset.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reset_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_IND */
ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) that the peer
CCS user has requested be reset.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) from the
beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will not be issued for call control addresses in modes other than NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued for call control addresses for which no reset indication (CCS_IDLE) is already
pending.
New State
The new state is CCS_WRES_RESIND.
4.3.2.3 Circuit Management Reset Response
CC_RESET_RES
This primitive request the CCS provider to complete the reset operation for the specified call control address(es)
(signalling interface and circuit identifiers) which was previously indicated with a
CC_RESET_IND.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reset_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_RES */
ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Indicates options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which the
CCS user has accepted a reset.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) from the
beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Rules
The following rules apply to the reset of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit identifiers):
- The set of addresses specified must be a non-empty subset of the addresses which were specified in the indication primitive to which this primitive is responding.
- Only once the primitive is successfully accepted by the CCS provider should the CCS provider take any actions whatsoever with regard to reset.
- Call control addresses included in the call control address list which are not equipped may be ignored by the CCS provider.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WRES_RESIND for the specified address(es).
New State
The new state is CCS_WACK_RESRES for the specified address(es).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to perform the operation on the specified call control addresses.
CCNOADDR- The call control address was not provided (cc_addr_length coded zero).
CCBADADDR- The call control address(es) contained in the primitive were poorly formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling interface identifier was provided in the
call control address.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
4.3.2.4 Circuit Management Reset Confirmation
CC_RESET_CON
This primitive confirms to the requesting CCS user that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) have been successfully confirmed reset to the peer CCS user.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_reset_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_CON */
ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which the
CCS provider has confirmed a reset.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) from the
beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for call control addresses in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_RESREQ for the specified addresses.
New State
The new state is CCS_IDLE for the specified addresses.
4.3.2.5 Circuit Management Blocking Request
CC_BLOCKING_REQ
This primitive request that the CCS provider locally block the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) with the peer CCS user. For the NNI, this primitive supports both the Circuit Blocking Service as well as the Circuit Group Blocking Service.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_blocking_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_REQ */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which local blocking is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in
Section 2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Rules
The following rules apply to the blocking of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers):
- If the stream upon which the blocking request is issued is not bound (see
CC_BIND_REQ), the call control address must contain a signalling interface identifier and a circuit or circuit group identifier. - If the stream upon which the blocking request is bound to a signalling interface and trunk group, and no call control address(es) are provided (i.e, cc_addr_length is set to zero), the CCS provider may interpret the primitive to be requesting blocking on all circuits in the trunk group.
- At any time that the primitive is issued without specifying a call control address (i.e, cc_addr_length is zero to zero), the CCS provider may assign a call control address or addresses.
- If the CCS provider fails to assign a call control address or addresses, the primitive will fail with error
CCNOADDR.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for call control address(es) (signalling interfaces) in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the requested address(es).
New State
The new state is CCS_WCON_BLREQ for the specified address(es).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive.
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_BLOCKING_CONprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDorCC_RESET_INDprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to invoke the operation on the specified addresses.
CCFLAGS- The flags were invalid or unsupported.
CCNOADDR- An address or addresses was not provided by the CCS user (i.e., cc_addr_length set to zero) and the CCS provider
could not assign an address or addresses.
CCBADADDR- The call control address contained in the primitive were illegally formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling interface identifier was provided in the
call control address.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state for the requested address(es).
CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
4.3.2.6 Circuit Management Blocking Indication
CC_BLOCKING_IND
This primitive indicates that the peer CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) be remotely blocked.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_blocking_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_IND */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags. See "Flags" below.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) that the peer
CCS user has requested to be remotely blocked.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider if the remote blocking state of the specified address(es) is CCS_UNBLOCKED or CCS_BLOCKED.
New State
The new remote blocking state will be CCS_WRES_BLIND for the specified call control addresses.
4.3.2.7 Circuit Management Blocking Response
CC_BLOCKING_RES
This primitive requests that the CCS provider respond to the previous blocking indication.
Format
The format is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_blocking_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_RES */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which local blocking is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in
Section 2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for indications for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is only valid for the previous CC_BLOCKING_IND (call control addresses in the CCS_WRES_BLIND state).
New State
The new blocking state of the previously specified call control addresses is the CCS_BLOCKED state.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDor CCS_RESET_IND primitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.3.2.8 Circuit Management Blocking Confirmation
CC_BLOCKING_CON
This primitive confirms a previous blocking request (or indicates failure of a previous blocking request).
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_blocking_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_CON */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags and result of the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers) for
which local blocking is confirmed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider if the local blocking state of the specified address(es) is CCS_WCON_BLREQ.
New State
The new local blocking state will be CCS_BLOCKED for the specified call control addresses.
4.3.2.9 Circuit Management Unblocking Request
CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider locally unblock the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) with the peer CCS user. For the NNI, this primitive supports both Circuit Unblocking Service as well as the Circuit Group Unblocking Service.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_unblocking_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ */
ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which local unblocking is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in
Section 2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Rules
The following rules apply to the unblocking of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers):
- If the stream upon which the unblocking request is issued is not bound (see
CC_BIND_REQ), the call control address must contain a signalling interface identifier and a circuit or circuit group identifier. - If the stream upon which the unblocking request is bound to a signalling interface and trunk group, and no call control address(es) are provided (i.e, cc_addr_length is set to zero), the CCS provider may interpret the primitive to be requesting unblocking on all circuits in the trunk group.
- At any time that the primitive is issued without specifying a call control address (i.e, cc_addr_length is zero to zero), the CCS provider may assign a call control address or addresses.
- If the CCS provider fails to assign a call control address or addresses, the primitive will fail with error
CCNOADDR.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for call control address(es) (signalling interfaces) in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the requested address(es).
New State
The new state is CCS_WCON_BLREQ for the specified address(es).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive.
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_BLOCKING_CONprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDorCC_RESET_INDprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to invoke the operation on the specified addresses.
CCFLAGS- The flags were invalid or unsupported.
CCNOADDR- An address or addresses was not provided by the CCS user (i.e., cc_addr_length set to zero) and the CCS provider
could not assign an address or addresses.
CCBADADDR- The call control address contained in the primitive were illegally formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling interface identifier was provided in the
call control address.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state for the requested address(es).
CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
4.3.2.10 Circuit Management Unblocking Indication
CC_UNBLOCKING_IND
This primitive indicates that the peer CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) be remotely unblocked.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_unblocking_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_IND */
ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags. See "Flags" below.
cc_addr_length- \Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) that the peer
CCS user has requested to be remotely unblocked.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider if the remote blocking state of the specified address(es) is CCS_UNBLOCKED or CCS_BLOCKED.
New State
The new remote blocking state will be CCS_WRES_UBIND for the specified call control addresses.
4.3.2.11 Circuit Management Unblocking Response
CC_UNBLOCKING_RES
This primitive requests that the CCS provider respond to the previous unblocking indication.
Format
The format is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_unblocking_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_RES */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which local unblocking is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in
Section 2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for indications for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is only valid for the previous CC_BLOCKING_IND (call control addresses in the CCS_WRES_BLIND state).
New State
The new blocking state of the previously specified call control addresses is the CCS_UNBLOCKED state.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDor CCS_RESET_IND primitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.3.2.12 Circuit Management Unblocking Confirmation
CC_UNBLOCKING_CON
This primitive confirms a previous unblocking request (or indicates failure of a previous unblocking request).
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_unblocking_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_CON */
ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags and result of the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers) for
which local unblocking is confirmed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider if the local unblocking state of the specified address(es) is CCS_WCON_UBREQ.
New State
The new local unblocking state will be CCS_UNBLOCKED for the specified call control addresses.
4.3.2.13 Circuit Management Query Request
CC_QUERY_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider query specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group) to the peer CCS user. For the NNI, this primitive supports the Circuit Group Query Service.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_query_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_REQ */
ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which the query is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in Section
2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Rules
The following rules apply to the querying of call control addresses (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers):
- If the stream upon which the query request is issued is not bound (see
CC_BIND_REQ), the call control address must contain a signalling interface identifier and a circuit or circuit group identifier. - If the stream upon which the query request is bound to a signalling interface and trunk group, and no call control address(es) are provided (i.e, cc_addr_length is set to zero), the CCS provider may interpret the primitive to be requesting status on all circuits in the trunk group.
- At any time that the primitive is issued without specifying a call control address (i.e, cc_addr_length is zero to zero), the CCS provider may assign a call control address or addresses.
- If the CCS provider fails to assign a call control address or addresses, the primitive will fail with error
CCNOADDR.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for call control address(es) (signalling interfaces) in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the requested address(es).
New State
The new state is CCS_WCON_BLREQ for the specified address(es).
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive.
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_BLOCKING_CONprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDorCC_RESET_INDprimitive. - Non-fatal errors: Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to invoke the operation on the specified addresses.
CCFLAGS- The flags were invalid or unsupported.
CCNOADDR- An address or addresses was not provided by the CCS user (i.e., cc_addr_length set to zero) and the CCS provider
could not assign an address or addresses.
CCBADADDR- The call control address contained in the primitive were illegally formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling interface identifier was provided in the
call control address.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state for the requested address(es).
CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
4.3.2.14 Circuit Management Query Indication
CC_QUERY_IND
This primitive indicates that the peer CCS user has requested that the specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) be queried.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_query_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_IND */
ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags. See "Flags" below.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) that the peer
CCS user has requested to be queried.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state for the specified address(es).
New State
The new query state will be CCS_WRES_QIND for the specified call control addresses and the number of outstanding queries for the specified call control addresses will be incremented.
4.3.2.15 Circuit Management Query Response
CC_QUERY_RES
This primitive requests that the CCS provider respond to the previous query indication.
Format
The format is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_query_res {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_RES */
ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_res_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies options flags for the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers)
upon which the query is requested. The semantics of the values in the call control address is described in Section
2.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for indications for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is only valid for the previous CC_BLOCKING_IND (call control addresses in the CCS_WRES_BLIND state).
New State
The new query state of the previously specified call control addresses is the CCS_IDLE or CCS_WRES_QIND state and
the query backlog is decremented.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful: Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_RELEASE_INDor CCS_RESET_IND primitive. - Non-fatal errors:
Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.3.2.16 Circuit Management Query Confirmation
CC_QUERY_CON
This primitive confirms a previous query request (or indicates failure of a previous query request).
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_query_con {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_CON */
ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_con_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_flags- Specifies the options flags and result of the operation. (See "Flags" below.)
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit or circuit group identifiers) for
which status is confirmed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Flags
The options flags are protocol and provider-specific. For additional information, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider for signalling interfaces in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider if the query state of the specified address(es) is CCS_WCON_QREQ.
New State
The new query state will be CCS_IDLE for the specified call control addresses.
4.3.3 Maintenance Primitives
4.3.3.1 Maintenance Indication
CC_MAINT_IND
This primitive indicates that the CCS provider has observed an event on the indicated call control address(es) which requires a maintenance action.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block followed by zero or more M_DATA blocks. The structure of
the M_PROTO message block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_maint_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MAINT_IND */
ulong cc_reason; /* reason for indication */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* length of address */
} CC_maint_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_reason- Indicates the reason for the maintenance indication. Maintenance indication reasons are protocol and
provider-specific. For additional information see the Addendum.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference. The call reference is used by the CCS provider to identify the call.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers) upon which the
CCS provider is giving a maintenance indication.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address(es) from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid in UNI (Network) mode and NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in any state.
New State
The new state is unchanged.
4.3.4 Circuit Continuity Test Primitives
This section describes the format of the NNI circuit continuity test primitives and rules associated with these primitives. Continuity test primitives are used by NNI management interfaces for performing continuity test requests or responding to continuity test indications for specified or indicated circuits. These primitives are provided to allow the NNI to meet Q.764 conformance.
4.3.4.1 Circuit Continuity Check Request
CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider perform a continuity check procedure.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_check_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_check_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the call control address (circuit identifier) upon which the CCS user is requesting a
continuity check.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the call control address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Rules
The following rules apply to the continuity check of call control addresses (circuit identifiers):
- If the CCS user does not specify a call control address (i.e, cc_addr_length is set to zero), then the CCS provider may attempt to assign a call control address and associate it with the stream for the duration of the continuity test procedure. This can be useful for automated continuity testing.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the selected circuit.
New State
The new state is CKS_WIND_CTEST for the selected address.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCNOADDR- The call control address was not provided (cc_addr_length coded zero).
CCBADADDR- The call control address contained in the primitive were poorly formatted or contained invalid information.
CCNOTSUPP- The primitive is not supported for the UNI interface and a UNI signalling address was provided in the call control
address or the address was issued to a UNI CCS provider.
CCACCESS- The user did not have sufficient permission to perform the operation on the specified call control addresses.
4.3.4.2 Circuit Continuity Check Indication
CC_CONT_CHECK_IND
This primitive indicates to the CCS user that a continuity check is being requested by the CCS user peer on the
specified call control address(es) (signalling interface and circuit identifiers). Upon receipt of this primitive,
the CCS user should establish a loop back device on the specified channel and issues the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ primitive
confirming the loop back. The CCS user should then wait for the CC_CONT_REPORT_IND indicating the success or
failure of the continuity check.
This primitive is only delivered to listening streams listening on the specified call control addresses or to a
stream bound as a default listener in the same manner as the CC_SETUP_IND. (A continuity test indication is treated
as a special form of call setup.)
This primitive is only issued to CCS users that successfully bound using the CC_BIND_REQ primitive with flag CC_TEST
set and a non-zero number of setup indications was provided in the CC_BIND_REQ and returned in the CC_BIND_ACK.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_check_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_check_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Identifies the call reference that can be used by the CCS user to associate this message with the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQorCC_RELEASE_REQprimitive that is to follow. This value must be unique among the outstanding CC_CONT_CHECK_IND messages. cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (circuit identifier) upon which a continuity check is indicated.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the requesting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is only valid for addresses in the NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_IDLE for the specified addresses.
New State
The new state is CKS_WREQ_CTEST for the specified addresses.
4.3.4.3 Circuit Continuity Test Request
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ
This message is used either to respond to a CC_SETUP_IND primitive which contains the
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED
flag, or to respond to a CC_CONT_CHECK_IND primitive. Before responding to either primitive, the CCS User should
install a loop back device on the requested channel and then respond with this response primitive to confirm the
loop back.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_test_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_REQ */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_token_value; /* token value */
} CC_cont_test_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference of the
CC_CONT_TEST_REQmessage. It is used by the CCS provider to associate theCC_CONT_TEST_REQmessage with an outstandingCC_SETUP_INDmessage. An invalid call reference should result in error with the error typeCCBADCLR. cc_token_value- Is used to identify the stream that the CCS user wants to establish the continuity check call on. (Its value is
determined by the CCS user by issuing a
CC_BIND_REQprimitive with theCC_TOKEN_REQflag set. The token value is returned in theCC_BIND_ACK.) The value of this field should be non-zero when the CCS user wants to establish the call on a stream other than the stream on which the CC_CONT_CHECK_IND arrived. If the CCS user wants to establish a call on the same stream that the CC_CONT_CHECK_IND arrived on, then the value of this field should be zero.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CKS_WREQ_CTEST.
New State
The new state is CKS_WIND_CCREP.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful:
Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_REPORT_INDin the case that the primitive was issued in response to aCC_SETUP_IND, orCC_RELEASE_INDprimitive in the case that the primitive was issued in response to the CC_CONT_CHECK_IND primitive. - Unsuccessful:
Unsuccessful completion is indicated via the
CC_CONT_REPORT_INDprimitive. - Non-fatal errors:
Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:CCSYSERR- A system error has occurred and the UNIX system error is indicated in the primitive.
CCOUTSTATE- The primitive was issued from an invalid state.
CCBADCLR- The call reference specified in the primitive was incorrect or illegal.
CCACCESS- The user did not have proper permissions for the operation.
CCNOTSUPP- The CCS provider does not support the operation.
4.3.4.4 Circuit Continuity Test Indication
CC_CONT_TEST_IND
This message confirms to the testing CCS user that a loop back device has been (or will be) installed on the
specified call control address (circuit). Upon receiving this message, the testing CCS user should connect tone
generation and detection equipment to the specified circuit, perform the continuity test and issue a report using
the CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ primitive.
This primitive will only be issued to streams successfully bound with the CC_BIND_REQ primitive with a non-zero
number of setup indications and the CC_TEST bind flag set.
Format
The format of this message is on M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_test_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_cont_test_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference associated with the continuity check call for the specified call control address
(circuit identifier).
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (signalling interface and circuit identifier) upon which a
continuity check is confirmed. The semantics of the values in the
CC_CONT_TEST_INDis identical to the values in theCC_BIND_REQ. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the connecting address from the beginning of the
M_PROTOmessage block.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WCON_CREQ.
New State
The new state is CCS_WAIT_COR.
4.3.4.5 Circuit Continuity Report Request
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ
This primitive requests that the CCS provider indicate to the called CCS user that the continuity check succeeded or failed. The CCS user should remove any continuity test tone generator/detection device from the circuit and verify silent code loop back before issuing this primitive.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_report_req {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ */
ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_req_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Specifies the primitive type.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the CCS user reference of the associated
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive. This value is non-zero when theCC_CONT_REPORT_REQprimitive is issued subsequent to aCC_SETUP_REQprimitive which had the flag ISUP_NCI_CONTINUITY_CHECK_PREVIOUS set to indicate the result of the continuity check on the previous circuit. Otherwise, this value is coded zero. cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the associated
CC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive for the continuity check call. This value is non-zero when theCC_CONT_REPORT_REQprimitive is issued in response to aCC_CONT_TEST_INDprimitive. Otherwise, this value is coded zero. cc_result- Specifies the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. The value of the cc_result is protocol specific. For values representing success and values representing failure, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_CCREP.
New State
When issued in response to the CC_CONT_TEST_IND primitive, the new state is CCS_IDLE. When issued subsequent to a
CC_SETUP_REQ primitive, the new state is either CCS_WREQ_MORE or CCS_WREQ_PROCEED, depending upon whether the sent
address contain an ST pulse.
Acknowledgements
The CCS provider should generate one of the following acknowledgements upon receipt of this primitive:
- Successful: Successful completion is indicated via the
CC_OK_ACKprimitive. - Unsuccessful (Non-fatal errors): Errors are indicated via the
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive. The applicable non-fatal errors are defined as follows:
4.3.4.6 Circuit Continuity Report Indication
CC_CONT_REPORT_IND
This primitive indicates to the called CCS user that the continuity check succeeded or failed. The called CCS user can remove the loop back or tone generation/detection devices from the circuit and the call either moves to the idle state or a call setup state.
Format
The format of this message is one M_PROTO message block. The structure of the M_PROTO block is as follows:
typedef struct CC_cont_report_ind {
ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_IND */
ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_ind_t;
Parameters
cc_primitive- Indicates the primitive type.
cc_call_ref- Indicates the call reference associated with the continuity check report as it appeared in the associated
CC_CONT_CHECK_IND primitive.
cc_result- Indicates the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. The value of the cc_result is protocol specific. For values representing success and values representing failure, see the Addendum.
Valid Modes
This primitive is valid only in NNI mode.
Valid States
This primitive is valid in state CCS_WREQ_CTEST or CCS_WIND_CCREP.
New State
If the primitive is issued subsequent to the CC_SETUP_REQ, the new state is CCS_WCON_SREQ. If the primitive is
issued in response to the CC_CONT_TEST_IND primitive, the new state is CCS_IDLE.
4.3.5 Collecting Information Phase
The following call control service primitive pertain to the collecting information phase of a call.
5 Diagnostics Requirements
Two error handling facilities should be provided to the call control service user: one to handle non-fatal errors, ant the other to handle fatal errors.
5.1 Non-Fatal Error Handling Facility
These are errors that do not change the state of the call control service interface or the call reference as seen by
the call control service user, and provide the user the option of reissuing the call control service primitive with
the corrected options specification. The non-fatal error handling is provided only to those primitive that require
acknowledgements, and uses the CC_ERROR_ACK primitive to report these errors. These errors retain the state of the
call control service interface and call reference the same as it was before the call control service provider
received the primitive that was in error. Syntax errors and rule violations are reported via the non-fatal error
handling facility.
5.2 Fatal Error Handling Facility
These errors are issued by the CCS provider when it detects errors that are not correctable by the call control service
user, or if it is unable to report a correctable error to the call control service user. Fatal errors are indicated via
the STREAMS
message type M_ERROR with the UNIX system error EPROTO. The M_ERROR STREAMS
message type will result in the failure of all the UNIX system calls on the stream. The call control service user can
recover from a fatal error by having all the processes close the files associated with the stream, and then reopening
them for processing.
Addendum for Q.931 Conformance
This addendum describes the formats and rules that are specific to ISDN Q.931. The addendum must be used along with the generic CCI as defined in the main document when implementing a CCS provider that will be configured with the Q.931 call processing layer.
Primitives and Rules for Q.931 Conformance
The following are the rules that apply to the CCI primitives for Q.931 compatibility.
Common Primitive Parameters
Call Control Addresses
Format
The format of call control addresses is as follows:
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Specifies or indicates the length of the call control address. If a call control address is not included in the
primitive, this parameter must be coded zero (0).
cc_addr_offset- Specifies or indicates the offset of the address from the begining of the primitive. If a call control address is not included with the primitive, this parameter must be coded zero (0).
Address Format
The format of the call control addresses for Q.931 conforming CCS providers is as follows:
typedef struct isdn_addr { ulong scope; /* the scope of the identifier */ ulong id; /* the identifier within the scope */ ulong ci; /* channel identifier within the scope */ } isdn_addr_t;#define ISDN_SCOPE_CH 1 /* channel scope */ #define ISDN_SCOPE_FG 2 /* facility group scope */ #define ISDN_SCOPE_TG 3 /* transmission group scope */ #define ISDN_SCOPE_EG 4 /* equipment group scope */ #define ISDN_SCOPE_XG 5 /* customer/provider group scope */ #define ISDN_SCOPE_DF 6 /* default scope */
Address Fields
scope- Specifies or indicates the scope of the call control address. See "Scope" below.
id- Specifies or indicates the identifier within the scope.
cic- Specifies or indicates the Channel Indicator significant within the scope.
Scope
The scope of the address is one of the following:
ISDN_SCOPE_CH- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is an ISDN B-channel. The identifier within the
scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies the channel to the CCS provider. Channel scope addresses may also
be used to specify or indicate transmission groups, equipment groups and customer/provider groups. When used in an
indication or confirmation primitive, the CCS provider includes the Channel Identification associated with the
circuit in the address.
For multi-rate calls where multiple channels are involved, the channel scoped address specifies the lowest numerical Channel Identifier in the group of circuits and the Channel Identifier provides the channel map of the group of channels.
ISDN_SCOPE_FG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is an ISDN facility group (group of one or more
redundant D-channels). The identifier within the scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies the ISDN
interface to the CCS provider. Facility group scope addresses may also be used to specify or indicate channels,
equipment groups or customer/provider groups. When used in an indication or confirmation primitive, the CCS
provider includes the Channel Identifier associated with the indicated channels.
ISDN_SCOPE_TG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is an ISDN transmission group (PRI interface).
The identifier within the scope is an indentifier which uniquely identifies the ISDN physical interface to the CCS
provider. Transmission group scope addresses may also be used to specify or indicate equipment groups or
customer/provider groups. When used in an indication or confirmation primitive, the CCS provider may include the
Channel Identifier associated with the facility group for the physical interface.
ISDN_SCOPE_EG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is an ISDN equipment group. The identifier within
the scope is an identifier that uniquely identifies the equipment group to the CCS provider. Equipment group scoped
addresses may aslo be used to specify or indicate customer/provider groups.
ISDN_SCOPE_XG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is an ISDN customer/provider group. The
identifier within the scope is an identifier that uniquely identifies the customer/provider group to the CCS
provider.
ISDN_SCOPE_DF- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is the default scope. The identifier within the scope and Channel Identifier are unused and should be ignored by the CCS user and will be coded zero (0) by the CCS provider.
Rules
Rules for scope:
- In primitives in which the address parameter occurs, the scope field setting indicates the scope of the address parameter.
- Only one call control address can be specified with a signle scope.
- Not all scopes are necessarily supported by all primitives. See the particular primitive in this addendum.
Rules for addresses:
- The address contained in the primitive contains the following:
- A scope.
- An identifier within the scope or zero (0).
- A channel indication within the scope or zero (0).
- If the scope of the address is
ISDN_SCOPE_DF, then both the identifier and channel indication fields should be coded zero (0) and will be ignored by the CCS user or provider. - If the scope of the address is
ISDN_SCOPE_EGorISDN_SCOPE_XG, then the channel indication field should be coded zero (0) and will be ignored by the CCS user or provider. - In all other scopes, the channel indication field is optional and is coded zero (0) if unused.
Optional Information Elements
Format
The format of the optional information elements is as follows:
Parameters
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional information elements associated with the primitive. For Q.931 conforming CCS
providers, the format of the optional information elements is the format of a Information Element list as specified
in Q.931.
cc_opt_offset- indicates the offset of the option information elements from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for optional information elements:
- The optional information elements provided by the CCS user may be checked for syntax by the CCS provider. If the
CCS provider discovers a syntax error in the format of the optional information elements, the CCS provider should
respond with a
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive with errorCCBADOPT. - For some primitives, specific optional information elements might be interpreted by the CCS provider and alter the function of some primitives. See the specific primitive descriptions later in this addendum.
- Except for optional information elements interpreted by the CCS provider as specified later in this addendum, the optional information elements are treated as opaque and the optional information element list only is checked for syntax. Opaque information elements will be passed to the ISDN message without examination by the CCS provider.
- To perform specific functions, additional optional information elements may be added to ISDN messages by the CCS provider.
- To perform specific functions, optional information elements may be modified by the CCS provider before they are added to ISDN messages.
Local Management Primitives
CC_INFO_ACK
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_BIND_REQ
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the address to bind.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address to bind.
cc_setup_ind- Specifies the requested maximum number of setup indications that will be outstanding for the listening stream.
Flags
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERCC_CHANNELCC_CHANNEL_GROUPCC_TRUNK_GROUP- When on of these flags are set, it indicates that the address is interpreted by the CCS provider as unspecified
(
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER), a channel (CC_CHANNEL), as a channel group (CC_CHANNEL_GROUP), or as a trunk group (CC_TRUNK_GROUP).
Rules
Rules for address specification:
- The address contained in the primitive must be either a unspecified, a channel, a channel group or a trunk group.
- If the
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERflag is set, the address should be left unspecified by the CCS user and should be ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules for setup indicatesion:
- If the number of setup indications is non-zero, the stream is bound as a listening stream. Listening streams will
receive all calls that are incoming on the address bound:
- If the address bound is a channel (
CC_CHANNELflag set), all incoming calls on the channel will be delivered to the stream listening on the channel. These streams will have a maximum number of setup indications of one (1). - If the address bound is a channel group (
CC_CHANNEL_GROUPflag set), all incoming calls on the channel group will be delivered to the stream listening on the channel group. These streams will have a maximum number of setup indications no higher than the number of channels in the channel group. - If the address bound is a trunk group (
CC_TRUNK_GROUPflag set), all incoming calls on the trunk group will be delivered to the stream listening on the trunk group. These streams will have a maximum number of setup indications no higher than the number of channels in the trunk group.
- If the address bound is a channel (
Rules for bind flags:
- For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERwill receive incoming calls that have no other listening stream. There can only be one stream bound with theCC_DEFAULT_LISTENERflag set. - Only one of
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER,CC_CHANNEL,CC_CHANNEL_GROUPorCC_TRUNK_GROUPmay be set.
CC_BIND_ACK
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_OPTMGMT_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Call Setup Primitives
Call Type and Flags
Call type and flags are used in the following primitives:
CC_SETUP_REQ and
CC_SETUP_IND.
Parameters
cc_call_type- Indicates the type of call to be set up. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call type can be one of the call
types listed under "Call Type" below.
cc_call_flags- Specifies the options flags associated with the call. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call flags can be any of the flags listed under "Flags" below.
Call Type
The following call types are defined for Q.931 conforming CCS providers:
CC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH- The call type is speech. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information transfer capability of Speech, and an
Information transfer rate of 64kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 64kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO- The call type is 3.1 kHz audio. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information transfer capability of
Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 64kbits/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_128KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 2 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 2x64 kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 384 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 384 kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 1536 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 1536 kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 1920 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of 1920 kbit/s.
CC_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 2 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 2.
CC_CALL_TYPE_3x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 3 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 3.
CC_CALL_TYPE_4x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 4 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 4.
CC_CALL_TYPE_5x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 5 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 5.
CC_CALL_TYPE_6x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 6 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 6.
CC_CALL_TYPE_7x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 7 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 7.
CC_CALL_TYPE_8x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 8 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 8.
CC_CALL_TYPE_9x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 9 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 9.
CC_CALL_TYPE_10x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 10 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 10.
CC_CALL_TYPE_11x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 11 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 11.
CC_CALL_TYPE_12x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 12 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 12.
CC_CALL_TYPE_13x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 13 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 13.
CC_CALL_TYPE_14x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 14 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 14.
CC_CALL_TYPE_15x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 15 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 15.
CC_CALL_TYPE_16x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 16 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 16.
CC_CALL_TYPE_17x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 17 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 17.
CC_CALL_TYPE_18x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 18 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 18.
CC_CALL_TYPE_19x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 19 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 19.
CC_CALL_TYPE_20x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 20 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 20.
CC_CALL_TYPE_21x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 21 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 21.
CC_CALL_TYPE_22x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 22 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 22.
CC_CALL_TYPE_23x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 23 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 23.
CC_CALL_TYPE_24x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 24 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 24.
CC_CALL_TYPE_25x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 25 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 25.
CC_CALL_TYPE_26x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 26 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 26.
CC_CALL_TYPE_27x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 27 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 27.
CC_CALL_TYPE_28x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 28 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 28.
CC_CALL_TYPE_29x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 29 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information
transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s
and a multiplier of 29.
CC_CALL_TYPE_30x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 30 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.931 Information transfer capability of Unrestricted, and an Information transfer rate of multi-rate with a base rate of 64 kbit/s and a multiplier of 30.
Flags
The following call flags are defined for Q.931 conforming CCS providers:
CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS"- When set, this flag indicates that the unrestricted digital information includes tones and announcements.
Rules
CC_SETUP_REQ
Parameters
cc_call_type- Specifies the type of call to be set up. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call type can be one of the call
types listed under "Call Type and Flags" in this addendum.
cc_call_flags- Specifies the options flags associated with the call. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call flags can be any
of the flags listed under "Call Type and Flags" in this addendum.
cc_cdpn_length- Specifies the length of the called party number. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the format of the called party
number is the format of the Called Party Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.931.
cc_cdpn_offset- Specifies the offset of the called party number from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for call type:
- A CCS provider need not support all of the call types listed.
Rules for call flags:
- The CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS flag may only be set when the call type is unrestricted digital information. When the call type is not unrestricted digital information, this flag should be ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules for called party number:
Rules for generating a SETUP message:
- The mandatory (first) Bearer Capability information element in the SETUP message will be derived from the call type
and flags. The Bearer Capability information element will contain the Information transfer capability, rate, base
and multiplier indicated above.
- When the call type is CC_CALL_TYPE_128KBS_UNRESTRICTED, the Bearer Capability information element will be coded with an Information transfer capability of unrestricted (or unrestricted with tones an announcements if the flag CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS i set) and an Information transfer rate of 2 x 64 kbit/s uni-rate call. For a multi-rate call, the call type should be coded as CC_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
- When the call type is CC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED, the Bearer Capability information element will be coded with an Information transfer capability of unrestricted (or unrestricted with tones an announcements if the flag CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS i set) and an Information transfer rate of 384 kbit/s uni-rate call. For a multi-rate call, the call type should be coded as CC_CALL_TYPE_6x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
- When the call type is CC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED, the Bearer Capability information element will be coded with an Information transfer capability of unrestricted (or unrestricted with tones an announcements if the flag CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS i set) and an Information transfer rate of 1536 kbit/s uni-rate call. For a multi-rate call, the call type should be coded as CC_CALL_TYPE_24x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
- When the call type is CC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED, the Bearer Capability information element will be coded
with an Information transfer capability of unrestricted (or unrestricted with tones an announcements if the flag
CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS i set) and an Information transfer rate of 1920 kbit/s uni-rate call. For a
multi-rate call, the call type should be coded as CC_CALL_TYPE_29x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
- The mandatory Channel Identification information element in the SETUP message will be derived from the address to which the stream is bound.
- If the stream is bound to a channel group (the one or more interfaces), then a free channel will be selected automatically by the CCS provider (if possible).
- If the stream is bound to a channel, then the channel identifier of the bound channel will be used.
Rules for state transitions:
- If the optional information element contains a Sending Complete information element, then the CCS provider will not
accept any subsequent
CC_INFORMATION_REQprimitives from the CCS user, nor will the CCS provider issue any subsequent CC_MORE_INFO_IND primitives to the CCS user.
CC_SETUP_IND
Parameters
cc_call_type- Specifies the type of call to be set up. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call type can be one of the call
types listed under "Call Type and Flags" in this addendum.
cc_call_flags- Specifies the options flags associated with the call. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the call flags can be any
of the flags listed under "Call Type and Flags" in this addendum.
cc_cdpn_length- Specifies the length of the called party number. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the format of the called party
number is the format of the Called Party Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.931.
cc_cdpn_offset- Specifies the offset of the called party number from the beginning of the block.
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the address which contains the channel identifier selected for the call.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address from the beginning of the block.
Flags
Call flags can be any of the call flags supported by the CCS provider listed under CC_SETUP_REQ in this addendum.
Rules
Rules for call type:
- A CCS provider need not support all of the call types listed.
Rules for call flags:
- The CC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS flag may only be set when the call type is unrestricted digital information. When the call type is not unrestricted digital information, this flag should be ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules for called party number:
Rules for obtaining parameters from a SETUP message:
- The mandatory (first) Bearer Capability information element in the SETUP message will be translated into the call type and flags. The call type and flags correspond to the Bearer Capability information element will contain the Information transfer capability, rate, base and multiplier indicated under "Call Type" and "Flags".
- The mandatory Channel Identification information element in the SETUP message will be provided in the address parameter.
Rules for state transitions:
- If the optional information element contains a Sending Complete information element, then the CCS provider will not
accept any subsequent
CC_MORE_INFO_REQprimitives from the CCS user, nor will the CCS provider issue any subsequentCC_INFORMATION_INDprimitives to the CCS user.
CC_SETUP_RES
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_SETUP_CON
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND
Rules
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Continuity Check Primitives
CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Call Establishment Primitives
CC_MORE_INFO_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_MORE_INFO_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_INFORMATION_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_INFORMATION_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- If the Q.931 conforming CCS provider is expecting additional digits (it has previously issued a
CC_MORE_INFO_REQ) and timer T302 expires, the CCS provider will issue this primitive to the CCS user. - Upon receipt of this primitive, it is the CCS user's responsibility to determine whether the address digits are
sufficient and to issue a
CC_SETUP_RESorCC_REJECT_REQprimitive.
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS user
receives a CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_PROCEEDING_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_ALERTING_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_ALERTING_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_PROGRESS_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_PROGRESS_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_IBI_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_IBI_IND
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Call Established Primitives
CC_SUSPEND_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Q.931 conforming CCS providers do not support suspend flags. This field should be coded zero (0) by the CCS user and ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- Only the CCS user on the User side of the Q.931 interface can issue a
CC_SUSPEND_REQprimitive. If the CCS provider is in Network mode and it receives a CCS_SUSPEND_REQ, it should respond with aCC_ERROR_ACKwith errorCCNOTSUPP.
CC_SUSPEND_IND
Flags
Q.931 conforming CCS providers do not support suspend flags. This field will be coded zero (0) by the CCS provider and may be ignored by the CCS provider.
CC_SUSPEND_RES
Parameters
Rules
CC_SUSPEND_CON
Parameters
Rules
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause values can be any of the values listed in "Cause Values" in this addendum with the exception of CCS_CAUS_NONE.
Flags
Rules
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause values can be any of the values listed in "Cause Values" in this addendum with the exception of CCS_CAUS_NONE.
Flags
Rules
CC_RESUME_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Q.931 conforming CCS providers do not support resume flags. This field should be coded zero (0) by the CCS user and ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules
CC_RESUME_IND
Parameters
Flags
Q.931 conforming CCS providers do not support resume flags. This field should be coded zero (0) by the CCS user and ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules
CC_RESUME_RES
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_RESUME_CON
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause values can be any of the values listed in "Cause Values" in this addendum with the exception of CCS_CAUS_NONE.
Flags
Rules
CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND
cc_cause- Specifies the cause for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause values can be any of the values listed in "Cause Values" in this addendum with the exception of CCS_CAUS_NONE.
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Call Termination Primitives
Cause Values
Cause values are used in the following primitives:
CC_REJECT_REQ,
CC_REJECT_IND,
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ,
CC_DISCONNECT_IND,
CC_RELEASE_REQ, and
CC_RELEASE_IND.
Parameters
cc_cause- Indicates the case for the rejection, disconnection, or release of a call. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause values can be any of the cause values listed in Q.850 listed under "Cause Value" below.
Cause Value
Cause values are essentially opaque and cause values will be transferred directly to the corresponding Q.931 message. The following cause values are defined for Q.931 conforming CCS providers:
CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER- The called party number does not correspond to number allocated to a subscriber or terminal.
CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_USER_BUSY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT- (no description)
CC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_REDIRECT- (no description)
CC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INTERWORKING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP- (no description)
CC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26- (no description)
CC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS- (no description)
Rules
In addition to these cause values, the CCS provider might support additional variant-specific cause values.
CC_REJECT_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this Addendum.
Flags
Rules
CC_REJECT_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the rejection. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this Addendum.
Flags
Rules
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND
Parameters
cc_reason- Specifies the reason for the failure indication. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the reason will be one of the
reasons listed under "Call Failure Reasons" below.
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the error indication. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this addendum.
Call Failure Reasons
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_ERROR- Indicates that the data link failed and recovered during overlap sending or overlap receiving.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_STATUS- Indicates that the CCS provider received a STATUS message from the peer with a unrecoverable mismatch in state.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RESTART- Indicates that the CCS provider received or issued a RESTART message for the channel.
Flags
Rules
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the disconnect. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this addendum.
Rules
CC_DISCONNECT_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Indicates the case values for the disconnect. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value wil be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Value" in this addendum.
Rules
CC_RELEASE_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the release. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this addendum.
Rules
Rules for cause:
- If the request is not the first step in the clearing phase (i.e, the call is not in state CC_WREQ_REL), then the cause value must be specified. Otherwise, the cause value should be coded CC_CAUS_NONE by the CCS user and ignored by the CCS provider.
CC_RELEASE_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Specifies the cause value for the release. For Q.931 conforming CCS providers, the cause value will be one of the cause values listed under "Cause Values" in this addendum.
Rules
Rules for cause:
- If the request is not the first step in the clearing phase (i.e, the call is not in state CC_WIND_REL), then the cause value will be indicated by the CCS provider. Otherwise, the cause value will be coded CC_CAUS_NONE by the CCS provider and should be ignored by the CCS user.
CC_RELEASE_RES
Parameters
Rules
CC_RELEASE_CON
Parameters
Rules
Management Primitives
CC_RESTART_REQ
Parameters
cc_flagscc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the address which contains the interface identifier(s) and optional channel identification
for the interface(s) or channels to restart.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address from the beginning of the block.
Flags
Rules
CC_RESTART_CON
Parameters
cc_flagscc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the address which contains the interface identifier(s) and optional channel identification
for the interface(s) or channels to restart.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address from the beginning of the block.
Flags
Rules
Q.931 Header File Listing
/*
* ISDN address
*/
typedef struct isdn_addr {
cc_ulong scope; /* the scope of the identifier */
cc_ulong id; /* the identifier within the scope */
cc_ulong ci; /* channel identifier within the scope */
} isdn_addr_t;
#define ISDN_SCOPE_CH 1 /* channel scope */
#define ISDN_SCOPE_FG 2 /* facility group scope */
#define ISDN_SCOPE_TG 3 /* transmission group scope */
#define ISDN_SCOPE_EG 4 /* equipment group scope */
#define ISDN_SCOPE_XG 5 /* customer/provider group scope */
#define ISDN_SCOPE_DF 6 /* default scope */
enum {
U0_NULL,
U1_CALL_INITIATED,
U2_OVERLAP_SENDING,
U3_OUTGOING_CALL_PROCEEDING,
U4_CALL_DELIVERED,
U6_CALL_PRESENT,
U7_CALL_RECEIVED,
U8_CONNECT_REQUEST,
U9_INCOMING_CALL_PROCEEDING,
U10_ACTIVE,
U11_DISCONNECT_REQUEST,
U12_DISCONNECT_INDICATION,
U15_SUSPEND_REQUEST,
U17_RESUME_REQUEST,
U19_RELEASE_REQUEST,
U25_OVERLAP_RECEIVING,
N0_NULL,
N1_CALL_INITIATED,
N2_OVERLAP_SENDING,
N3_OUTGOING_CALL_PROCEEDING,
N4_CALL_DELIVERED,
N6_CALL_PRESENT,
N7_CALL_RECEIVED,
N8_CONNECT_REQUEST,
N9_INCOMING_CALL_PROCEEDING,
N10_ACTIVE,
N11_DISCONNECT_REQUEST,
N12_DISCONNECT_INDICATION,
N15_SUSPEND_REQUEST,
N17_RESUME_REQUEST,
N19_RELEASE_REQUEST,
N22_CALL_ABORT,
N25_OVERLAP_RECEIVING,
};
enum {
CMS_IDLE = 0,
};
#define ISDN_PI_INTERWORKING 0x0 /* FIXME */
/*
* Q.850 Cause Values
*/
/*
Normal class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER 1 /* Unallocated (unassigned)
number */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK 2 /* No route to specified transit
network */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION 3 /* No route to destination */
#define CC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE 4 /* Send special information tone */
#define CC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX 5 /* Misdialled trunk prefix */
#define CC_CAUS_CALL_ABANDONNED 6 /* Call abandonned */
#define CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION 8 /* Preemption */
#define CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED 9 /* Preemption - circuit reserved
for reuse */
#define CC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING 16 /* Normal call clearing */
#define CC_CAUS_USER_BUSY 17 /* User busy */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING 18 /* No user responding */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER 19 /* No answer from user (user
alerted) */
#define CC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT 20 /* Subscriber absent */
#define CC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED 21 /* Call rejected */
#define CC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED 22 /* Number changed */
#define CC_CAUS_REDIRECT 23 /* Redirect to new destination */
#define CC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER 27 /* Desitination out of order */
#define CC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE 28 /* Invalid number format (address
incomplete) */
#define CC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED 29 /* Facility rejected */
#define CC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED 31 /* Normal unspecified */
/*
Resource Unavailable Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE 34 /* No circuit/channel available */
#define CC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER 38 /* Network out of order */
#define CC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE 41 /* Temporary failure */
#define CC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION 42 /* Switching equipment congestion
*/
#define CC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED 43 /* Access information discarded */
#define CC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE 44 /* Requested circuit/channel not
available */
#define CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED 46 /* Precedence call blocked */
#define CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE 47 /* Resource unavailable,
unspecified */
/*
Service or Option Unavaialble Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED 50 /* Requested facility not
subscribed */
#define CC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG 53 /* Outgoing calls barred within
CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG 55 /* Incoming calls barred within
CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED 57 /* Bearer capability not
authorized */
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE 58 /* Bearer capability not
presently available */
#define CC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY 62 /* Inconsistency in designated
outgoing access information
and subscriber class */
#define CC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE 63 /* Service or option not
available, unspecified */
/*
Service or Option Not Implemented Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 65 /* Bearer capability not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 69 /* Requested facility not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY 70 /* Only restricted digital
information bearer capability
is available */
#define CC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 79 /* Service or option not
implemented, unspecified */
/*
Invalid Message (e.g., Parameter out of Range) Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNEXPECTED_MESSAGE 81 /* Unexpected message */
#define CC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG 87 /* User not member of CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION 88 /* Incompatible destination */
#define CC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG 90 /* Non-existent CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION 91 /* Invalid transit network
selection */
#define CC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE 95 /* Invalid message, unspecified */
#define CC_CAUS_MISSING_MANDATORY_PARAMETER 96 /* Invalid message, missing
mandatory parameter */
/*
Protocol Error (e.g., Unknwon Message) Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 97 /* Message typ non-existent or
not implemented. */
#define CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 99 /* Information element/Parameter
non-existent or not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_INVALID_MANDATORY_PARAMETER 100 /* Invalid mandatory parameter */
#define CC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY 102 /* Recovery on timer expiry */
#define CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON 103 /* Parameter non-existent or not
implemented - passed on */
#define CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED 110 /* Message with unrecognized
parameter discarded */
#define CC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR 111 /* Protocol error, unspecified */
/*
Interworking Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_INTERWORKING 127 /* Interworking, unspecified */
/*
* ANSI Standard Causes
*/
/*
Normal Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER 23 /* Unallocated destination number
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP 24 /* Unknown business group */
#define CC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR 25 /* Exchange routing error */
#define CC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26 /* Misrouted call to a ported
number */
#define CC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND 27 /* Number portability Query on
Release (QoR) number not
found. */
/*
Resource Unavailable Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_PREEMPTION 45 /* Preemption. */
#define CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED 46 /* Precedence call blocked. */
/*
Service or Option Not Available Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE 51 /* Call type incompatible with
service request */
#define CC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS 54 /* Call blocked due to group
restrictions */
Addendum for Q.764 Conformance
This addendum describes the formats and rules that are specific to ISUP Q.764. The addendum must be used along with the generic CCI as defined in the main document when implementing a CCS provider that will be configured with the Q.764 call processing layer.
Primitives and Rules for Q.764 Conformance
The following are the rules that apply to the CCI primitives for Q.764 compatibility.
Common Primitive Parameters
Call Control Addresses
Format
The format of call control addresses is as follows:
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Specifies or indicates the length of the call control address. If a call control address is not included in the
primitive, this parameter must be coded zero (0).
cc_addr_offset- Specifies or indicates the offset of the address from the begining of the primitive. If a call control address is not included with the primitive, this parameter must be coded zero (0).
Address Format
The format of the call control addresses for Q.764 conforming CCS providers is as follows:
typedef struct isup_addr {
ulong scope; /* the scope of the identifier */
ulong id; /* the identifier within the scope */
ulong cic; /* circuit identification code within the scope */
} isup_addr_t;
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CT 1 /* circuit scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CG 2 /* circuit group scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_TG 3 /* trunk group scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_SR 4 /* signalling relation scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_SP 5 /* signalling point scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_DF 6 /* default scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CIC 7 /* for unidentified cic addresses */
Address Fields
scope- Specifies or indicates the scope of the call control address. See "Scope" below.
id- Specifies or indicates the identifier within the scope.
cic- Specifies or indicates the Circuit Identification Code significant within the scope.
Scope
The scope of the address is one of the following:
ISUP_SCOPE_CT- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is a ISUP circuit. The identifier within the
scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies a circuit to the CCS provider. Circuit scope addresses may also be
used to specify or indicate circuit groups, trunk groups, signalling relations and signalling points. When used in
an indication or confirmation primitive, the CCS provider includes the Circuit Identification Code associated with
the circuit in the address.
For multi-rate calls where multiple circuits are involved, the circuit scoped address specifies the lowest numerical Circuit Identification Code in the group of circuits.
ISUP_SCOPE_CG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is a ISUP circuit group. The identifier within
the scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies a circuit group to the CCS provider. Circuit group scope
addresses may also be used to specify or indicate signalling relations and signalling points. When used in an
indication or confirmation primitive, the CCS provider includes the Circuit Identification Code associated with the
circuit group (lowest numerical value CIC in the circuit group range).
ISUP_SCOPE_TG- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is a ISUP trunk group. The identifier within the
scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies a trunk group to the CCS provider. Trunk group scope addresses may
also be used to specify or indicate circuits, signalling relations and signalling points. The Circuit
Identification Code must be used to specify a circuit within the trunk group.
ISUP_SCOPE_SR- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is a ISUP signalling relation. The identifier
within the scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies a signalling relation to the CCS provider. Signalling
relation scope addresses may also be used to specify or indicate circuits and signalling points. The Circuit
Identification Code must be used to sepcify a circuit (equipped or unequipped) within the signalling relation.
ISUP_SCOPE_SP- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is a ISUP signalling point. The identifier within
the scope is an identifier which uniquely identifies a local signalling point to the CCS provider. Signalling point
scope addresses may only indicate local signalling points. The Circuit Identification Code is unused and should be
ignored by the CCS user and will be coded zero (0) by the CCS provider.
ISUP_SCOPE_DF- Specifies or indicates that the scope of the call control address is the default scope. The identifier within the scope and Circuit Identification Code are unused and should be ignored by the CCS user and will be coded zero (0) by the CCS provider.
Rules
Rules for scope:
- In primitives in which the address parameter occurs, the scope field setting indicates the scope of the address parameter.
- Only one call control address can be specified with a signle scope.
- Not all scopes are necessarily supported by all primitives. See the particular primitive in this addendum.
Rules for addresses:
- The address contained in the primitive contains the following:
- A scope.
- An identifier within the scope or zero (0).
- A circuit identification code within the scope or zero (0).
- If the scope of the address is
ISUP_SCOPE_DF, then both the identifier and circuit identification code fields should be coded zero (0) and will be ignored by the CCS user or provider. - If the scope of the address is
ISUP_SCOPE_SP, then the circuit identification code field should be coded zero (0) and will be ignored by the CCS user or provider. - In all other scopes, the circuit identification code is optional and is coded zero (0) if unused.
Optional Parameters
Format
The format of the optional parameters for Q.764 conforming CCS providers is as follows:
Parameters
cc_opt_length- Specifies or indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the primitive. For Q.764 conforming
CCS providers, the format of the optional parameters is the format of the Optional Parameters list (without the
pointer or End of Optional Parameters octets) as specified in Q.763.
cc_opt_offset- Specifies the offset of the optional parameters from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for optional parameters:
- The optional parameters provided by the CCS user may be checked for syntax by the CCS provider. If the CCS provider
discovers a syntax error in the format of the optional parameters, the CCS provider should respond with a
CC_ERROR_ACKprimitive with errorCCBADOPT. - For some primitives, specific optional parameters might be interpreted by the CCS provider and alter the function of some primitives. See the specific primitive descriptions later in this addendum.
- Except for optional parameters interpreted by the CCS provider as specified later in this addendum, the optional parameters are treated as opaque and the optional parameter list only is checked for syntax. Opaque parameters will be passed to the ISUP message without examination by the CCS provider.
- To perform specific functions, additional optional parameters may be added to ISUP messages by the CCS provider.
- To perform specific functions, optional parameters may be modified by the CCS provider before being added to ISUP messages.
Local Management Primitives
CC_INFO_ACK
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_BIND_REQ
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address to bind.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address to bind from the beginning of the block.
cc_setup_ind- Indicates the maximum number of setup (or continuity check) indications that will be outstanding for the listening
stream.
cc_bind_flags- Indicates the options assocated with the bind. The bind flags can be as follows:
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER- When set, this flag specifies that this stream is the "default listener stream." This stream is used to pass setup
indications (or continuity check requests) for all incoming calls that contain protocol identifiers that are not
bound to any other listener, or when a listener stream with cc_setup_ind value of greater than zero is not found.
Also, the default listener will receive all incoming call indications that contain no user data (i.e., test calls)
and all maintenance indications (i.e.,
CC_MAINT_IND). Only one default listener stream is allowed per occurrence of CCI. An attempt to bind a default listener stream when one is already bound should result in an error (of typeCCADDRBUSY). CC_TOKEN_REQUEST- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that the CCS user has requested that a "token" be assigned to the
stream (to be used in the call response message), and the token value be returned to the CCS user via the
CC_BIND_ACKprimitive. The token assigned by the CCS provider can then be used by the CCS user in a subsequentCC_SETUP_RESprimitive to identify the stream on which the call is to be established. CC_MANAGEMENT- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for circuit management indications
for the specified addresses.
CC_TEST- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for continuity and test call
indications for the specified addresses.
CC_MAINTENANCE- When set, this flag specifies to the CCS provider that this stream is to be used for maintenance indications for the specified addresses.
Rules
Rules for address specification:
- The address contained in the primitive as indicated by
cc_addr_lengthandcc_addr_offsetparameters. The address can be of any ISUP scope. - If the
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERflag is set, the parameterscc_addr_lengthandcc_addr_offsetshould be coded zero, and will be ignored by the CCS provider.
Rules for setup indications:
- If the number of setup indications is non-zero, the stream is bound as a listening stream. Listening streams will
receive all calls, test calls, and continuity tests that are incoming on the address bound.
- If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_CT, only incoming calls on the bound circuit will be delivered to the listening stream. - If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_CG, only incoming calls on the bound circuit group will be delivered to the listening stream. - If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_TG, only incoming calls on the bound trunk group will be delivered to the listening stream (this is the normal case). - If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_SR, only incoming calls on the bound signalling relation (from the associated remote point code) will be delivered to the listening stream. - If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_SP, only incoming calls on the bound local signalling point will be delivered to the listening stream. - If the address bound is of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_DF, all incoming calls will be delivered to the listening stream. - Streams bound at one scope takes precedence over a stream bound at another scope in the order: circuit, circuit group, trunk group, signalling relation, signalling point and default scope.
- If the address bound is of scope
- Once a stream has successfully bound as a listening stream, it should be prepared to receive incoming calls, test calls and continuity tests.
Rules for bind flags:
- For Q.764 conformance, the
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENERwill receive all incoming calls, test calls, continuity tests, circuit management indications and maintenance indications that have no other listening stream. There can only be one stream bound with theCC_DEFAULT_LISTENERflag set. - Only one of
CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER,CC_MANAGEMENT,CC_TESTandCC_MAINTENANCEmay be set. - Streams bound with the
CC_MANAGEMENTflag set will receive only circuit management indications and will not receive any calls. - Streams bound with the
CC_TESTflag set will receive only continuity test and test call indications and will not receive normal calls, circuit management or maintenance indications. - Streams bound with the
CC_MAINTENANCEflag set will receive only maintenance indications and will not receive any circuit management indications or calls.
CC_BIND_ACK
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address to bind.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address to bind from the beginning of the block.
cc_setup_ind- Indicates the maximum number of setup (or continuity check) indications that will be outstanding for the listening stream.
Flags
See CC_BIND_REQ in this Addendum.
Rules
See CC_BIND_REQ in this Addendum.
CC_OPTMGMT_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
Call Setup Primitives
CC_SETUP_REQ
Parameters
cc_call_type- Specifies the type of call to be set up.
Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support the following call types:
CC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH- The call type is speech. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission medium requirement of Speech.
CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission
medium requirement of 64 kbit/s Unrestricted Digital Information.
CC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO- The call type is 3.1 kHz audio. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission medium requirement of 3.1
kHz Audio.
CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_PREFERRED- The call type is 64 kbit/s preferred. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission medium requirement of
64 kbit/s Preferred.
CC_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 2 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission
medium requirement of 2 x 64 kbit/s Unrestricted Digital Information.
CC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 384 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission
medium requirement of 384 kbit/s Unrestricted Digital Information.
CC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 1536 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission
medium requirement of 1536 kbit/s Unrestricted Digital Information.
CC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 1920 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a Q.764 transmission medium requirement of 1920 kbit/s Unrestricted Digital Information.
cc_user_ref- Specifies the CCS user call reference to be associated with the call setup request. The CCS provider will use this
user call reference in any indications given before the
CC_SETUP_CONprimitive is issued. cc_call_flags- Specifies the options associated with the call. Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support the following flags:
The following flags correspond to bits in the Nature of Connection Indicators parameter of Q.763:
ISUP_NCI_ONE_SATELLITE_CCTISUP_NCI_TWO_SATELLITE_CCT- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either one or two satellite circuits are present in the connection.
Otherwise, it indicates that no satellite circuits are present in the connection.
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIREDISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUS- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either a continuity check is required on the connection, or that a
continuity check was performed on a previous connection. Otherwise, it indicates that a continuity check is not
required on the connection.
ISUP_NCI_OG_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE- When set it indicates that an outgoing half echo control device is included on the connection. Otherwise, it indicates that no outgoing half echo control device is included on the connection.
The following flags correspond to bits in the Forward Call Indicators parameter of Q.763:
ISUP_FCI_INTERNATIONAL_CALL- When this flag is set, the call is to be treated as an international call. Otherwise, the call is to be treated as
a national call.
ISUP_FCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_FCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE- When one of these flags is set, either the pass along end-to-end method is available or the SCCP end-to-end method
is available. Otherwise, no end-to-end method is available and only link-by-link method is available.
ISUP_FCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED- When this flag is set, interworking has been encountered on the call. Otherwise, no interworking has been
encountered on the call.
ISUP_FCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE- When this flag is set, end-to-end information is now available. Otherwise, no end-to-end information is available.
ISUP_FCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY- When this flag is set, ISDN User Part has been used all the way on the call. Otherwise, ISDN User Part has not been
used all the way.
ISUP_FCI_ORIGINATING_ACCESS_ISDN- When this flag is set, the originating access is ISDN. Otherwise, the originating access is non-ISDN.
ISUP_FCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_FCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_FCI_SCCP_ALL_METHODS_AVAILABLE- When one of these flags is set, either the connectionless SCCP method is available, the connection oriented SCCP method is available, or both methods are available. Otherwise, no SCCP method is indicated as available.
cc_cdpn_length- Specifies the length of the called party number. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, the format of the called party
number is the format of the Called Party Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.763.
cc_cdpn_offset- Specifies the offset of the called party number from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- If the ISUP user wishes to setup multiple outgoing calls on the same stream, the ISUP user associates a user call reference with each of the setup requests so that the indication, confirmation and acknowledgement primitives can be associated with the specific call setup request.
- User call references are only necessary if multiple outgoing calls are to setup at the same time.
- User call references only need by valid until a setup confirmation, call reattempt indication, release indication or call failure indication has been received in response to the setup request. A setup confirmation will contain a CCS provider call reference which can be used to distinguish the call from other calls to the CCS provider.
Rules for call type:
- All Q.764 conforming CCS provider must support the following call types:
CC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH, CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED, CC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO, and CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_PREFERRED.
- Support for other call types is optional and implementation-specific.
Rules for flags:
- Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support all of the flags listed above.
- Only one of the following flags may be set:
ISUP_NCI_ONE_SATELLITE and ISUP_NCI_TWO_SATELLITE.
- Only one of the following flags may be set:
ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED andISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUS. - Only one of the following flags may be set:
ISUP_FCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLEandISUP_FCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE. - Only one of the following flags may be set,
and only if
ISUP_FCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLEis also set:ISUP_FCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLE,ISUP_FCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLEandISUP_FCI_SCCP_ALL_METHODS_AVAILABLE.
CC_SETUP_IND
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider-assigned call reference associated with the call.
cc_call_type- Indicates the type of call to be set up. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, the call type can be one of the call
types listed in this addendum under
CC_SETUP_REQ. cc_call_flags- Indicates the options associated with the call.
Q.764 conforming CCS providers indicate the flags listed in this addendum under
CC_SETUP_REQ. cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (circuit(s)) upon which the call setup is indicated.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address from the start of the block.
cc_cdpn_length- Indicates the length of the called party number. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, the format of the called party
number is the format of the Called Party Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.763.
cc_cdpn_offset- Indicates the offset of the called party number from the beginning of the block.
cc_opt_length- Indicates the length of the optional parameters associated with the IAM, excluding the end of optional parameters
tag.
cc_opt_offset- Indicates the offset of the options from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The ISUP provider will indicate a unique call reference to the CCS user which is used to associate response and request primitives with the call setup indication.
- Provider call references will always be indicated.
- Provider call references are only valid until a call failure or release indication has been issued by the CCS provider.
- Provider call references are only valid for streams upon which the
CC_SETUP_INDis issued, or for streams upon which the call was accepted by the CCS user with aCC_SETUP_RESprimitive. - Provider call references are unique across the provider.
Rules for call type:
- The rules for call type in section
CC_SETUP_REQin this addendum also apply to theCC_SETUP_IND. All Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support the following call types:CC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH, CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED, CC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO, and CC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_PREFERRED.
- Support for additional call types is optional and implementation-specific.
Rules for setup flags:
Rules for addresses:
- Call control addresses in the
CC_SETUP_INDare of scopeISUP_SCOPE_CTand identify the circuit(s) upon which the call setup is indicated. - For multi-rate calls, the call control address indicates the base circuit (numerically lowest Circuit Identification Code) of the multi-rate call.
CC_SETUP_RES
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Specifies the call reference of the
CC_SETUP_INDto which the CCS user is responding. cc_token_value- Specifies the token of a stream upon which to accept the call setup.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The call reference specified by the CCS User must be a call reference which was previously indicated by the CCS
provider in an outstanding
CC_SETUP_IND. Otherwise the CCS provider will respond with aCC_ERROR_ACKprimitive with errorCCBADCLR.
Rules for token value:
- If the token is the token value of the stream upon which the corresponding
CC_SETUP_INDwas received, or zero (0), then the call setup will be accepted on the stream upon which theCC_SETUP_INDwas received. - If the token is non-zero and different from the listening stream, the call setup will be accepted on the specified stream.
CC_SETUP_CON
Parameters
cc_user_ref- Indicates the CCS user call reference that was specified in the
CC_SETUP_REQ. This call reference is used by the CCS user to associated theCC_SETUP_CONwith an outstandingCC_SETUP_REQprimitive. cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider call reference that is to be associated with the call. This call reference is used by
the CCS provider to identify the call and is to be used by the CCS user in all subsequent primitives referencing the
call.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the identifier of the circuit upon which the call setup is confirmed.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the identifier from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The CCS user call reference will be the same as the call reference provided by the user in the
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive. - The CCS provider call reference will follow the rules of the
CC_SETUP_INDin this Addendum.
Rules for addresses:
- The call control address indicated in the
CC_SETUP_CONis aISUP_SCOPE_CT(circuit scoped) call control address which identifies the circuit(s) upon which the outgoing call will be connected. - For multi-rate calls, the call control address specifies the base circuit (lowest numerical Circuit Identification Code) for the multi-rate call.
CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND
Parameters
cc_user_ref- Indicates the CCS user call reference for the call. This reference identifies the corresponding
CC_SETUP_REQprimitives to the CCS user for which the call reattempt need be performed. cc_reason- Indicates the reason for the reattempt. The reason can be one of the following values:
ISUP_REATTEMPT_DUAL_SEIZURE- Indicates that the circuit was seized by a controlling exchange during the initial setup of the call (i.e, before
any backward message was received).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_RESET- Indicates that the circuit was reset during the initial setup of the call (i.e, before any backward message was
received).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_BLOCKING- Indicates that the circuit was blocked during the initial setup of the call (i.e, before any backward message was
received).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_T24_TIMEOUT- Indicates that COT failure occurred on the circuit (due to T24 timeout).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_UNEXPECTED- Indicates that an unexpected message was received for the call during the initial setup of the call (i.e, before any
backward message was received).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_COT_FAILURE- Indicates that COT failed on the circuit (due to transmission of COT message indicating failure).
ISUP_REATTEMPT_CIRCUIT_BUSY- Indicates that the specified circuit was busy.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The CCS user call reference is a call reference associated with an outstanding
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive to which the CCS provider is responding.
Rules for reason:
- The Q.764 conforming CCS provider will provide one of the reasons listed above.
- The ISUP_REATTEMPT_DUAL_SEIZURE reason will only be indicated if the CCS user represents a non-controlling exchange for the associated trunk group.
- The ISUP_REATTEMPT_T24_TIMEOUT reason will only be indicated if the outgoing call includes a continuity test and a
positive
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQwas not issued to the CCS provider by a test stream within T24. - The ISUP_REATTEMPT_COT_FAILURE reason will only be indicated if the outgoing call includes a continuity test and a
negative
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQwas issued to the CCS provider by a test stream within T24. - The ISUP_REATTEMPT_CIRCUIT_BUSY reason will only be indicated if the stream issuing the
CC_SETUP_REQprimitive is bound to a circuit (ISUP_SCOPE_CT) and the circuit is busy with another call.
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ
Rules
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if a CCS provider
conforming to Q.764 receives a CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ for a call reference in the CCS_ANSWERED state
(CCS_ICC_ANSWERED), the CCS provider will ignore the primitive.
CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND
Rules
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if a CCS provider
conforming to Q.764 issues a CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND for a call reference in the CCS_ANSWERED state, the CCS user may
ignore the primitive.
Continuity Check Phase
CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ
Parameters
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the circuit test address (circuit) upon which the continuity check is to be performed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the circuit test address from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for addresses:
- The parameter
cc_addr_lengthcannot be zero: i.e, an address must be provided or the CCS provider should respond withCC_ERROR_ACKwith an error ofCCNOADDR. - The address provided must be of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_CTand must provide the identifier of the circuit upon which the CCS user is requesting a continuity check. - The specified circuit identifier must be equipped else the CCS provider should response with
CC_ERROR_ACKand an error ofCCBADADDR.
CC_CONT_CHECK_IND
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider call reference.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the identifier of the circuit upon which the continuity check is to be performed.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The parameter
cc_addr_lengthcannot be zero: i.e, an address must be provided or the CCS provider should respond withCC_ERROR_ACKwith an error ofCCNOADDR. - The address provided must be of scope
ISUP_SCOPE_CTand must provide the identifier of the circuit upon which the CCS user is requesting a continuity check. - The specified circuit test address (circuit identifier) must be equipped else the CCS provider should response with
CC_ERROR_ACKand an error ofCCBADADDR.
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ
This primitive is only supported when the Loop Back Acknowledgement is used as a national option under Q.764. For
compatibility with CCS providers not supporting the national option, if such a CCS provider receives a
CC_CONT_TEST_REQ while waiting for a CC_CONT_REPORT_IND, the CCS provider should silently discard the primitive.
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Specifies the CCS provider call reference.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the call control address (
ISUP_SCOPE_CTcircuit identifier) upon which the continuity check is to be performed. cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the call control address from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for addresses:
- The parameter
cc_addr_lengthcannot be zero: i.e, an address must be provided or the CCS provider should respond withCC_ERROR_ACKwith an error ofCCNOADDR. - The address provided must be the identifier of the circuit upon which the CCS user is requesting a continuity check.
- The specified circuit identifier must be equipped else the CCS provider should response with
CC_ERROR_ACKand an error ofCCBADADDR.
CC_CONT_TEST_IND
This primitive is only supported when the Loop Back Acknowledgement is used as a national option under Q.764. For
compatibility with CCS providers not supporting the national option, such a CCS provider will issue a
CC_CONT_TEST_IND in response to a CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ following the CC_OK_ACK.
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Specifies the CCS provider call reference.
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the identifier of the circuit upon which the continuity check is to be performed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for call reference:
- The CCS provider assigned call reference is used to associate an outstanding continuity test indication
(CC_CONT_CHECK_IND or call setup indication
CC_SETUP_INDincluding a continuity test (ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED).
Rules for addresses:
- The parameter
cc_addr_lengthcannot be zero: i.e, an address must be provided or the CCS provider should respond withCC_ERROR_ACKwith an error ofCCNOADDR. - The address provided must be the identifier of the circuit upon which the CCS user is requesting a continuity check.
- The specified circuit identifier must be equipped else the CCS provider should response with
CC_ERROR_ACKand an error ofCCBADADDR.
CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ
Parameters
cc_user_ref- Specifies the CCS User assigned call reference.
cc_call_ref- Specifies the CCS Provider assigned call reference.
cc_result- Specifies the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. For Q.764 conforming CCS provider, the
result parameter can be one of the following values:
ISUP_COT_SUCCESS- Indicates that the continuity check test was successful.
ISUP_COT_FAILURE- Indicates that the continuity check test failed.
cc_addr_length- Specifies the length of the identifier of the circuit upon which the continuity check is to be performed.
cc_addr_offset- Specifies the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
Rules for addresses:
- The parameter
cc_addr_lengthcannot be zero: i.e, an address must be provided or the CCS provider should respond withCC_ERROR_ACKwith an error ofCCNOADDR. - The address provided must be the identifier of the circuit upon which the CCS user is requesting a continuity check.
- The specified circuit identifier must be equipped else the CCS provider should response with
CC_ERROR_ACKand an error ofCCBADADDR.
CC_CONT_REPORT_IND
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider assigned call reference.
cc_result- Indicates the result of the continuity test, whether success or failure. For Q.764 conforming CCS provider, the result parameter can be one of the following values:
Rules
Rules for call reference:
Call Establishment Primitives
CC_MORE_INFO_REQ
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive is not directly supported by Q.764 conforming CCS providers. For compatibility with Q.931 conforming
CCS providers, if the Q.764 conforming CCS provider receives a
CC_MORE_INFO_REQin stateCCS_WRES_SIND, it should invoke any interworking procedures and silently discard the primitive.
CC_MORE_INFO_IND
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive may optionally be issued by a Q.764 conforming CCS provider in the overlap signalling mode, if the appropriate timer has expired and the CCS provider has not received an indication that the provided address is complete.
CC_INFORMATION_REQ
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Specifies the CCS provider assigned call reference for the call.
cc_subn_length- Specifies the length of the subsequent number. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, the format of the called party
address is the format of the Subsequent Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.763.
cc_subn_offset- Specifies the offset of the subsequent number from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive will only be issued before any
CC_PROCEEDING_IND,CC_ALERTING_IND,CC_PROGRESS_IND, orCC_IBI_INDhas occurred on the stream while in theCCS_WCON_SREQstate. If not, the CCS provider should respond with aCC_ERROR_ACKprimitive with errorCCOUTSTATE. - This primitive must not be issued if the preceding
CC_SETUP_REQcontained a called party address which was complete (i.e, contains a ST code following the digits). If it is, the CCS provider should respond with aCC_ERROR_ACKwith errorCCBADADDR. - This primitive must not be issued if the trunk group or circuit to which the stream is bound is configured for
en bloc operation. If it is, the CCS provider should respond with a
CC_ERROR_ACKwith errorCCNOTSUPP.
CC_INFORMATION_IND
Parameters
cc_call_ref- Indicates the CCS provider assigned call reference.
cc_subn_length- Indicates the length of the subsequent number. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, the format of the subsequent
number is the format of the Subsequent Number parameter (without the parameter type or length octets) as specified
in Q.763.
cc_subn_offset- Indicates the offset of the subsequent number from the beginning of the block.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider before any
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ,CC_ALERTING_REQ,CC_PROGRESS_REQ, orCC_IBI_REQhas been received in stateCCS_WCON_SREQ. - This primitive will not be issued by the CCS provider if the preceding
CC_SETUP_REQcontained a complete called party address (i.e, contains an ST code following the digits), or if the trunk group or circuit is configured for en bloc operation.
CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- If the Q.764 conforming CCS provider encounters interworking on a call and is not expecting an address complete message, and timer T11 expires, the CCS provider will issue this primitive to the CCS user.
- Upon receipt of this primitive, it is the CCS user's responsibility to determine whether the address digits are
sufficient and to issue a
CC_SETUP_RESorCC_REJECT_REQprimitive.
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS user
receives a CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND
CC_PROCEEDING_REQ
Parameters
cc_flags- Specifies the options associated with the call.
Indicates the flags associated with the primitive. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, call flags can be an of the following:
Q.764 conforming CCS provider must support the following flags:
The following flags correspond to bits in the Backward Call Indicators parameter of Q.763:
ISUP_BCI_NO_CHARGEISUP_BCI_CHARGE- When one of these flags is set, it indicates that the call is not to be charged, or the call is to be charged.
Otherwise, it indicates that there is no indication with regard to charging.
ISUP_BCI_SUBSCRIBER_FREEISUP_BCI_CONNECT_FREE- When one of these flags is set, it indicates that the terminating subscriber is free, or that the connection is
free. Otherwise, no indication is given.
ISUP_BCI_ORDINARY_SUBSCRIBERISUP_BCI_PAYPHONE- When one of these flags is set, it indicates that the call has terminated to an ordinary subscriber, or that the
call has terminated to a pay phone.
ISUP_BCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_BCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE- When one of these flags is set, either the pass along end-to-end method is available, or the SCCP end-to-end method
is available. Otherwise, no end-to-end method is available and only link-by-link method is available.
ISUP_BCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED- When this flag is set, interworking has been encountered on the call. Otherwise, to interworking has been
encountered on the call.
ISUP_BCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE- When this flag is set, end-to-end information is now available. Otherwise, no end-to-end information is available.
ISUP_BCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY- When this flag is set, ISDN User Part has been used all the way on the call, Otherwise, ISDN User Part has not be
used all the way.
ISUP_BCI_HOLDING_REQUESTED- When this flag is set, holding is requested. Otherwise, holding is not requested.
ISUP_BCI_TERMINATING_ACCESS_ISDN- When this flag is set, the terminating access is ISDN. Otherwise, the terminating access is non-ISDN.
ISUP_BCI_IC_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE- When set, this flag indicates that an incoming half echo control device is included on the connection. Otherwise,
it indicates that no incoming half echo control device is included in the connection.
ISUP_BCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_BCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLEISUP_BCI_SCCP_ALL_METHODS_AVAILABLE- When one of these flags is set, either the connectionless SCCP method is available, the connection oriented SCCP method is available, or both methods are available. Otherwise, no SCCP method is indicated as available.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive can only be issued by the CCS user before any
CC_ALERTING_REQ,CC_PROGRESS_REQorCC_IBI_REQhas been issued while in stateCCS_WRES_SIND.
CC_PROCEEDING_IND
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider before any
CC_ALERTING_IND,CC_PROGRESS_INDorCC_IBI_INDhas been issued while in stateCCS_WCON_SREQ.
CC_ALERTING_REQ
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive can only be issued by the CCS user before any
CC_PROGRESS_REQorCC_IBI_REQhas been issued while in stateCCS_WRES_SIND.
CC_ALERTING_IND
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider before any
CC_PROGRESS_INDorCC_IBI_INDhas been issued while in stateCCS_WCON_SREQ.
CC_PROGRESS_REQ
Parameters
cc_event- Indicates the progress event. For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, this can be one of the following:
ISUP_EVNT_ALERTING- Indicates that the called party is being alerted. This event is indicated only if a CC_CALL_PROCEEDING_IND
primitive has already been received.
ISUP_EVNT_PROGRESS- Indicates that the call is progressing with the specified optional parameters.
ISUP_EVNT_IBI- This event is indicated only by the
CC_IBI_INDprimitive and will not appear here. ISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_ON_BUSY- This event indicates that the call has been forwarded on busy and the optional parameters (if any) contain the
attributes of the forwarding (e.g., redirecting number, etc.).
ISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_ON_NO_ANSWER- This event indicates that the call has been forwarded on no answer and the optional parameters (if any) contain the
attributes of the forwarding (e.g., redirecting number, etc.).
ISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_UNCONDITIONAL- This event indicates that the call has been forwarded unconditionally and the optional parameters (if any) contain the attributes of the forwarding (e.g., redirecting number, etc.).
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive can only be issued by the CCS user before any
CC_IBI_REQhas been issued while in stateCCS_WRES_SIND.
Rules for progress event:
- Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support the complete list of progress events listed above.
- When this primitive is issued with the event ISUP_EVNT_ALERTING, it must follow the rules for the primitive
CC_ALERTING_REQ. - When this primitive is issued with the event ISUP_EVNT_IBI, it must follow the rules for the primitive
CC_IBI_REQ.
Rules for progress flags:
- The flag ISUP_EVNT_PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED cannot be set when the event is ISUP_EVNT_ALERTING, ISUP_EVNT_PROGRESS or ISUP_EVNT_IBI.
CC_PROGRESS_IND
Parameters
cc_event- Indicates the progress event. The event can be any of the events listed in this addendum under
CC_PROGRESS_REQ. cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- This primitive will only be issued by the CCS provider before any
CC_IBI_INDhas been issued while in stateCCS_WCON_SREQ.
Rules for progress event:
- Q.764 conforming CCS providers must support the complete list of progress events listed above.
- This primitive will not be issued by the CCS provider with event ISUP_EVNT_ALERTING or event ISUP_EVNT_IBI: instead,
a
CC_ALERTING_INDorCC_IBI_INDevent will be issued.
Rules for progress flags:
- The flag ISUP_EVNT_PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED cannot be set when the vent is ISUP_EVNT_PROGRESS.
CC_IBI_REQ
Rules
CC_IBI_IND
Rules
Call Established Primitives
CC_SUSPEND_REQ
Parameters
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, suspend can be requested by independently either via local provider or the
remote provider. A call can be:
- Not Suspended
- Locally Suspended
- Remotely Suspended
- Locally and Remotely Suspended
- Requests to locally suspend a call which is already locally suspended should be ignored by the CCS provider.
CC_SUSPEND_IND
Parameters
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
- For Q.764 conforming CCS providers, suspend can be requested by independently either via local provider or the
remote provider. A call can be:
- Not Suspended
- Locally Suspended
- Remotely Suspended
- Locally and Remotely Suspended
- Indications of remote suspension of a call which is already remotely suspended will not be issued by the CCS provider.
CC_SUSPEND_RES
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_SUSPEND_RES in the CCS_WRES_SUSIND or CCS_SUSPENDED states, the CCS provider should ignore
the CC_SUSPEND_RES primitive and move directly to the CCS_SUSPENDED state if it has not already done so.
CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ in the CCS_WRES_SUSIND or CCS_SUSPENDED states, the CCS provider should
reply with a CC_ERROR_ACK primitive with error CCNOTSUPP.
CC_RESUME_REQ
Parameters
Rules
CC_RESUME_IND
Parameters
Rules
CC_RESUME_RES
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_RESUME_RES in the CCS_WRES_SUSIND or CCS_ANSWERED states, the CCS provider should ignore the
CC_RESUME_RES primitive and move directly to the CCS_RESUMEED state if it has not already done so.
CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ in the CCS_WRES_SUSIND or CCS_ANSWERED states, the CCS provider should
reply with a CC_ERROR_ACK primitive with error CCNOTSUPP.
Call Termination Primitives
CC_REJECT_REQ
Rules
Rules for issuing primitive:
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_REJECT_REQ in the CCS_WRES_SIND (CCS_ICC_WAIT_COT or CCS_ICC_WAIT_ACM) states, the provider
should perform an automatic release procedure and move to the CCS_WAIT_RLC state.
CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Indicates the cause of the failure. The cc_cause can have one of the following values:
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_COT_FAILURE- Indicates that the continuity check on the circuit failed. This applies to incoming calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RESETISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RECV_RLC- Indicates that the circuit was not completely released by the distant end. This applies to incoming calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_BLOCKING- Indicates that the circuit was blocked during call setup. This applies to incoming calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T2_TIMEOUTISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T3_TIMEOUTISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T6_TIMEOUT- Indicates that the call was suspended beyond the allowable period. This applies to all established calls.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T7_TIMEOUT- Indicates that there was no response to the call setup request. This applies to outgoing calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T8_TIMEOUT- Indicates that the call failed waiting for a continuity check report from the distant end. This applies to incoming
calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T9_TIMEOUT- Indicates that the call failed while waiting for the distant end to answer. This applies to outgoing calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T35_TIMEOUT- Indicates that additional information (digits) were not received from the caller within a sufficient period. This
applies to incoming calls only.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T38_TIMEOUT- Indicates that the call was suspended beyond the allowable period. This applies to all established calls.
ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_CIRCUIT_BUSY
Rules
CC_DISCONNECT_REQ
Rules
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS providers conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider receives a CC_DISCONNECT_REQ, the provider should respond with CC_ERROR_ACK with the error CCNOTSUPP.
CC_RELEASE_REQ
Parameters
cc_cause- Indicates the cause of the release. Cause can be one of the following values:
CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_USER_BUSY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT- (no description)
CC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_REDIRECT- (no description)
CC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR- (no description)
CC_CAUS_INTERWORKING- (no description)
CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER- (no description)
CC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP- (no description)
CC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR- (no description)
CC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26- (no description)
CC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION- (no description)
CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED- (no description)
CC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE- (no description)
CC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS- (no description)
Rules
CC_RELEASE_IND
Parameters
cc_cause- Indicates the cause of the release. Cause can be one of the cause value listed in this addendum under CC_RELEASE_REQ.
Rules
Management Primitives
CC_RESTART_REQ
Rules
For compatibility between CCS providers conforming to Q.931 and CCS provider conforming to Q.764, if the CCS
provider conforming to Q.764 receives a CC_RESTART_REQ, the provider should respond with CC_ERROR_ACK with the error
CCNOTSUPP.
CC_RESET_REQ
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_RESET_IND
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_RESET_RES
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_RESET_CON
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_BLOCKING_REQ
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_BLOCKING_IND
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_BLOCKING_RES
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_BLOCKING_CON
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_UNBLOCKING_IND
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_UNBLOCKING_RES
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_UNBLOCKING_CON
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that
any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit
group identifier.
ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTEDISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED- When one of these flags is set it indicates that either maintenance oriented or hardware failure oriented blocking
is to be performed. If both or neither of these flags are set, the primitive will fail with error
CCBADFLAG.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_QUERY_REQ
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_QUERY_IND
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_QUERY_RES
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
CC_QUERY_CON
Parameters
cc_flags- Indicates the options flags.
ISUP_GROUP- When set, this flag indicates that the operation is to be performed on a group of call control addresses and that any circuit identifier in the specified call control address is to be interpreted by the CCS provider as a circuit group identifier.
cc_addr_length- Indicates the length of the address which consists of a circuit identifier.
cc_addr_offset- Indicates the offset of the address from the start of the block.
Rules
Q.764 Header File Listing
/*
* ISUP addresss
*/
typedef struct isup_addr {
cc_ulong scope; /* the scope of the identifier */
cc_ulong id; /* the identifier within the scope */
cc_ulong cic; /* circuit identification code within the scope */
} isup_addr_t;
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CT 1 /* circuit scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CG 2 /* circuit group scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_TG 3 /* trunk group scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_SR 4 /* signalling relation scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_SP 5 /* signalling point scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_DF 6 /* default scope */
#define ISUP_SCOPE_CIC 7 /* for unidentified cic addresses */
/*
* Definitions for CCI for Q.764 Conforming CCS Providers.
*/
enum {
ISUP_INCOMING_INTERNATIONAL_EXCHANGE = 0x00000001UL,
ISUP_SUSPEND_NATIONALLY_PERFORMED = 0x00000002UL,
};
enum {
CMS_IDLE = 0,
CMS_WCON_BLREQ,
CMS_WRES_BLIND,
CMS_WACK_BLRES,
CMS_WCON_UBREQ,
CMS_WRES_UBIND,
CMS_WACK_UBRES,
CMS_WCON_RESREQ,
CMS_WRES_RESIND,
CMS_WACK_RESRES,
CMS_WCON_QRYREQ,
CMS_WRES_QRYIND,
CMS_WACK_QRYRES,
};
enum {
CKS_IDLE = 0,
CKS_WIND_CONT,
CKS_WRES_CONT,
CKS_WIND_CTEST,
CKS_WREQ_CTEST,
CKS_WIND_CCREP,
CKS_WREQ_CCREP,
CKS_WCON_RELREQ,
CKS_WRES_RELIND,
};
/*
* Circuit States:
*/
#define CTS_ICC 0x00000010
#define CTS_OGC 0x00000020
#define CTS_COT 0x00000040
#define CTS_LPA 0x00000080
#define CTS_COR 0x00000100
#define CTS_MASK 0x0000000f
#define CTS_DIRECTION(__val) (__val & (CTS_ICC|CTS_OGC))
#define CTS_CONT_CHECK(__val) (__val & (CTS_COT|CTS_LPA|CTS_COR))
#define CTS_MESSAGE(__val) (__val & CTS_MASK)
#define CTS_IDLE 0x00000000
#define CTS_WAIT_IAM 0x00000001
#define CTS_WAIT_CCR 0x00000002
#define CTS_WAIT_LPA 0x00000003
#define CTS_WAIT_SAM 0x00000004
#define CTS_WAIT_ACM 0x00000005
#define CTS_WAIT_ANM 0x00000006
#define CTS_ANSWERED 0x00000007
#define CTS_SUSPENDED 0x00000008
#define CTS_WAIT_RLC 0x00000009
#define CTS_SEND_RLC 0x0000000a
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_COT_CCR ( CTS_ICC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_COT_CCR ( CTS_OGC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_LPA_CCR ( CTS_ICC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_LPA_CCR ( CTS_OGC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_CCR ( CTS_ICC | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_CCR ( CTS_OGC | CTS_WAIT_CCR )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_COR_SAM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_COR | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_COR_SAM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_COR | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_COT_SAM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_COT_SAM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_LPA_SAM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_LPA_SAM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_SAM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_SAM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_WAIT_SAM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_COR_ACM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_COR | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_COR_ACM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_COR | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_COT_ACM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_COT_ACM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_COT | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_LPA_ACM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_LPA_ACM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_LPA | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_ACM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_ACM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_WAIT_ACM )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_ANM ( CTS_ICC | CTS_WAIT_ANM )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_ANM ( CTS_OGC | CTS_WAIT_ANM )
#define CTS_ICC_ANSWERED ( CTS_ICC | CTS_ANSWERED )
#define CTS_OGC_ANSWERED ( CTS_OGC | CTS_ANSWERED )
#define CTS_ICC_SUSPENDED ( CTS_ICC | CTS_SUSPENDED )
#define CTS_OGC_SUSPENDED ( CTS_OGC | CTS_SUSPENDED )
#define CTS_ICC_WAIT_RLC ( CTS_ICC | CTS_WAIT_RLC )
#define CTS_OGC_WAIT_RLC ( CTS_OGC | CTS_WAIT_RLC )
#define CTS_ICC_SEND_RLC ( CTS_ICC | CTS_SEND_RLC )
#define CTS_OGC_SEND_RLC ( CTS_OGC | CTS_SEND_RLC )
/*
* Circuit, Group and MTP Flags
*/
#define CCTF_LOC_M_BLOCKED 0x00000001UL
#define CCTF_REM_M_BLOCKED 0x00000002UL
#define CCTF_LOC_H_BLOCKED 0x00000004UL
#define CCTF_REM_H_BLOCKED 0x00000008UL
#define CCTF_LOC_M_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00000010UL
#define CCTF_REM_M_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00000020UL
#define CCTF_LOC_H_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00000040UL
#define CCTF_REM_H_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00000080UL
#define CCTF_LOC_M_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00000100UL
#define CCTF_REM_M_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00000200UL
#define CCTF_LOC_H_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00000400UL
#define CCTF_REM_H_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00000800UL
#define CCTF_LOC_RESET_PENDING 0x00001000UL
#define CCTF_REM_RESET_PENDING 0x00002000UL
#define CCTF_LOC_QUERY_PENDING 0x00004000UL
#define CCTF_REM_QUERY_PENDING 0x00008000UL
#define CCTF_ORIG_SUSPENDED 0x00010000UL
#define CCTF_TERM_SUSPENDED 0x00020000UL
#define CCTF_UPT_PENDING 0x00040000UL
#define CCTF_LOC_S_BLOCKED 0x00080000UL
#define CCTF_LOC_G_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00100000UL
#define CCTF_REM_G_BLOCK_PENDING 0x00200000UL
#define CCTF_LOC_G_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00400000UL
#define CCTF_REM_G_UNBLOCK_PENDING 0x00800000UL
#define CCTF_COR_PENDING 0x01000000UL
#define CCTF_COT_PENDING 0x02000000UL
#define CCTF_LPA_PENDING 0x04000000UL
#define CCTM_OUT_OF_SERVICE ( \
CCTF_LOC_S_BLOCKED | \
CCTF_REM_M_BLOCKED | \
CCTF_REM_H_BLOCKED | \
CCTF_REM_M_BLOCK_PENDING | \
CCTF_REM_H_BLOCK_PENDING | \
CCTF_REM_G_BLOCK_PENDING | \
CCTF_LOC_RESET_PENDING | \
CCTF_REM_RESET_PENDING | \
0 \
)
#define CCTM_CONT_CHECK ( \
CCTF_COR_PENDING | \
CCTF_COT_PENDING | \
CCTF_LPA_PENDING | \
0 \
)
/*
Cause values for CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND
*/
/*
Cause values -- Q.764 conforming
*/
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_DUAL_SIEZURE 1UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_RESET 2UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_BLOCKING 3UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_T24_TIMEOUT 4UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_UNEXPECTED 5UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_COT_FAILURE 6UL
#define ISUP_REATTEMPT_CIRCUIT_BUSY 7UL
/*
Call types for CC_SETUP_REQ and CC_SETUP_IND
*/
/*
Call types -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH 0x00000000UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED 0x00000002UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO 0x00000003UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_PREFERRED 0x00000006UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED 0x00000007UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED 0x00000008UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED 0x00000009UL
#define ISUP_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED 0x0000000aUL
/*
Call flags for CC_SETUP_REQ and CC_SETUP_IND
*/
/*
Call flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_NCI_ONE_SATELLITE_CCT 0x00000001UL
#define ISUP_NCI_TWO_SATELLITE_CCT 0x00000002UL
#define ISUP_NCI_SATELLITE_MASK 0x00000003UL
#define ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED 0x00000004UL
#define ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUS 0x00000008UL
#define ISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_MASK 0x0000000cUL
#define ISUP_NCI_OG_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE 0x00000010UL
/*
Call flags for CC_SETUP_REQ and CC_SETUP_IND
*/
/*
Call flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_FCI_INTERNATIONAL_CALL 0x00000100UL
#define ISUP_FCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAIL 0x00000200UL
#define ISUP_FCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00000400UL
#define ISUP_FCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED 0x00000800UL
#define ISUP_FCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE 0x00001000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY 0x00002000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_ISDN_USER_PART_NOT_REQUIRED 0x00004000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_ISDN_USER_PART_REQUIRED 0x00008000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_ORIGINATING_ACCESS_ISDN 0x00010000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00020000UL
#define ISUP_FCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00040000UL
/*
Call flags for CC_SETUP_REQ and CC_SETUP_IND
*/
/*
Call flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_CPC_MASK 0xff000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_UNKNOWN 0x00000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_FRENCH 0x01000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_ENGLISH 0x02000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_GERMAN 0x03000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_RUSSIAN 0x04000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_SPANISH 0x05000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_LANGUAGE_6 0x06000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_LANGUAGE_7 0x07000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_LANGUAGE_8 0x08000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_OPERATOR_CODE_9 0x09000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_SUBSCRIBER_ORDINARY 0x0a000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_SUBSCRIBER_PRIORITY 0x0b000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_VOICE_BAND_DATA 0x0c000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_TEST_CALL 0x0d000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_SPARE 0x0e000000UL
#define ISUP_CPC_PAYPHONE 0x0f000000UL
/*
Flags for CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ and CC_CONT_REPORT_IND
*/
/*
Flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_COT_FAILURE 0x00000000UL
#define ISUP_COT_SUCCESS 0x00000001UL
/*
Flags for CC_PROCEEDING, CC_ALERTING, CC_PROGRESS, CC_IBI
*/
/*
Flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_BCI_NO_CHARGE 0x00000001UL
#define ISUP_BCI_CHARGE 0x00000002UL
#define ISUP_BCI_CHARGE_MASK 0x00000003UL
#define ISUP_BCI_SUBSCRIBER_FREE 0x00000004UL
#define ISUP_BCI_CONNECT_FREE 0x00000008UL
#define ISUP_BCI_CPS_MASK 0x0000000cUL
#define ISUP_BCI_ORDINARY_SUBSCRIBER 0x00000010UL
#define ISUP_BCI_PAYPHONE 0x00000020UL
#define ISUP_BCI_CPI_MASK 0x00000030UL
#define ISUP_BCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAIL 0x00000040UL
#define ISUP_BCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00000080UL
#define ISUP_BCI_E2E_MASK 0x000000c0UL
#define ISUP_BCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED 0x00000100UL
#define ISUP_BCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE 0x00000200UL
#define ISUP_BCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY 0x00000400UL
#define ISUP_BCI_HOLDING_REQUESTED 0x00000800UL
#define ISUP_BCI_TERMINATING_ACCESS_ISDN 0x00001000UL
#define ISUP_BCI_IC_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE 0x00002000UL
#define ISUP_BCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00004000UL
#define ISUP_BCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLE 0x00008000UL
#define ISUP_BCI_SCCP_METHOD_MASK 0x0000c000UL
#define ISUP_OBCI_INBAND_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE 0x00010000UL
#define ISUP_OBCI_CALL_DIVERSION_MAY_OCCUR 0x00020000UL
#define ISUP_OBCI_ADDITIONAL_INFO_IN_SEG 0x00040000UL
#define ISUP_OBCI_MLPP_USER 0x00080000UL
/*
Events for CC_PROGRESS_REQ and CC_PROGRESS_IND
*/
/*
Events -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_EVNT_PRES_RESTRICT 0x80
#define ISUP_EVNT_ALERTING 0x01 /* alerting */
#define ISUP_EVNT_PROGRESS 0x02 /* progress */
#define ISUP_EVNT_IBI 0x03 /* in-band info or approp pattern
avail */
#define ISUP_EVNT_CFB 0x04 /* call forwarded busy */
#define ISUP_EVNT_CFNA 0x05 /* call forwarded no reply */
#define ISUP_EVNT_CFU 0x06 /* call forwarded unconditional */
#define ISUP_EVNT_MASK 0x7f
/*
Cause values CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_COT_FAILURE 1UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RESET 2UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RECV_RLC 3UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_BLOCKING 4UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T2_TIMEOUT 5UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T3_TIMEOUT 6UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T6_TIMEOUT 7UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T7_TIMEOUT 8UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T8_TIMEOUT 9UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T9_TIMEOUT 10UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T35_TIMEOUT 11UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T38_TIMEOUT 12UL
#define ISUP_CALL_FAILURE_CIRCUIT_BUSY 13UL
/*
* Q.850 Cause Values
*/
/*
Normal class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER 1 /* Unallocated (unassigned)
number */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK 2 /* No route to specified transit
network */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION 3 /* No route to destination */
#define CC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE 4 /* Send special information tone */
#define CC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX 5 /* Misdialled trunk prefix */
#define CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION 8 /* Preemption */
#define CC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED 9 /* Preemption - circuit reserved
for reuse */
#define CC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING 16 /* Normal call clearing */
#define CC_CAUS_USER_BUSY 17 /* User busy */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING 18 /* No user responding */
#define CC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER 19 /* No answer from user (user
alerted) */
#define CC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT 20 /* Subscriber absent */
#define CC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED 21 /* Call rejected */
#define CC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED 22 /* Number changed */
#define CC_CAUS_REDIRECT 23 /* Redirect to new destination */
#define CC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER 27 /* Desitination out of order */
#define CC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE 28 /* Invalid number format (address
incomplete) */
#define CC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED 29 /* Facility rejected */
#define CC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED 31 /* Normal unspecified */
/*
Resource Unavailable Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE 34 /* No circuit/channel available */
#define CC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER 38 /* Network out of order */
#define CC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE 41 /* Temporary failure */
#define CC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION 42 /* Switching equipment congestion
*/
#define CC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED 43 /* Access information discarded */
#define CC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE 44 /* Requested circuit/channel not
available */
#define CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED 46 /* Precedence call blocked */
#define CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE 47 /* Resource unavailable,
unspecified */
/*
Service or Option Unavaialble Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED 50 /* Requested facility not
subscribed */
#define CC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG 53 /* Outgoing calls barred within
CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG 55 /* Incoming calls barred within
CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED 57 /* Bearer capability not
authorized */
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE 58 /* Bearer capability not
presently available */
#define CC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY 62 /* Inconsistency in designated
outgoing access information
and subscriber class */
#define CC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE 63 /* Service or option not
available, unspecified */
/*
Service or Option Not Implemented Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 65 /* Bearer capability not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 69 /* Requested facility not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY 70 /* Only restricted digital
information bearer capability
is available */
#define CC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 79 /* Service or option not
implemented, unspecified */
/*
Invalid Message (e.g., Parameter out of Range) Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG 87 /* User not member of CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION 88 /* Incompatible destination */
#define CC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG 90 /* Non-existent CUG */
#define CC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION 91 /* Invalid transit network
selection */
#define CC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE 95 /* Invalid message, unspecified */
/*
Protocol Error (e.g., Unknwon Message) Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 97 /* Message typ non-existent or
not implemented. */
#define CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED 99 /* Information element/Parameter
non-existent or not
implemented */
#define CC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY 102 /* Recovery on timer expiry */
#define CC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON 103 /* Parameter non-existent or not
implemented - passed on */
#define CC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED 110 /* Message with unrecognized
parameter discarded */
#define CC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR 111 /* Protocol error, unspecified */
/*
Interworking Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_INTERWORKING 127 /* Interworking, unspecified */
/*
* ANSI Standard Causes
*/
/*
Normal Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER 23 /* Unallocated destination number
*/
#define CC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP 24 /* Unknown business group */
#define CC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR 25 /* Exchange routing error */
#define CC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26 /* Misrouted call to a ported
number */
#define CC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND 27 /* Number portability Query on
Release (QoR) number not
found. */
/*
Resource Unavailable Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_RESOURCE_PREEMPTION 45 /* Preemption. */
#define CC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED 46 /* Precedence call blocked. */
/*
Service or Option Not Available Class
*/
#define CC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE 51 /* Call type incompatible with
service request */
#define CC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS 54 /* Call blocked due to group
restrictions */
/*
Management flags -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_GROUP 0x00010000UL
#define ISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTED 0x00000000UL
#define ISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED 0x00000001UL
#define ISUP_SRIS_MASK 0x3
#define ISUP_SRIS_NETWORK_INITIATED 0x1
#define ISUP_SRIS_USER_INITIATED 0x2
/*
Maintenance indications -- Q.764 Conforming
*/
#define ISUP_MAINT_T5_TIMEOUT 3UL /* Q.752 12.5 on occrence */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T13_TIMEOUT 4UL /* Q.752 12.16 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T15_TIMEOUT 5UL /* Q.752 12.17 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T17_TIMEOUT 6UL /* Q.752 12.1 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T19_TIMEOUT 7UL /* Q.752 12.18 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T21_TIMEOUT 8UL /* Q.752 12.19 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T23_TIMEOUT 9UL /* Q.752 12.2 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_T25_TIMEOUT 10UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_T26_TIMEOUT 11UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_T27_TIMEOUT 12UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_T28_TIMEOUT 13UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_T36_TIMEOUT 14UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEXPECTED_CGBA 15UL /* Q.752 12.12 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEXPECTED_CGUA 16UL /* Q.752 12.13 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEXPECTED_MESSAGE 17UL /* Q.752 12.21 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEQUIPPED_CIC 18UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_SEGMENTATION_DISCARDED 19UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_UNEQUIPPED 20UL
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_UNAVAILABLE 21UL /* Q.752 10.1, 10.8 on occrence */
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_AVAILABLE 22UL /* Q.752 10.3, 10.9 on occrence */
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_MAN_MADE_BUSY 23UL /* Q.752 10.2 on occrence */ /* XXX
*/
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_CONGESTED 24UL /* Q.752 10.5, 10.11 on occrence */
#define ISUP_MAINT_USER_PART_UNCONGESTED 25UL /* Q.752 10.6, 10.12 on occrence */
#define ISUP_MAINT_MISSING_ACK_IN_CGBA 26UL /* Q.752 12.8 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_MISSING_ACK_IN_CGUA 27UL /* Q.752 12.9 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_ABNORMAL_ACK_IN_CGBA 28UL /* Q.752 12.10 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_ABNORMAL_ACK_IN_CGUA 29UL /* Q.752 12.11 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEXPECTED_BLA 30UL /* Q.752 12.14 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_UNEXPECTED_UBA 31UL /* Q.752 12.15 1st and delta */
#define ISUP_MAINT_RELEASE_UNREC_INFO 32UL /* Q.752 12.22 1st and delta */ /* XXX
*/
#define ISUP_MAINT_RELEASE_FAILURE 33UL /* Q.752 12.23 1st and delta */ /* XXX
*/
#define ISUP_MAINT_MESSAGE_FORMAT_ERROR 34UL /* Q.752 12.20 1st and delta */ /* XXX
Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformance
This addendum describes the formats and rules that are specific to ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2. The addendum must be used along with the generic CCI as defined in the main document, and the Q.764 conformance defined in Addendum for Q.764 Conformance. when implementing a CCS provider that will be configured with the EN 300 356-1 call processing layer.
Primitives and Rules for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformance
The following are the additional rules that apply to the CCI primitives for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 compatibility.
Local Management Primitives
Call Setup Primitives
CC_SETUP_REQ
Parameters
Flags
Rules
CC_SETUP_IND
Parameters
cc_call_type- Specifies the call type to be set up. In addition to Q.764 values, for EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 conforming CCS providers, the call type can also be one of the values listed under "Call Type" below.
Call Type
The following call types are defined for EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 conforming CCS providers in addition to the Q.931 values shown in Addendum for Q.931 Conformance.
CC_CALL_TYPE_3x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 3 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 3 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_4x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 4 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 4 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_5x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 5 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 5 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_6x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 6 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of 384 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type can be
synonymous with CC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
CC_CALL_TYPE_7x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 7 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 7 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_8x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 8 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 8 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_9x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 9 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 9 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_10x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 10 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 10 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_11x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 11 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 11 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_12x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 12 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 12 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_13x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 13 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 13 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_14x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 14 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 14 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_15x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 15 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 15 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_16x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 16 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 16 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_17x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 17 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 17 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_18x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 18 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 28 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_19x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 19 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 19 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_20x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 20 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 20 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_21x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 21 x 64 kbit/s
unrestricted digital information". The call type is 21 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information.
CC_CALL_TYPE_22x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 22 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 22 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_23x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 23 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 23 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_24x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 24 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "1536 kbit/s unrestricted digital information". This call type can be
synonymous with CC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
CC_CALL_TYPE_25x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 25 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 25 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_26x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 26 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 26 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_27x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 27 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 27 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_28x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 28 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1
V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "reserved for 28 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information".
CC_CALL_TYPE_29x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED- The call type is 29 x 64 kbit/s unrestricted digital information. This call type corresponds to a EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 transmission medium requirement of "1920 kbit/s unrestricted digital information". This call type can be synonymous with CC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED.
Rules
Rules for call type:
- Only multi-rate connection types for 384 kbit/s (6 x 64 kbit/s), 1536 kbit/s (24 x 64 kbit/s) and 1920 kbit/s (29 x 64 kbit/s) are supported. For EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 compliant CCS providers.
ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Header File Listing
Appendix A Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931
The mapping of CCI primitives to Q.931 primitives is shown in Table 2. For the most part, this mapping is a one to one mapping of service primitives, with the exception of Setup Response and Setup Confirm.

In Q.931 the Setup Response and Setup Confirm primitives and issued only once the voice channel is
connected. In OpenSS7 CCI, the CC_SETUP_RES and CC_SETUP_CON primitives are used to accept the addressing and
assign a stream and correspond to the first backward message (i.e, Processing, Alerting or
Progress Request or Indication; and Setup Indication or Confirm).
Appendix B Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764
The mapping of CCI primitives to Q.764 primitives is shown in Table 3. For the most part this is a one to one mapping of service primitives, with the exception of Setup Response and Setup Confirm.

In Q.764 the Setup Response and Setup Confirm primitives and issued only once the voice channel is
connected. In OpenSS7 CCI, the CC_SETUP_RES and CC_SETUP_CON primitives are used to accept the addressing and
assign a stream and correspond to the first backward message (i.e, Processing, Alerting or
Progress Request or Indication; and Setup Indication or Confirm).
Appendix C State/Event Tables
Appendix D Primitive Precedence Tables
Appendix E CCI Header File Listing
typedef lmi_long cc_long;
typedef lmi_ulong cc_ulong;
typedef lmi_ushort cc_ushort;
typedef lmi_uchar cc_uchar;
#define CC_INFO_REQ 0
#define CC_OPTMGMT_REQ 1
#define CC_BIND_REQ 2
#define CC_UNBIND_REQ 3
#define CC_ADDR_REQ 4
#define CC_SETUP_REQ 5
#define CC_MORE_INFO_REQ 6 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_INFORMATION_REQ 7
#define CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ 8 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_CONT_TEST_REQ 9 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ 10 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_SETUP_RES 11
#define CC_PROCEEDING_REQ 12
#define CC_ALERTING_REQ 13
#define CC_PROGRESS_REQ 14
#define CC_IBI_REQ 15 /* (same as CC_DISCONNECT_REQ in ISDN) */
#define CC_DISCONNECT_REQ 15
#define CC_CONNECT_REQ 16
#define CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ 17 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_FORWXFER_REQ 18 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_SUSPEND_REQ 19
#define CC_SUSPEND_RES 20 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ 21 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESUME_REQ 22
#define CC_RESUME_RES 23 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ 24 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_REJECT_REQ 25 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RELEASE_REQ 26
#define CC_RELEASE_RES 27 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_NOTIFY_REQ 28 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESTART_REQ 29 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESET_REQ 30 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_RESET_RES 31 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_BLOCKING_REQ 32 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_BLOCKING_RES 33 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ 34 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_UNBLOCKING_RES 35 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_QUERY_REQ 36 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_QUERY_RES 37 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_STOP_REQ 38 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_OK_ACK 64
#define CC_ERROR_ACK 65
#define CC_INFO_ACK 66
#define CC_BIND_ACK 67
#define CC_OPTMGMT_ACK 68
#define CC_ADDR_ACK 69
#define CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND 70 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_SETUP_IND 71 /* recv IAM */
#define CC_MORE_INFO_IND 72 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_INFORMATION_IND 73 /* recv SAM */
#define CC_CONT_CHECK_IND 74 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_CONT_TEST_IND 75 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_CONT_REPORT_IND 76 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_SETUP_CON 77
#define CC_PROCEEDING_IND 78 /* recv ACM w/ no indication if proceeding not
sent before */
#define CC_ALERTING_IND 79 /* recv ACM w/ subscriber free indication */
#define CC_PROGRESS_IND 80 /* recv ACM w/ no indication and ATP parameter
and call proceeding sent */
#define CC_IBI_IND 81 /* recv ACM or CPG w/ inband info (same as
CC_DISCONNECT_IND in ISDN) */
#define CC_DISCONNECT_IND 81
#define CC_CONNECT_IND 82
#define CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND 83 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_FORWXFER_IND 84 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_SUSPEND_IND 85
#define CC_SUSPEND_CON 86 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND 87 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESUME_IND 88
#define CC_RESUME_CON 89 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND 90 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_REJECT_IND 91 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND 92 /* ISUP only (ERROR_IND?) */
#define CC_RELEASE_IND 93
#define CC_RELEASE_CON 94
#define CC_NOTIFY_IND 95 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_RESTART_CON 96 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_STATUS_IND 97 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_ERROR_IND 98 /* ISDN only (CALL_FAILURE_IND?) */
#define CC_DATALINK_FAILURE_IND 99 /* ISDN only */
#define CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND 100
#define CC_RESET_IND 101 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_RESET_CON 102 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_BLOCKING_IND 103 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_BLOCKING_CON 104 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_UNBLOCKING_IND 105 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_UNBLOCKING_CON 106 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_QUERY_IND 107 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_QUERY_CON 108 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_STOP_IND 109 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_MAINT_IND 110 /* ISUP only */
#define CC_START_RESET_IND 111 /* ISUP only */
/*
* Interface state
*/
enum {
CCS_UNBND,
CCS_IDLE,
CCS_WIND_SETUP,
CCS_WREQ_SETUP,
CCS_WREQ_MORE,
CCS_WIND_MORE,
CCS_WREQ_INFO,
CCS_WIND_INFO,
CCS_WACK_INFO,
CCS_WCON_SREQ,
CCS_WRES_SIND,
CCS_WREQ_CCREP,
CCS_WIND_CCREP,
CCS_WREQ_PROCEED,
CCS_WIND_PROCEED,
CCS_WACK_PROCEED,
CCS_WREQ_ALERTING,
CCS_WIND_ALERTING,
CCS_WACK_ALERTING,
CCS_WREQ_PROGRESS,
CCS_WIND_PROGRESS,
CCS_WACK_PROGRESS,
CCS_WREQ_IBI,
CCS_WIND_IBI,
CCS_WACK_IBI,
CCS_WREQ_CONNECT,
CCS_WIND_CONNECT,
CCS_WCON_CREQ,
CCS_WACK_FORWXFER,
CCS_WCON_SUSREQ,
CCS_CONNECTED,
CCS_SUSPENDED,
CCS_WIND_RELEASE,
CCS_WCON_RELREQ,
CCS_WRES_RELIND,
CCS_UNUSABLE,
};
typedef struct CC_ok_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OK_ACK */
cc_ulong cc_correct_prim; /* primitive being acknowledged */
cc_ulong cc_state; /* current state */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_ok_ack_t;
typedef struct CC_error_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ERROR_ACK */
cc_ulong cc_error_primitive; /* primitive in error */
cc_ulong cc_error_type; /* CCI error code */
cc_ulong cc_unix_error; /* UNIX system error code */
cc_ulong cc_state; /* current state */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_error_ack_t;
enum {
CCSYSERR = 0,
CCOUTSTATE,
CCBADADDR,
CCBADDIGS,
CCBADOPT,
CCNOADDR,
CCADDRBUSY,
CCBADCLR,
CCBADTOK,
CCBADFLAG,
CCNOTSUPP,
CCBADPRIM,
CCACCESS,
};
typedef struct CC_info_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_REQ */
} CC_info_req_t;
typedef struct CC_info_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_ACK */
/* FIXME ... more ... */
} CC_info_ack_t;
typedef struct CC_bind_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BIND_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* offset of address */
cc_ulong cc_setup_ind; /* req # of setup inds to be queued */
cc_ulong cc_bind_flags; /* bind options flags */
} CC_bind_req_t;
/*
Flags associated with CC_BIND_REQ
*/
#define CC_DEFAULT_LISTENER 0x000000001UL
#define CC_TOKEN_REQUEST 0x000000002UL
#define CC_MANAGEMENT 0x000000004UL
#define CC_TEST 0x000000008UL
#define CC_MAINTENANCE 0x000000010UL
#define CC_MONITOR 0x000000020UL
typedef struct CC_bind_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BIND_ACK */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* offset of address */
cc_ulong cc_setup_ind; /* setup indications */
cc_ulong cc_token_value; /* setup response token value */
} CC_bind_ack_t;
typedef struct CC_unbind_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBIND_REQ */
} CC_unbind_req_t;
typedef struct CC_addr_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ADDR_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_addr_req_t;
typedef struct CC_addr_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ADDR_ACK */
cc_ulong cc_bind_length; /* length of bound address */
cc_ulong cc_bind_offset; /* offset of bound address */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_conn_length; /* length of connected address */
cc_ulong cc_conn_offset; /* offset of connected address */
} CC_addr_ack_t;
typedef struct CC_optmgmt_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OPTMGMT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* length of option values */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* offset of option values */
cc_ulong cc_opt_flags; /* option flags */
} CC_optmgmt_req_t;
typedef struct CC_optmgmt_ack {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_OPTMGMT_ACK */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* length of option values */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* offset of option values */
cc_ulong cc_opt_flags; /* option flags */
} CC_optmgmt_ack_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_type; /* call type */
cc_ulong cc_call_flags; /* call flags */
cc_ulong cc_cdpn_length; /* called party number length */
cc_ulong cc_cdpn_offset; /* called party number offset */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameters length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameters offset */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* connect to address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connect to address offset */
} CC_setup_req_t;
typedef struct CC_call_reattempt_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_reason; /* reason for reattempt */
} CC_call_reattempt_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_type; /* call type */
cc_ulong cc_call_flags; /* call flags */
cc_ulong cc_cdpn_length; /* called party number length */
cc_ulong cc_cdpn_offset; /* called party number offset */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameters length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameters offset */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* connecting address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connecting address offset */
} CC_setup_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_RES */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_token_value; /* call response token value */
} CC_setup_res_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_CON */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* connecting address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* connecting address offset */
} CC_setup_con_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_check_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adress offset */
} CC_cont_check_req_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_check_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_CHECK_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adress offset */
} CC_cont_check_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_test_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_token_value; /* token value */
} CC_cont_test_req_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_test_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_TEST_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adress offset */
} CC_cont_test_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_report_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_req_t;
typedef struct CC_cont_report_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONT_REPORT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_result; /* result of continuity check */
} CC_cont_report_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_more_info_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MORE_INFO_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_more_info_req_t;
typedef struct CC_more_info_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MORE_INFO_IND */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_more_info_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_information_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFORMATION_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_subn_length; /* subsequent number length */
cc_ulong cc_subn_offset; /* subsequent number offset */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_information_req_t;
typedef struct CC_information_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFORMATION_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_subn_length; /* subsequent number length */
cc_ulong cc_subn_offset; /* subsequent number offset */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_information_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_info_timeout_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_info_timeout_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_proceeding_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROCEEDING_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* proceeding flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_proceeding_req_t;
typedef struct CC_proceeding_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROCEEDING_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* proceeding flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_proceeding_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_alerting_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ALERTING_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* alerting flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_alerting_req_t;
typedef struct CC_alerting_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ALERTING_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* alerting flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_alerting_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_progress_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROGRESS_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_event; /* progress event */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* progress flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_progress_req_t;
typedef struct CC_progress_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_PROGRESS_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_event; /* progress event */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* progress flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_progress_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_ibi_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_IBI_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* ibi flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_ibi_req_t;
typedef struct CC_ibi_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_IBI_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* ibi flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_ibi_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_connect_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONNECT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* connect flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_connect_req_t;
typedef struct CC_connect_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CONNECT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* connect flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_connect_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_complete_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_setup_complete_req_t;
typedef struct CC_setup_complete_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_setup_complete_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_forwxfer_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_FORWXFER_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_forwxfer_req_t;
typedef struct CC_forwxfer_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_FORWXFER_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_forwxfer_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_req_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_RES */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_res_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_CON */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_con_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_reject_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_reject_req_t;
typedef struct CC_suspend_reject_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_suspend_reject_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_req_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* suspend flags */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_RES */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_res_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_CON */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_con_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_reject_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_reject_req_t;
typedef struct CC_resume_reject_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESUME_REJECT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_resume_reject_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_reject_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_REJECT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_reject_req_t;
typedef struct CC_reject_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_REJECT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_reject_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_error_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_ERROR_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_error_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_call_failure_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_CALL_FAILURE_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_reason; /* reason for failure */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause to use in release */
} CC_call_failure_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_disconnect_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_DISCONNECT_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_disconnect_req_t;
typedef struct CC_disconnect_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_DISCONNECT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_disconnect_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_release_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_req_t;
typedef struct CC_release_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_IND */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_cause; /* cause value */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_release_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_RES */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_res_t;
typedef struct CC_release_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RELEASE_CON */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_release_con_t;
typedef struct CC_notify_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_NOTIFY_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_notify_req_t;
typedef struct CC_notify_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_NOTIFY_IND */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_opt_length; /* optional parameter length */
cc_ulong cc_opt_offset; /* optional parameter offset */
} CC_notify_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_restart_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESTART_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* restart flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adddress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adddress offset */
} CC_restart_req_t;
typedef struct CC_restart_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESTART_CON */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* restart flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adddress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adddress offset */
} CC_restart_con_t;
typedef struct CC_status_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_STATUS_IND */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* status flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* adddress length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* adddress offset */
} CC_status_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_datalink_failure_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_DATALINK_FAILURE_IND */
cc_ulong cc_user_ref; /* user call reference */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
} CC_datalink_failure_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_reset_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_req_t;
typedef struct CC_reset_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_IND */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_reset_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_RES */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_res_t;
typedef struct CC_reset_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_RESET_CON */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* reset flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_reset_con_t;
typedef struct CC_blocking_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_req_t;
typedef struct CC_blocking_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_IND */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_blocking_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_RES */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_res_t;
typedef struct CC_blocking_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_BLOCKING_CON */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_blocking_con_t;
typedef struct CC_unblocking_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_req_t;
typedef struct CC_unblocking_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_IND */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_unblocking_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_RES */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_res_t;
typedef struct CC_unblocking_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_UNBLOCKING_CON */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* unblocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_unblocking_con_t;
typedef struct CC_query_req {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_REQ */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_req_t;
typedef struct CC_query_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_IND */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_ind_t;
typedef struct CC_query_res {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_RES */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* blocking flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_res_t;
typedef struct CC_query_con {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_QUERY_CON */
cc_ulong cc_flags; /* query flags */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* address length */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* address offset */
} CC_query_con_t;
typedef struct CC_maint_ind {
cc_ulong cc_primitive; /* always CC_MAINT_IND */
cc_ulong cc_reason; /* reason for indication */
cc_ulong cc_call_ref; /* call reference */
cc_ulong cc_addr_length; /* length of address */
cc_ulong cc_addr_offset; /* length of address */
} CC_maint_ind_t;
union CC_primitives {
cc_ulong cc_primitive;
CC_ok_ack_t ok_ack;
CC_error_ack_t error_ack;
CC_info_req_t info_req;
CC_info_ack_t info_ack;
CC_bind_req_t bind_req;
CC_bind_ack_t bind_ack;
CC_unbind_req_t unbind_req;
CC_addr_req_t addr_req;
CC_addr_ack_t addr_ack;
CC_optmgmt_req_t optmgmt_req;
CC_optmgmt_ack_t optmgmt_ack;
CC_setup_req_t setup_req;
CC_call_reattempt_ind_t call_reattempt_ind;
CC_setup_ind_t setup_ind;
CC_setup_res_t setup_res;
CC_setup_con_t setup_con;
CC_cont_check_req_t cont_check_req;
CC_cont_check_ind_t cont_check_ind;
CC_cont_test_req_t cont_test_req;
CC_cont_test_ind_t cont_test_ind;
CC_cont_report_req_t cont_report_req;
CC_cont_report_ind_t cont_report_ind;
CC_more_info_req_t more_info_req;
CC_more_info_ind_t more_info_ind;
CC_information_req_t information_req;
CC_information_ind_t information_ind;
CC_proceeding_req_t proceeding_req;
CC_proceeding_ind_t proceeding_ind;
CC_alerting_req_t alerting_req;
CC_alerting_ind_t alerting_ind;
CC_progress_req_t progress_req;
CC_progress_ind_t progress_ind;
CC_ibi_req_t ibi_req;
CC_ibi_ind_t ibi_ind;
CC_connect_req_t connect_req;
CC_connect_ind_t connect_ind;
CC_setup_complete_req_t setup_complete_req;
CC_setup_complete_ind_t setup_complete_ind;
CC_forwxfer_req_t forwxfer_req;
CC_forwxfer_ind_t forwxfer_ind;
CC_suspend_req_t suspend_req;
CC_suspend_ind_t suspend_ind;
CC_suspend_res_t suspend_res;
CC_suspend_con_t suspend_con;
CC_suspend_reject_req_t suspend_reject_req;
CC_suspend_reject_ind_t suspend_reject_ind;
CC_resume_req_t resume_req;
CC_resume_ind_t resume_ind;
CC_resume_res_t resume_res;
CC_resume_con_t resume_con;
CC_resume_reject_req_t resume_reject_req;
CC_resume_reject_ind_t resume_reject_ind;
CC_reject_req_t reject_req;
CC_reject_ind_t reject_ind;
CC_error_ind_t error_ind;
CC_call_failure_ind_t call_failure_ind;
CC_disconnect_req_t disconnect_req;
CC_disconnect_ind_t disconnect_ind;
CC_release_req_t release_req;
CC_release_ind_t release_ind;
CC_release_res_t release_res;
CC_release_con_t release_con;
CC_restart_req_t restart_req;
CC_restart_con_t restart_con;
CC_status_ind_t status_ind;
CC_datalink_failure_ind_t datalink_failure_ind;
CC_reset_req_t reset_req;
CC_reset_ind_t reset_ind;
CC_reset_res_t reset_res;
CC_reset_con_t reset_con;
CC_blocking_req_t blocking_req;
CC_blocking_ind_t blocking_ind;
CC_blocking_res_t blocking_res;
CC_blocking_con_t blocking_con;
CC_unblocking_req_t unblocking_req;
CC_unblocking_ind_t unblocking_ind;
CC_unblocking_res_t unblocking_res;
CC_unblocking_con_t unblocking_con;
CC_query_req_t query_req;
CC_query_ind_t query_ind;
CC_query_res_t query_res;
CC_query_con_t query_con;
CC_maint_ind_t maint_ind;
};
License
GNU Free Documentation License
Copyright © 2000 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
Preamble
The purpose of this License is to make a manual, textbook, or other written document free in the sense of freedom: to assure everyone the effective freedom to copy and redistribute it, with or without modifying it, either commercially or noncommercially. Secondarily, this License preserves for the author and publisher a way to get credit for their work, while not being considered responsible for modifications made by others.
This License is a kind of “copyleft”, which means that derivative works of the document must themselves be free in the same sense. It complements the GNU General Public License, which is a copyleft license designed for free software.
We have designed this License in order to use it for manuals for free software, because free software needs free documentation: a free program should come with manuals providing the same freedoms that the software does. But this License is not limited to software manuals; it can be used for any textual work, regardless of subject matter or whether it is published as a printed book. We recommend this License principally for works whose purpose is instruction or reference.
- APPLICABILITY AND DEFINITIONS
This License applies to any manual or other work that contains a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it can be distributed under the terms of this License. The “Document”, below, refers to any such manual or work. Any member of the public is a licensee, and is addressed as “you”.
A “Modified Version” of the Document means any work containing the Document or a portion of it, either copied verbatim, or with modifications and/or translated into another language.
A “Secondary Section” is a named appendix or a front-matter section of the Document that deals exclusively with the relationship of the publishers or authors of the Document to the Document's overall subject (or to related matters) and contains nothing that could fall directly within that overall subject. (For example, if the Document is in part a textbook of mathematics, a Secondary Section may not explain any mathematics.) The relationship could be a matter of historical connection with the subject or with related matters, or of legal, commercial, philosophical, ethical or political position regarding them.
The “Invariant Sections” are certain Secondary Sections whose titles are designated, as being those of Invariant Sections, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License.
The “Cover Texts” are certain short passages of text that are listed, as Front-Cover Texts or Back-Cover Texts, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License.
A “Transparent” copy of the Document means a machine-readable copy, represented in a format whose specification is available to the general public, whose contents can be viewed and edited directly and straightforwardly with generic text editors or (for images composed of pixels) generic paint programs or (for drawings) some widely available drawing editor, and that is suitable for input to text formatters or for automatic translation to a variety of formats suitable for input to text formatters. A copy made in an otherwise Transparent file format whose markup has been designed to thwart or discourage subsequent modification by readers is not Transparent. A copy that is not “Transparent” is called “Opaque”.
Examples of suitable formats for Transparent copies include plain ascii without markup, Texinfo input format, LaTeX input format, SGML or XML using a publicly available DTD, and standard-conforming simple HTML designed for human modification. Opaque formats include PostScript, PDF, proprietary formats that can be read and edited only by proprietary word processors, SGML or XML for which the DTD and/or processing tools are not generally available, and the machine-generated HTML produced by some word processors for output purposes only.
The “Title Page” means, for a printed book, the title page itself, plus such following pages as are needed to hold, legibly, the material this License requires to appear in the title page. For works in formats which do not have any title page as such, “Title Page” means the text near the most prominent appearance of the work's title, preceding the beginning of the body of the text.
- VERBATIM COPYING
You may copy and distribute the Document in any medium, either commercially or noncommercially, provided that this License, the copyright notices, and the license notice saying this License applies to the Document are reproduced in all copies, and that you add no other conditions whatsoever to those of this License. You may not use technical measures to obstruct or control the reading or further copying of the copies you make or distribute. However, you may accept compensation in exchange for copies. If you distribute a large enough number of copies you must also follow the conditions in section 3.
You may also lend copies, under the same conditions stated above, and you may publicly display copies.
- COPYING IN QUANTITY
If you publish printed copies of the Document numbering more than 100, and the Document's license notice requires Cover Texts, you must enclose the copies in covers that carry, clearly and legibly, all these Cover Texts: Front-Cover Texts on the front cover, and Back-Cover Texts on the back cover. Both covers must also clearly and legibly identify you as the publisher of these copies. The front cover must present the full title with all words of the title equally prominent and visible. You may add other material on the covers in addition. Copying with changes limited to the covers, as long as they preserve the title of the Document and satisfy these conditions, can be treated as verbatim copying in other respects.
If the required texts for either cover are too voluminous to fit legibly, you should put the first ones listed (as many as fit reasonably) on the actual cover, and continue the rest onto adjacent pages.
If you publish or distribute Opaque copies of the Document numbering more than 100, you must either include a machine-readable Transparent copy along with each Opaque copy, or state in or with each Opaque copy a publicly-accessible computer-network location containing a complete Transparent copy of the Document, free of added material, which the general network-using public has access to download anonymously at no charge using public-standard network protocols. If you use the latter option, you must take reasonably prudent steps, when you begin distribution of Opaque copies in quantity, to ensure that this Transparent copy will remain thus accessible at the stated location until at least one year after the last time you distribute an Opaque copy (directly or through your agents or retailers) of that edition to the public.
It is requested, but not required, that you contact the authors of the Document well before redistributing any large number of copies, to give them a chance to provide you with an updated version of the Document.
- MODIFICATIONS
You may copy and distribute a Modified Version of the Document under the conditions of sections 2 and 3 above, provided that you release the Modified Version under precisely this License, with the Modified Version filling the role of the Document, thus licensing distribution and modification of the Modified Version to whoever possesses a copy of it. In addition, you must do these things in the Modified Version:
- Use in the Title Page (and on the covers, if any) a title distinct from that of the Document, and from those of previous versions (which should, if there were any, be listed in the History section of the Document). You may use the same title as a previous version if the original publisher of that version gives permission.
- List on the Title Page, as authors, one or more persons or entities responsible for authorship of the modifications in the Modified Version, together with at least five of the principal authors of the Document (all of its principal authors, if it has less than five).
- State on the Title page the name of the publisher of the Modified Version, as the publisher.
- Preserve all the copyright notices of the Document.
- Add an appropriate copyright notice for your modifications adjacent to the other copyright notices.
- Include, immediately after the copyright notices, a license notice giving the public permission to use the Modified Version under the terms of this License, in the form shown in the Addendum below.
- Preserve in that license notice the full lists of Invariant Sections and required Cover Texts given in the Document's license notice.
- Include an unaltered copy of this License.
- Preserve the section entitled “History”, and its title, and add to it an item stating at least the title, year, new authors, and publisher of the Modified Version as given on the Title Page. If there is no section entitled “History” in the Document, create one stating the title, year, authors, and publisher of the Document as given on its Title Page, then add an item describing the Modified Version as stated in the previous sentence.
- Preserve the network location, if any, given in the Document for public access to a Transparent copy of the Document, and likewise the network locations given in the Document for previous versions it was based on. These may be placed in the “History” section. You may omit a network location for a work that was published at least four years before the Document itself, or if the original publisher of the version it refers to gives permission.
- In any section entitled “Acknowledgments” or “Dedications”, preserve the section's title, and preserve in the section all the substance and tone of each of the contributor acknowledgments and/or dedications given therein.
- Preserve all the Invariant Sections of the Document, unaltered in their text and in their titles. Section numbers or the equivalent are not considered part of the section titles.
- Delete any section entitled “Endorsements”. Such a section may not be included in the Modified Version.
- Do not retitle any existing section as “Endorsements” or to conflict in title with any Invariant Section.
If the Modified Version includes new front-matter sections or appendices that qualify as Secondary Sections and contain no material copied from the Document, you may at your option designate some or all of these sections as invariant. To do this, add their titles to the list of Invariant Sections in the Modified Version's license notice. These titles must be distinct from any other section titles.
You may add a section entitled “Endorsements”, provided it contains nothing but endorsements of your Modified Version by various parties—for example, statements of peer review or that the text has been approved by an organization as the authoritative definition of a standard.
You may add a passage of up to five words as a Front-Cover Text, and a passage of up to 25 words as a Back-Cover Text, to the end of the list of Cover Texts in the Modified Version. Only one passage of Front-Cover Text and one of Back-Cover Text may be added by (or through arrangements made by) any one entity. If the Document already includes a cover text for the same cover, previously added by you or by arrangement made by the same entity you are acting on behalf of, you may not add another; but you may replace the old one, on explicit permission from the previous publisher that added the old one.
The author(s) and publisher(s) of the Document do not by this License give permission to use their names for publicity for or to assert or imply endorsement of any Modified Version.
- COMBINING DOCUMENTS
You may combine the Document with other documents released under this License, under the terms defined in section 4 above for modified versions, provided that you include in the combination all of the Invariant Sections of all of the original documents, unmodified, and list them all as Invariant Sections of your combined work in its license notice.
The combined work need only contain one copy of this License, and multiple identical Invariant Sections may be replaced with a single copy. If there are multiple Invariant Sections with the same name but different contents, make the title of each such section unique by adding at the end of it, in parentheses, the name of the original author or publisher of that section if known, or else a unique number. Make the same adjustment to the section titles in the list of Invariant Sections in the license notice of the combined work.
In the combination, you must combine any sections entitled “History” in the various original documents, forming one section entitled “History”; likewise combine any sections entitled “Acknowledgments”, and any sections entitled “Dedications”. You must delete all sections entitled “Endorsements.”
- COLLECTIONS OF DOCUMENTS
You may make a collection consisting of the Document and other documents released under this License, and replace the individual copies of this License in the various documents with a single copy that is included in the collection, provided that you follow the rules of this License for verbatim copying of each of the documents in all other respects.
You may extract a single document from such a collection, and distribute it individually under this License, provided you insert a copy of this License into the extracted document, and follow this License in all other respects regarding verbatim copying of that document.
- AGGREGATION WITH INDEPENDENT WORKS
A compilation of the Document or its derivatives with other separate and independent documents or works, in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, does not as a whole count as a Modified Version of the Document, provided no compilation copyright is claimed for the compilation. Such a compilation is called an “aggregate”, and this License does not apply to the other self-contained works thus compiled with the Document, on account of their being thus compiled, if they are not themselves derivative works of the Document.
If the Cover Text requirement of section 3 is applicable to these copies of the Document, then if the Document is less than one quarter of the entire aggregate, the Document's Cover Texts may be placed on covers that surround only the Document within the aggregate. Otherwise they must appear on covers around the whole aggregate.
- TRANSLATION
Translation is considered a kind of modification, so you may distribute translations of the Document under the terms of section 4. Replacing Invariant Sections with translations requires special permission from their copyright holders, but you may include translations of some or all Invariant Sections in addition to the original versions of these Invariant Sections. You may include a translation of this License provided that you also include the original English version of this License. In case of a disagreement between the translation and the original English version of this License, the original English version will prevail.
- TERMINATION
You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Document except as expressly provided for under this License. Any other attempt to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Document is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such parties remain in full compliance.
- FUTURE REVISIONS OF THIS LICENSE
The Free Software Foundation may publish new, revised versions of the GNU Free Documentation License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns. See http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/.
Each version of the License is given a distinguishing version number. If the Document specifies that a particular numbered version of this License “or any later version” applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and conditions either of that specified version or of any later version that has been published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation. If the Document does not specify a version number of this License, you may choose any version ever published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation.
How to use this License for your documents
To use this License in a document you have written, include a copy of the License in the document and put the following copyright and license notices just after the title page:
Copyright (C) year your name.
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document
under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.1
or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation;
with the Invariant Sections being list their titles, with the
Front-Cover Texts being list, and with the Back-Cover Texts being list.
A copy of the license is included in the section entitled ``GNU
Free Documentation License''.
If you have no Invariant Sections, write “with no Invariant Sections” instead of saying which ones are invariant. If you have no Front-Cover Texts, write “no Front-Cover Texts” instead of “Front-Cover Texts being list”; likewise for Back-Cover Texts.
If your document contains nontrivial examples of program code, we recommend releasing these examples in parallel under your choice of free software license, such as the GNU General Public License, to permit their use in free software.
Glossary
- Signalling Data Link Service Data Unit
- A grouping of SDL user data whose boundaries are preserved from one end of the
signalling data link connection to the other.
- Data transfer
- The phase in connection and connectionless modes that supports the transfer of
data between to signalling data link users.
- SDL provider
- The signalling data link layer protocol that provides the services of the
signalling data link interface.
- SDL user
- The user-level application or user-level or kernel-level protocol that accesses
the services of the signalling data link layer.
- Local management
- The phase in connection and connectionless modes in which a SDL user initializes
a stream and attaches a PPA address to the stream. Primitives in this phase
generate local operations only.
- PPA
- The point at which a system attaches itself to a physical communications medium.
- PPA identifier
- An identifier of a particular physical medium over which communication transpires.
Acronyms
| ITU-T | International Telecommunications Union - Telecom Sector
|
| PPA | Physical Point of Attachment
|
| SDLI | Signalling Data Link Interface
|
| SDL SDU | Signalling Data Link Service Data Unit
|
| SDL | Signalling Data Link
|
References
- ITU-T Recommendation X.210, (Geneva, 1993), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Basic reference model: Conventions for the definition of OSI services,” ISO/IEC 10731:1994.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.217, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Service definition for the Association Control Service Element,” ISO/IEC 8649:1996.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.227, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connection-oriented protocol for the Association Control Service Element: Protocol Specification,” ISO/IEC 8650-1.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.237, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connectionless protocol for the Association Control Service Element: Protocol Specification,” ISO/IEC 10035-1 : 1995.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.216, (Geneva, 1994), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Presentation service definition,” ISO/IEC 8822:1994.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.226, (Geneva, 1994), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connection-oriented presentation protocol: Protocol specification,” ISO/IEC 8823-1:1994.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.236, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connectionless presentation protocol: Protocol specification,” ISO/IEC 9576-1:1995.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.215, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Session service definition,” ISO/IEC 8326:1996.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.225, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connection-oriented session protocol: Protocol specification,” ISO/IEC 8327-1:1996.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.235, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Connectionless session protocol: Protocol specification,” ISO/IEC 9548-1:1995.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.214, (Geneva, 1995), “Information Technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Transport service definition,” ISO/IEC 8072:1996.
- ITU-T Recommendation X.224
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.700
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.701
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.702
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.703
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.704
- Geoffrey Gerrien, “CDI - Application Program Interface Guide,” Gcom, Inc., March 1999.
- ITU-T Recommendation Q.771, (Geneva, 1993), “Signalling System No. 7 — Functional description of transaction capabilities,” (White Book).
Index
CC_ADDR_ACK: CCI PrimitivesCC_ADDR_ACK: CCI Services DefinitionCC_addr_ack_t: CCI Primitivescc_addr_length: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_addr_length: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_addr_length: CCI Primitivescc_addr_offset: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_addr_offset: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_addr_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_ADDR_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_ADDR_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_addr_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_ALERTING_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_ALERTING_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_ALERTING_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_ALERTING_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_alerting_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_ALERTING_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_ALERTING_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_ALERTING_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_ALERTING_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_alerting_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_BIND_ACK: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BIND_ACK: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_BIND_ACK: CCI PrimitivesCC_BIND_ACK: CCI Services DefinitionCC_bind_ack_t: CCI Primitivescc_bind_flags: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_bind_flags: CCI Primitivescc_bind_length: CCI Primitivescc_bind_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_BIND_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BIND_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_BIND_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_BIND_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_bind_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_CON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BLOCKING_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_blocking_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BLOCKING_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_blocking_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BLOCKING_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_blocking_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_RES: FootnotesCC_BLOCKING_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_BLOCKING_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_BLOCKING_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_blocking_res_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CALL_FAILURE_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_call_failure_ind_t: CCI Primitivescc_call_flags: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_call_flags: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_call_flags: CCI PrimitivesCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CALL_REATTEMPT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_call_reattempt_ind_t: CCI Primitivescc_call_ref: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_call_ref: CCI Primitivescc_call_type: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformancecc_call_type: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_call_type: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_call_type: CCI PrimitivesCC_CALL_TYPE_10x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_10x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_11x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_11x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_128KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_12x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_12x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_13x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_13x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_14x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_14x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_1536KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_15x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_15x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_16x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_16x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_17x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_17x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_18x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_18x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_1920KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_19x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_19x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_20x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_20x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_21x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_21x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_22x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_22x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_23x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_23x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_24x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_24x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_25x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_25x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_26x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_26x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_27x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_27x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_28x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_28x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_29x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_29x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_2x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_30x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_384KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_3_1kHZ_AUDIO: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_3x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_3x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_4x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_4x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_5x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_5x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_PREFERRED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_6x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_6x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_7x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_7x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_8x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_8x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_9x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_9x64KBS_UNRESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CALL_TYPE_SPEECH: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ACCESS_INFO_DISCARDED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ADDRESS_INCOMPLETE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AUTHORIZED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_BC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_CALL_REJECTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_CALL_TYPE_INCOMPATIBLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_EXCHANGE_ROUTING_ERROR: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_FACILITY_REJECTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_GROUP_RESTRICTIONS: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_ICC_BARRED WITHIN_CUG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INCOMPATIBLE_DESTINATION: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INCONSISTENCY: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INTERWORKING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INTERWORKING: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INVALID_MESSAGE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_INVALID_TRANSIT_NTWK_SELECTION: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_LNP_QOR_NUMBER_NOT_FOUND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MESSAGE_DISCARDED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MISDIALLED_TRUNK_PREFIX: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_MISROUTED_CALL_TO_PORTED_NUMBER 26: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ANSWER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_CCT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_DESTINATION: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_ROUTE_TO_TRANSIT_NETWORK: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NO_USER_RESPONDING: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NON_EXISTENT_CUG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NORMAL_CALL_CLEARING: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NORMAL_UNSPECIFIED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NOT_SUBSCRIBED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_NUMBER_CHANGED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_OGC_BARRED_WITHIN_CUG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_OUT_OF_ORDER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PARAMETER_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PARAMETER_PASSED_ON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PRECEDENCE_CALL_BLOCKED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PREEMPTION: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PREEMPTION: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PREEMPTION_CCT_RESERVED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_PROTOCOL_ERROR: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RECOVERY_ON_TIMER_EXPIRY: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_REDIRECT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_REDIRECT: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_REQUESTED_CCT_UNAVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RESOURCE_UNAVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_RESTRICTED_BC_ONLY: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SEND_SPECIAL_INFO_TONE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SERIVCE_OPTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SERVICE_OPTION_NOT_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SUBSCRIBER_ABSENT: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_SWITCHING_EQUIP_CONGESTION: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_TEMPORARY_FAILURE: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_DEST_NUMBER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNALLOCATED_NUMBER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_UNKNOWN_BUSINESS_GROUP: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_USER_BUSY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_USER_BUSY: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CAUS_USER_NOT_MEMBER_OF_CUG: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_cause: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_cause: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_cause: CCI Primitivescc_cdpn_length: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_cdpn_length: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_cdpn_length: CCI Primitivescc_cdpn_offset: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_cdpn_offset: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_cdpn_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_CHANNEL: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CHANNEL_GROUP: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_conn_length: CCI Primitivescc_conn_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONNECT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONNECT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_connect_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONNECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONNECT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_connect_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_CHECK_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_CHECK_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_CHECK_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_check_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_CHECK_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_CHECK_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CONT_CHECK_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_CHECK_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_check_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_REPORT_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_REPORT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_REPORT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_report_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_REPORT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_report_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_TEST_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_TEST_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_TEST_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_test_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_TEST_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_CONT_TEST_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_CONT_TEST_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_CONT_TEST_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_cont_test_req_t: CCI Primitivescc_correct_prim: CCI PrimitivesCC_DEFAULT_LISTENER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_DEFAULT_LISTENER: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_DEFAULT_LISTENER: CCI PrimitivesCC_DEFAULT_LISTENER: CCI Services DefinitionCC_DISCONNECT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_DISCONNECT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_DISCONNECT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_disconnect_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_DISCONNECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_DISCONNECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_DISCONNECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_DISCONNECT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_disconnect_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_ERROR_ACK: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_ERROR_ACK: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_ERROR_ACK: Diagnostics RequirementsCC_ERROR_ACK: CCI PrimitivesCC_ERROR_ACK: CCI Services DefinitionCC_error_ack_t: CCI Primitivescc_error_primitive: CCI Primitivescc_error_type: CCI Primitivescc_event: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_event: CCI Primitivescc_flags: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_flags: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_flags: CCI PrimitivesCC_FORWXFER_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_forwxfer_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_forwxfer_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_IBI_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_IBI_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_IBI_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_IBI_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_ibi_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_IBI_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_IBI_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_IBI_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_IBI_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_ibi_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_ACK: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_INFO_ACK: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_INFO_ACK: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_ACK: CCI Services DefinitionCC_info_ack_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_info_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFO_TIMEOUT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_info_timeout_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFORMATION_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_INFORMATION_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_INFORMATION_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFORMATION_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_information_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFORMATION_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_INFORMATION_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_INFORMATION_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_INFORMATION_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_information_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_ITC_WITH_TONES_AND_ANNOUNCEMENTS": Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_MAINT_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_MAINT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_MAINT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_maint_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_MAINTENANCE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_MAINTENANCE: CCI PrimitivesCC_MANAGEMENT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_MANAGEMENT: CCI PrimitivesCC_MORE_INFO_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_MORE_INFO_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_MORE_INFO_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_MORE_INFO_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_more_info_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_MORE_INFO_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_MORE_INFO_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_MORE_INFO_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_MORE_INFO_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_more_info_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_OK_ACK: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_OK_ACK: CCI PrimitivesCC_OK_ACK: CCI Services DefinitionCC_ok_ack_t: CCI Primitivescc_opt_flags: CCI Primitivescc_opt_length: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_opt_length: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_opt_length: CCI Primitivescc_opt_offset: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_opt_offset: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_opt_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_optmgmt_ack_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_OPTMGMT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_OPTMGMT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_OPTMGMT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_OPTMGMT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_optmgmt_req_t: CCI Primitivescc_primitive: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROCEEDING_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_PROCEEDING_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_PROCEEDING_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROCEEDING_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_proceeding_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROCEEDING_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_PROCEEDING_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_PROCEEDING_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROCEEDING_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_proceeding_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROGRESS_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_PROGRESS_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_PROGRESS_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROGRESS_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_progress_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROGRESS_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_PROGRESS_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_PROGRESS_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_PROGRESS_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_progress_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_CON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_QUERY_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_query_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_QUERY_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_query_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_QUERY_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_query_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_RES: FootnotesCC_QUERY_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_QUERY_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_QUERY_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_query_res_t: CCI Primitivescc_reason: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_reason: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_reason: CCI PrimitivesCC_REJECT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_REJECT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_REJECT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reject_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_REJECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_REJECT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reject_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_CON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_release_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_release_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_release_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_RES: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RELEASE_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_RELEASE_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_release_res_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_CON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESET_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reset_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESET_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reset_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESET_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reset_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_RES: FootnotesCC_RESET_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESET_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESET_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_reset_res_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESTART_CON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESTART_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESTART_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_restart_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESTART_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESTART_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESTART_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESTART_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_restart_req_t: CCI Primitivescc_result: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_result: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_CON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESUME_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REJECT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_REJECT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REJECT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_reject_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REJECT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_reject_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESUME_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_RESUME_RES: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_RESUME_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_RESUME_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_resume_res_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_complete_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_COMPLETE_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_complete_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_CON: Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764CC_SETUP_CON: Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931CC_SETUP_CON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_CON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_IND: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_SETUP_IND: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_setup_ind: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_IND: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancecc_setup_ind: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_IND: CCI Primitivescc_setup_ind: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_REQ: Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 ConformanceCC_SETUP_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_RES: Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764CC_SETUP_RES: Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931CC_SETUP_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SETUP_RES: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SETUP_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_SETUP_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_setup_res_t: CCI Primitivescc_state: CCI Primitivescc_subn_length: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_subn_length: CCI Primitivescc_subn_offset: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_subn_offset: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_CON: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_reject_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REJECT_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_reject_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_REQ: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_RES: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_SUSPEND_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSPEND_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_suspend_res_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_SUSRES_NETWORK_INITIATED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_TEST: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_TEST: CCI PrimitivesCC_TOKEN_REQUEST: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_TOKEN_REQUEST: CCI Primitivescc_token_value: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_token_value: CCI PrimitivesCC_TRUNK_GROUP: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCC_UNBIND_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBIND_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_unbind_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_CON: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_UNBLOCKING_CON: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_CON: CCI Services DefinitionCC_unblocking_con_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_IND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_UNBLOCKING_IND: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_IND: CCI Services DefinitionCC_unblocking_ind_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_REQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_UNBLOCKING_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_REQ: CCI Services DefinitionCC_unblocking_req_t: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_RES: FootnotesCC_UNBLOCKING_RES: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCC_UNBLOCKING_RES: CCI PrimitivesCC_UNBLOCKING_RES: CCI Services DefinitionCC_unblocking_res_t: CCI Primitivescc_unix_error: CCI Primitivescc_user_ref: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecc_user_ref: CCI PrimitivesCCACCESS: CCI PrimitivesCCADDRBUSY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCADDRBUSY: CCI PrimitivesCCBADADDR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCBADADDR: CCI PrimitivesCCBADCLR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCBADCLR: CCI PrimitivesCCBADDIGS: CCI PrimitivesCCBADFLAG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCBADFLAG: CCI PrimitivesCCBADOPT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCBADOPT: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCCBADOPT: CCI PrimitivesCCBADPRIM: CCI PrimitivesCCBADTOK: CCI PrimitivesCCFLAGS: CCI PrimitivesCCNOADDR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCNOADDR: CCI PrimitivesCCNOTSUPP: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCNOTSUPP: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceCCNOTSUPP: CCI PrimitivesCCOUTSTATE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCOUTSTATE: CCI PrimitivesCCS_ALERTING_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_CONNECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_CONNECTED: CCI PrimitivesCCS_DISCONNECT_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_IBI_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_IDLE: CCI PrimitivesCCS_IDLE: CCI Services DefinitionCCS_PROCEED_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_PROGRESS_REQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_SUSPENDED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCS_SUSPENDED: CCI PrimitivesCCS_UNBND: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WACK_AREQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WACK_BREQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WAIT_COR: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WCON_CREQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WCON_RELREQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WCON_SREQ: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCS_WCON_SREQ: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WCON_SUSREQ.: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_ALERTING: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_CCREP: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_CONNECT: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_INFO: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_MORE: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_PROCEED: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WIND_PROGRESS: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_ALERTING: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_CCREP: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_CONNECT: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_INFO: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_MORE: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_PROCEED: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WREQ_PROGRESS: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WRES_RELIND: CCI PrimitivesCCS_WRES_SIND: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceCCS_WRES_SIND: CCI PrimitivesCCSYSERR: CCI Primitivescic: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancecic: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancegetmsg(2s): Model of the CCIid: Addendum for Q.764 Conformanceid: Addendum for Q.931 Conformanceisdn_addr_t: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_CH: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_CH: Address FormatsISDN_SCOPE_DF: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_DF: Address FormatsISDN_SCOPE_EG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_EG: Address FormatsISDN_SCOPE_FG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_FG: Address FormatsISDN_SCOPE_TG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_TG: Address FormatsISDN_SCOPE_XG: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISDN_SCOPE_XG: Address Formatsisup_addr_t: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_CHARGE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_CONNECT_FREE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_HOLDING_REQUESTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_IC_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_NO_CHARGE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_ORDINARY_SUBSCRIBER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_PAYPHONE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_SCCP_ALL_METHODS_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_SUBSCRIBER_FREE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_BCI_TERMINATING_ACCESS_ISDN: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_BLOCKING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_CIRCUIT_BUSY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_COT_FAILURE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_ERROR: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RECV_RLC: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RESET: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_RESTART: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_STATUS: Addendum for Q.931 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T2_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T35_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T38_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T3_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T6_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T7_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T8_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_CALL_FAILURE_T9_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_COT_FAILURE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_COT_FAILURE: CCI Services DefinitionISUP_COT_SUCCESS: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_COT_SUCCESS: CCI Services DefinitionISUP_EVNT_ALERTING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_ON_BUSY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_ON_NO_ANSWER: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_CALL_FORWARDED_UNCONDITIONAL: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_IBI: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_EVNT_PROGRESS: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_E2E_INFORMATION_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_INTERNATIONAL_CALL: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_INTERWORKING_ENCOUNTERED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_ISDN_USER_PART_ALL_THE_WAY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_ORIGINATING_ACCESS_ISDN: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_PASS_ALONG_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_SCCP_ALL_METHODS_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_SCCP_CLNS_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_SCCP_CONS_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_FCI_SCCP_E2E_METHOD_AVAILABLE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_GROUP: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_HARDWARE_FAILURE_ORIENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_MAINTENANCE_ORIENTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUS: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_PREVIOUS: CCI PrimitivesISUP_NCI_CONT_CHECK_REQUIRED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_NCI_OG_ECHO_CONTROL_DEVICE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_NCI_ONE_SATELLITE_CCT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_NCI_TWO_SATELLITE_CCT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_BLOCKING: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_CIRCUIT_BUSY: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_COT_FAILURE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_DUAL_SEIZURE: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_RESET: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_T24_TIMEOUT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_REATTEMPT_UNEXPECTED: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_CG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_CG: Address FormatsISUP_SCOPE_CT: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_CT: Address FormatsISUP_SCOPE_DF: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_DF: Address FormatsISUP_SCOPE_SP: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_SP: Address FormatsISUP_SCOPE_SR: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_SR: Address FormatsISUP_SCOPE_TG: Addendum for Q.764 ConformanceISUP_SCOPE_TG: Address Formats- license, FDL: GNU Free Documentation License
- license, GNU Free Documentation License: GNU Free Documentation License
putmsg(2s): Model of the CCIscope: Addendum for Q.764 Conformancescope: Addendum for Q.931 Conformance- STREAMS: Diagnostics Requirements
- STREAMS: Model of the CCI
- STREAMS: Introduction
- STREAMS: Preface
struct CC_addr_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_addr_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_alerting_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_alerting_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_bind_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_bind_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_blocking_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_blocking_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_blocking_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_blocking_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_call_failure_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_call_reattempt_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_connect_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_connect_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_check_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_check_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_report_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_report_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_test_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_cont_test_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_disconnect_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_disconnect_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_error_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_forwxfer_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_forwxfer_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_ibi_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_ibi_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_info_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_info_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_info_timeout_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_information_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_information_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_maint_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_more_info_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_more_info_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_ok_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_optmgmt_ack: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_optmgmt_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_proceeding_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_proceeding_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_progress_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_progress_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_query_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_query_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_query_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_query_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reject_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reject_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_release_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_release_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_release_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_release_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reset_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reset_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reset_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_reset_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_restart_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_restart_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_reject_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_reject_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_resume_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_complete_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_complete_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_setup_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_reject_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_reject_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_suspend_res: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_unbind_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_unblocking_con: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_unblocking_ind: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_unblocking_req: CCI Primitivesstruct CC_unblocking_res: CCI Primitivesstruct isdn_addr: Addendum for Q.931 Conformancestruct isup_addr: Addendum for Q.764 Conformance
Short Contents
- Call Control Interface
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The Call Control Layer
- 3 CCI Services Definition
- 4 CCI Primitives
- 5 Diagnostics Requirements
- Addendum for Q.931 Conformance
- Addendum for Q.764 Conformance
- Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformance
- Appendix A Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931
- Appendix B Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764
- Appendix C State/Event Tables
- Appendix D Primitive Precedence Tables
- Appendix E CCI Header File Listing
- License
- Glossary
- Acronyms
- References
- Index
Table of Contents
- Call Control Interface
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The Call Control Layer
- 3 CCI Services Definition
- 3.1 Local Management Services Definition
- 3.2 User-Network Interface Services Definition
- 3.3 Network-Network Interface Services Definition
- 4 CCI Primitives
- 4.1 Management Primitives
- 4.1.1 Call Control Information Request
- 4.1.2 Call Control Information Acknowledgement
- 4.1.3 Protocol Address Request
- 4.1.4 Protocol Address Acknowledgement
- 4.1.5 Bind Protocol Address Request
- 4.1.6 Bind Protocol Address Acknowledgement
- 4.1.7 Unbind Protocol Address Request
- 4.1.8 Call Processing Options Management Request
- 4.1.9 Call Processing Options Management Acknowledgement
- 4.1.10 Error Acknowledgement
- 4.1.11 Successful Receipt Acknowledgements
- 4.2 Primitive Format and Rules
- 4.2.1 Call Setup Phase
- 4.2.2 Continuity Check Phase
- 4.2.3 Collecting Information Phase
- 4.2.4 Call Establishment Phase
- 4.2.4.1 Call Control Proceeding Request
- 4.2.4.2 Call Control Proceeding Indication
- 4.2.4.3 Call Control Alerting Request
- 4.2.4.4 Call Control Alerting Indication
- 4.2.4.5 Call Control Progress Request
- 4.2.4.6 Call Control Progress Indication
- 4.2.4.7 Call Control In-Band Information Request
- 4.2.4.8 Call Control In-Band Information Indication
- 4.2.4.9 Call Control Connect Request
- 4.2.4.10 Call Control Connect Indication
- 4.2.4.11 Call Control Setup Complete Request
- 4.2.4.12 Call Control Setup Complete Indication
- 4.2.5 Call Established Phase
- 4.2.5.1 Forward Transfer Request
- 4.2.5.2 Forward Transfer Indication
- 4.2.5.3 Call Control Suspend Request
- 4.2.5.4 Call Control Suspend Indication
- 4.2.5.5 Call Control Suspend Response
- 4.2.5.6 Call Control Suspend Confirmation
- 4.2.5.7 Call Control Suspend Reject Request
- 4.2.5.8 Call Control Suspend Reject Confirmation
- 4.2.5.9 Call Control Resume Request
- 4.2.5.10 Call Control Resume Indication
- 4.2.5.11 Call Control Resume Response
- 4.2.5.12 Call Control Resume Confirmation
- 4.2.5.13 Call Control Resume Reject Request
- 4.2.5.14 Call Control Resume Reject Indication
- 4.2.6 Call Termination Phase
- 4.2.6.1 Call Control Reject Request
- 4.2.6.2 Call Control Reject Indication
- 4.2.6.3 Call Control Call Failure Indication
- 4.2.6.4 Call Control Disconnect Request
- 4.2.6.5 Call Control Disconnect Indication
- 4.2.6.6 Call Control Release Request
- 4.2.6.7 Call Control Release Indication
- 4.2.6.8 Call Control Release Response
- 4.2.6.9 Call Control Release Confirmation
- 4.3 Management Primitive Formats and Rules
- 4.3.1 Interface Management Primitives
- 4.3.2 Circuit Management Primitives
- 4.3.2.1 Circuit Management Reset Request
- 4.3.2.2 Circuit Management Reset Indication
- 4.3.2.3 Circuit Management Reset Response
- 4.3.2.4 Circuit Management Reset Confirmation
- 4.3.2.5 Circuit Management Blocking Request
- 4.3.2.6 Circuit Management Blocking Indication
- 4.3.2.7 Circuit Management Blocking Response
- 4.3.2.8 Circuit Management Blocking Confirmation
- 4.3.2.9 Circuit Management Unblocking Request
- 4.3.2.10 Circuit Management Unblocking Indication
- 4.3.2.11 Circuit Management Unblocking Response
- 4.3.2.12 Circuit Management Unblocking Confirmation
- 4.3.2.13 Circuit Management Query Request
- 4.3.2.14 Circuit Management Query Indication
- 4.3.2.15 Circuit Management Query Response
- 4.3.2.16 Circuit Management Query Confirmation
- 4.3.3 Maintenance Primitives
- 4.3.4 Circuit Continuity Test Primitives
- 4.3.5 Collecting Information Phase
- 4.1 Management Primitives
- 5 Diagnostics Requirements
- Addendum for Q.931 Conformance
- Addendum for Q.764 Conformance
- Addendum for ETSI EN 300 356-1 V3.2.2 Conformance
- Appendix A Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.931
- Appendix B Mapping of CCI Primitives to Q.764
- Appendix C State/Event Tables
- Appendix D Primitive Precedence Tables
- Appendix E CCI Header File Listing
- License
- Glossary
- Acronyms
- References
- Index
Footnotes
[1] As a future extension to the interface, H.225, BSSAP, and SIP will be supported.
[2] In a later version of this document H.225, BSSAP, and SIP will also be supported.
[3] Note that the CC_RESET_RES
primitive is not required and is only provided for completeness. The CCS provider is allowed to acknowledge the reset
request to the peer CCS user upon receipt of the necessary protocol messages. This permits automatic completion of the
reset service at the receiving CCS provider without he presence or involvement of a management entity associated with
the receiving provider.
[4] Note that in Figure 48 additional primitives may be issued by the CCS provider to a CCS call control user if a CCS call control user is engaged in a call.
[5] Note that in Figure 49 additional primitives may be issued by the CCS provider to a CCS call control user if a CCS call control user is engaged in a call.
[6] Note that in Figure 50 additional primitives may be issued by the CCS provider to a CCS call control user if a CCS call control user is engaged in a call.
[7] Note that in Figure 51 additional primitives may be issued by the CCS provider to a CCS call control user if a CCS call control user is engaged in a call.
[8] Note that the CC_BLOCKING_RES
primitive is not required and is only provided for completeness. The CCS provider is allowed to acknowledge the
blocking request to the peer CCS user upon receipt of the necessary protocol messages. This permits automatic
completion of the blocking service at the receiving CCS provider without he presence or involvement of a management
entity associated with the receiving provider.
[9] Note that the CC_UNBLOCKING_RES
primitive is not required and is only provided for completeness. The CCS provider is allowed to acknowledge the
unblocking request to the peer CCS user upon receipt of the necessary protocol messages. This permits automatic
completion of the unblocking service at the receiving CCS provider without he presence or involvement of a management
entity associated with the receiving provider.
[10] Note that the CC_QUERY_RES
primitive is not required and is only provided for completeness. The CCS provider is allowed to acknowledge the query
request to the peer CCS user upon receipt of the necessary protocol messages. This permits automatic completion of the
query service at the receiving CCS provider without he presence or involvement of a management entity associated with
the receiving provider.
SS7 for the
Common Man
| Home |
© Copyright 1997-2007 OpenSS7 Corporation All Rights Reserved.